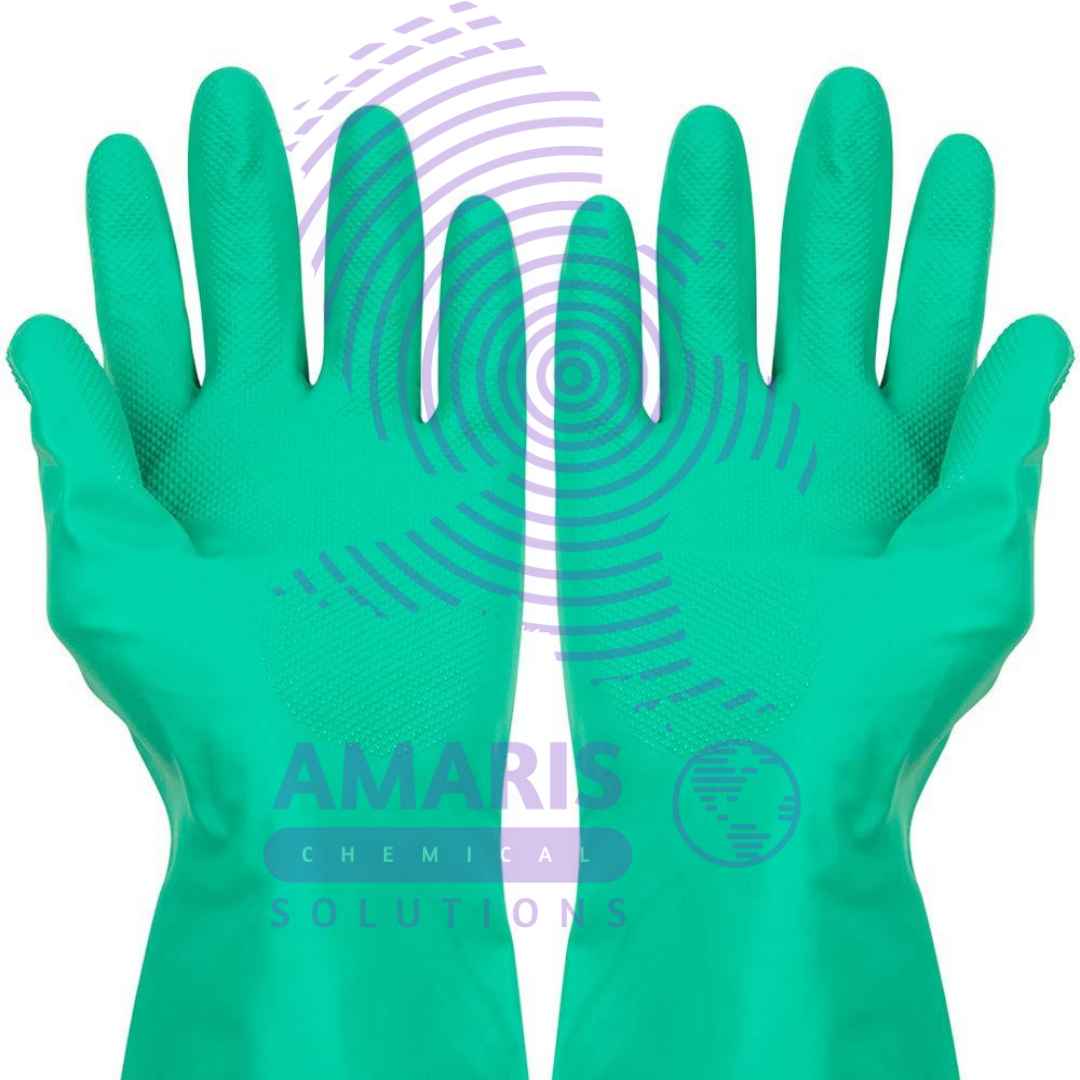
Acid Proof Gloves
KSh3,000.00 Original price was: KSh3,000.00.KSh2,500.00Current price is: KSh2,500.00.
Acid-proof gloves are an essential safety equipment used in laboratories where researchers handle corrosive chemicals. These gloves are designed to protect the wearer’s hands from coming into direct contact with acids, which can cause severe burns and skin damage. They are typically made from materials that are resistant to acids, such as neoprene, nitrile, or rubber.
When choosing acid-proof gloves for laboratory work, it’s important to consider the specific chemicals being used and select gloves that are compatible with those chemicals. Additionally, the gloves should fit well to provide adequate protection without compromising dexterity and comfort.
Proper usage of acid-proof gloves involves inspecting them for any signs of damage before each use, avoiding contact with incompatible chemicals, and promptly removing and properly disposing of gloves if they become contaminated. Regular maintenance and replacement of gloves are also necessary to ensure continued protection for laboratory personnel.
Uses of Acid Proof gloves
Protection from Chemical Burns:
Acid-proof gloves provide a barrier between the skin and corrosive acids, preventing direct contact and reducing the risk of chemical burns and skin damage.
Safety:
By wearing acid-proof gloves, laboratory personnel minimize the risk of accidental exposure to acids, which can cause severe injuries. This enhances overall laboratory safety and helps prevent accidents.
Handling Corrosive Chemicals:
Acid-proof gloves allow researchers to safely handle corrosive chemicals such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and others commonly used in laboratory experiments.
Maintaining Experiment Integrity:
Acid-proof gloves enable researchers to work with corrosive substances without compromising the integrity of their experiments. This is particularly important in experiments where contamination from skin oils or other substances could affect the results.
Compliance with Safety Regulations:
Many laboratories are required to adhere to safety regulations that mandate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as acid-proof gloves when working with hazardous chemicals. Wearing these gloves ensures compliance with such regulations.
