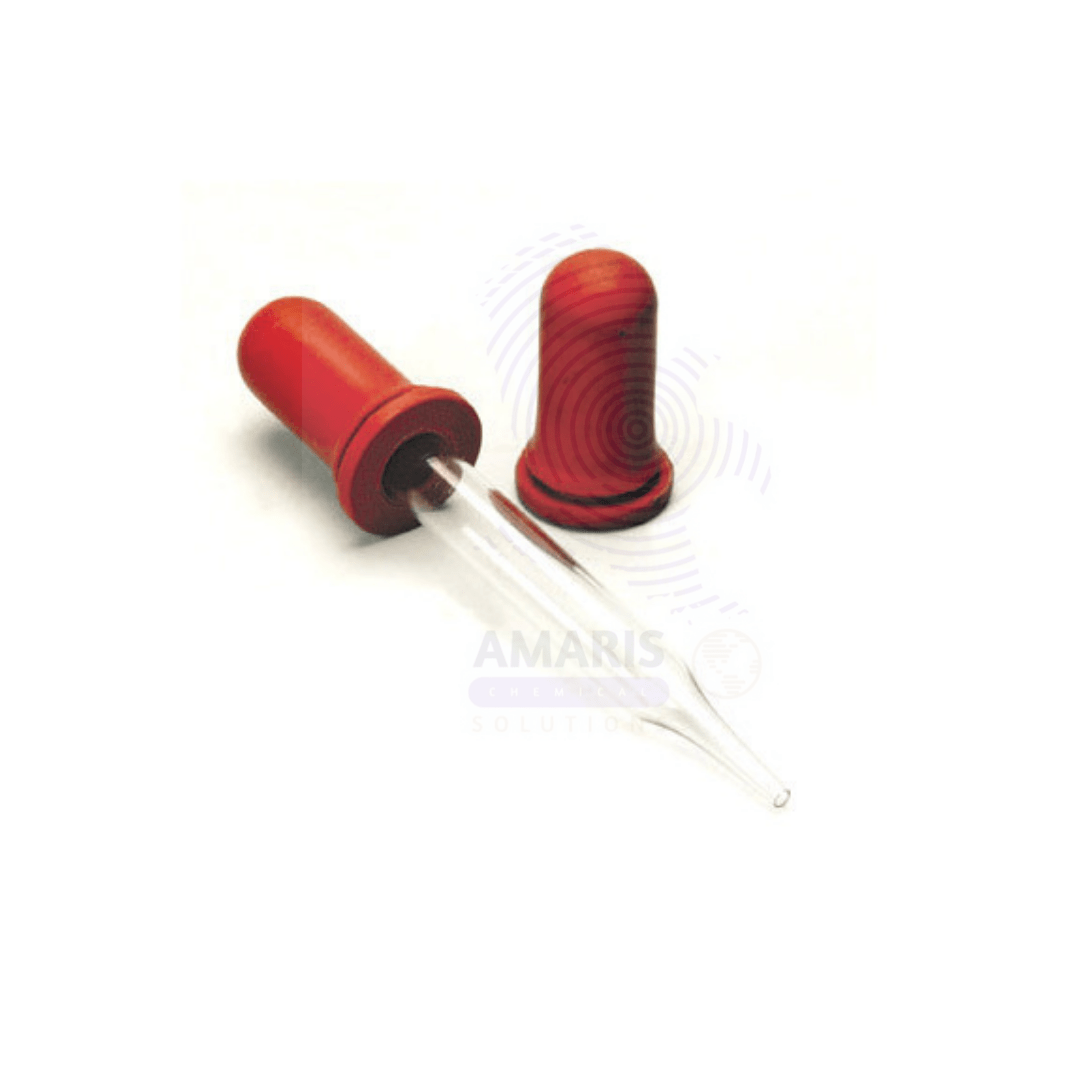
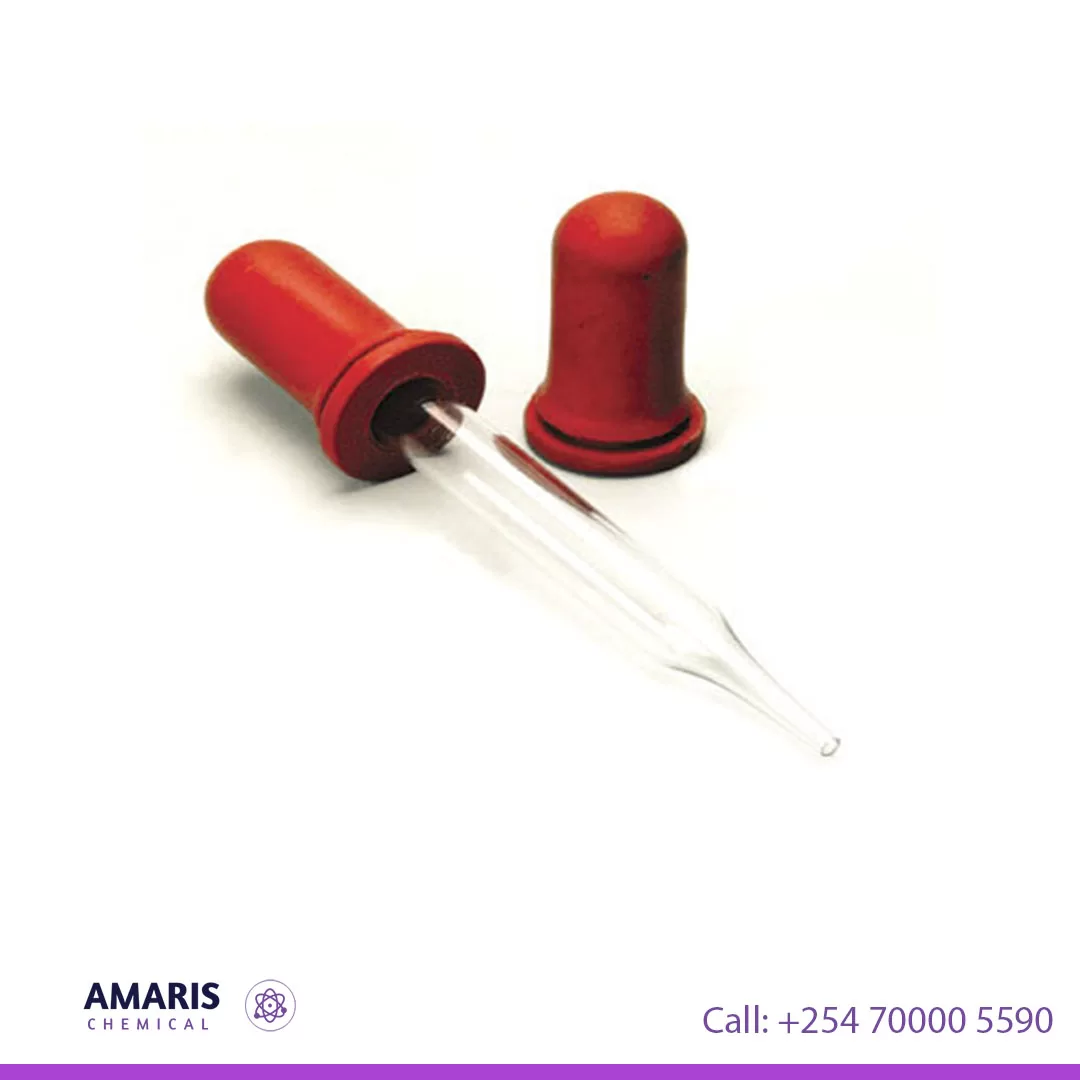
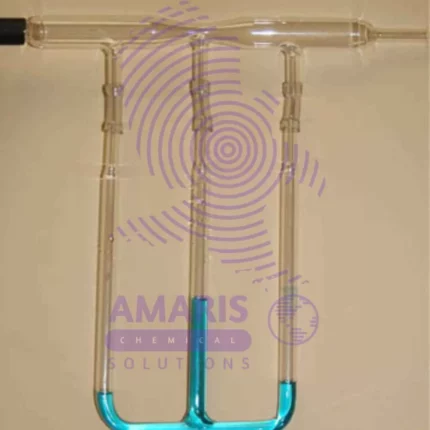
Description
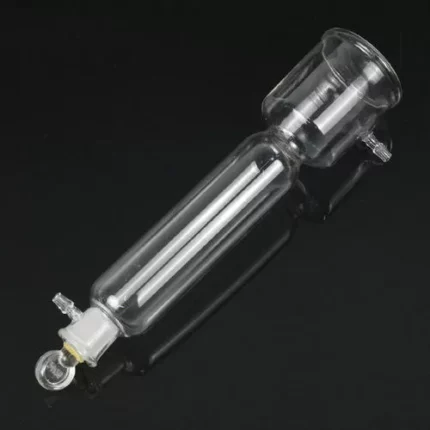
Dropper with teats help to add pre determined quantity of liquid to other jars in an experimental set up
Shipping & Delivery


MAECENAS IACULIS
Vestibulum curae torquent diam diam commodo parturient penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse parturient a.Parturient in parturient scelerisque nibh lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendrerit et pharetra fames nunc natoque dui.
ADIPISCING CONVALLIS BULUM
- Vestibulum penatibus nunc dui adipiscing convallis bulum parturient suspendisse.
- Abitur parturient praesent lectus quam a natoque adipiscing a vestibulum hendre.
- Diam parturient dictumst parturient scelerisque nibh lectus.
Scelerisque adipiscing bibendum sem vestibulum et in a a a purus lectus faucibus lobortis tincidunt purus lectus nisl class eros.Condimentum a et ullamcorper dictumst mus et tristique elementum nam inceptos hac parturient scelerisque vestibulum amet elit ut volutpat.
Related products
Absorption Tower
$0.01
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
Atomic Model Set
$0.01
A lab atomic model set is a collection of physical models and materials designed to represent the structure of atoms and molecules. It is commonly used in educational and scientific laboratory settings to visually demonstrate the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, as well as the bonding patterns between atoms in molecules. These sets typically include colored balls of various sizes representing different types of atoms, as well as connectors or magnets to simulate chemical bonds between them. The purpose of these sets is to help students and researchers better understand the principles of atomic and molecular structure in a tangible and interactive way.
bar and gauge apparatus
$0.01
beaker pyrex
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Bernoulli Tube Apparatus
$0.01
The Bernoulli tube apparatus, also known as a Venturi tube apparatus, is a scientific device used to demonstrate the principles of fluid dynamics, particularly the Bernoulli's principle. It consists of a specially shaped tube with a constricted region, often referred to as a Venturi section. When fluid (liquid or gas) flows through the tube, the constricted section leads to changes in pressure and velocity according to Bernoulli's principle, which states that as the velocity of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases and vice versa. This apparatus is commonly used in educational settings to visually illustrate how the flow of a fluid can affect its pressure, helping to explain various phenomena like lift in aircraft wings, fluid flow through pipes, and more.