Preventing Cross-Contamination:
Acid-proof gloves help prevent cross-contamination by providing a barrier between the hands and chemicals. This is crucial in laboratories where multiple substances are handled, as it reduces the risk of transferring acids or other chemicals from one experiment to another.
Related products
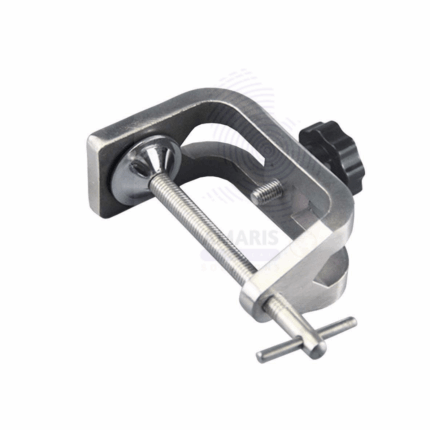
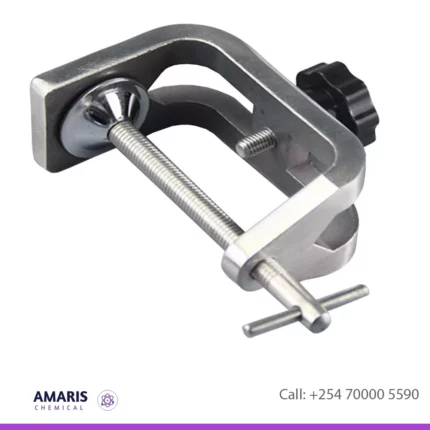
G-Clamp
- Holding Apparatus: In experiments where stability is crucial, G-clamps are used to secure laboratory apparatus to benches or tables. This ensures that the equipment remains in place during experiments, minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Securing Glassware: When conducting experiments involving glassware like beakers, flasks, or test tubes, G-clamps can be used to secure them to a stand or support rod. This prevents the glassware from tipping over or falling during the experiment.
- Supporting Heavy Objects: In situations where heavy objects need to be held in place temporarily, G-clamps provide a sturdy grip. This could be useful when setting up equipment or securing heavy components during an experiment.
- Fixing Materials for Cutting or Drilling: G-clamps are handy for securing materials like wood or metal in place while they are being cut, drilled, or manipulated in some other way. This ensures precision and safety during such tasks.
- Custom Setup: Sometimes, experiments require customized setups that aren't readily available with standard laboratory equipment. G-clamps allow researchers to create temporary fixtures or arrangements tailored to their specific experimental needs.
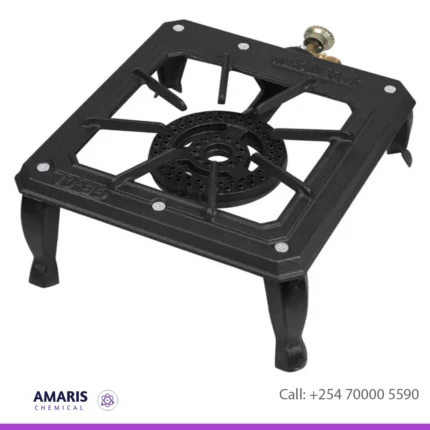
Gas Stove Portable
Rectangular Glass Block
- Windows: In laboratory buildings, rectangular glass blocks are often used as windows to allow natural light into the space while maintaining safety and privacy.
- Partition Walls: Glass blocks can be used to construct partition walls within the laboratory, separating different work areas while still allowing visibility and light transmission.
- Observation Windows: In controlled environments such as cleanrooms or containment labs, rectangular glass blocks may be installed as observation windows, allowing researchers to monitor experiments or processes from outside the controlled area.
- Fume Hood Windows: Glass blocks are sometimes used as windows in fume hoods, providing a transparent barrier between the user and hazardous chemicals or fumes while still allowing observation of experiments.
- Light Transmission: Glass blocks can also be used in experimental setups where controlled light transmission is required, such as in optical experiments or photobiology studies.
- Decorative Elements: In some cases, glass blocks are used for aesthetic purposes in laboratory design, adding visual interest to the space while still providing functional benefits like light transmission and visibility.
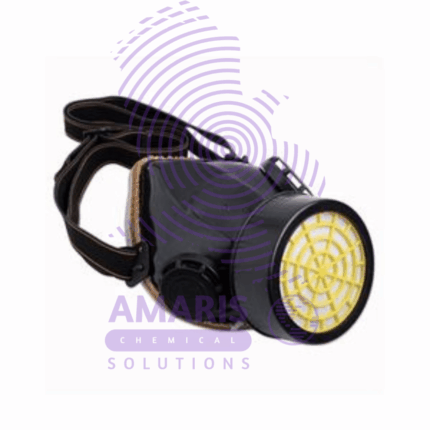
Single Gas Mask
- Facepiece: The main part of the mask that covers the nose, mouth, and sometimes the eyes. It's usually made of rubber or silicone for flexibility and a proper seal.
- Filter Cartridges: These cartridges are attached to the mask and contain various filter materials to purify the air. They can be specific to certain types of contaminants or provide broader protection.
- Straps: Adjustable straps secure the mask to the wearer's face, ensuring a snug fit.
- Exhalation Valve: This valve allows the wearer to exhale air without letting outside air in, maintaining a closed system for breathing.
- Visibility: Some masks feature transparent facepieces or additional eyepieces to ensure proper vision while wearing the mask.
- Comfort Features: Some masks include features like padding or adjustable nose bridges for added comfort during extended wear