Aspirator Bottle Glass
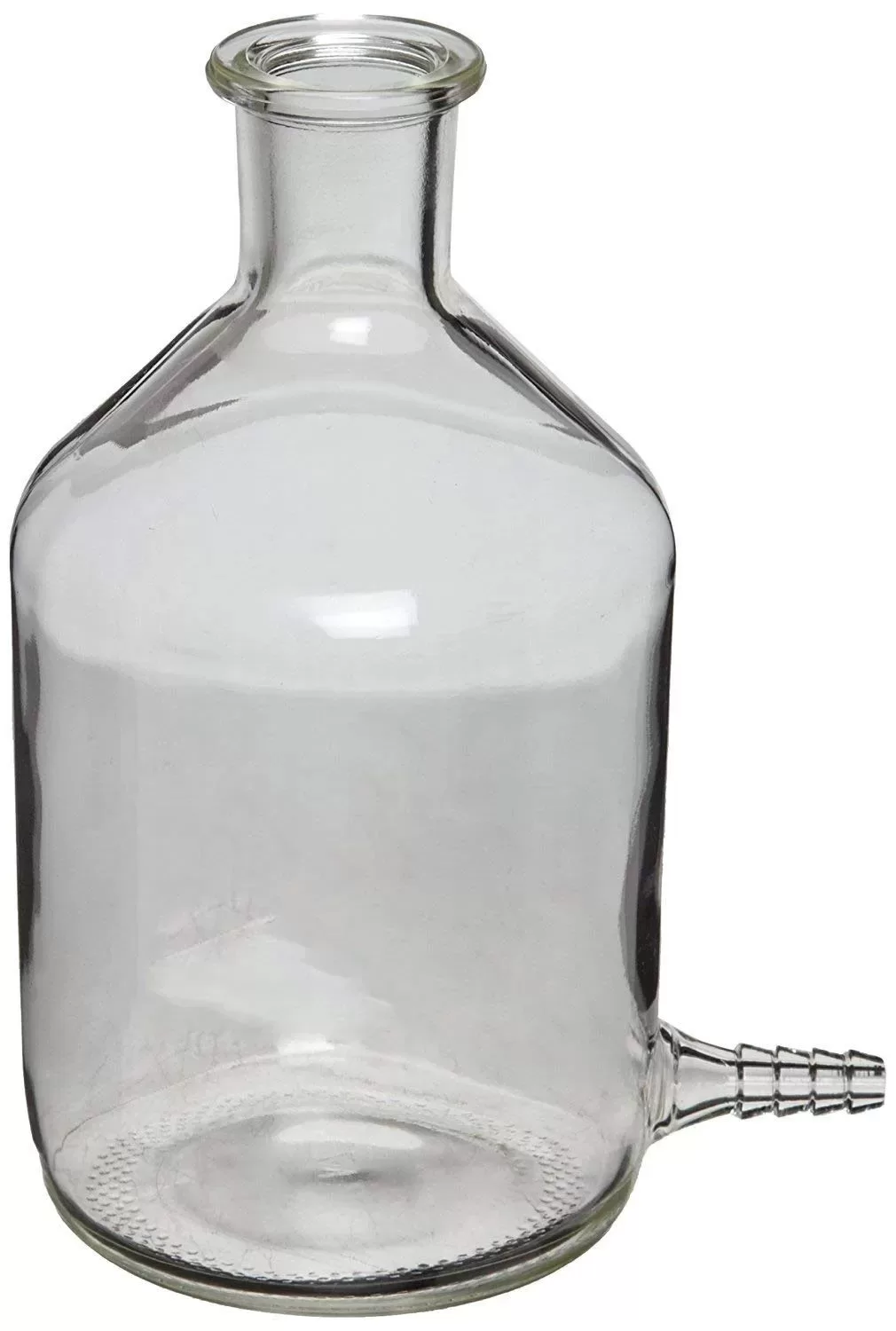
A laboratory aspirator glass bottle, also known as a vacuum aspirator bottle or a vacuum filtration flask, is a specialized glass container used in scientific laboratories for various applications. It is designed to create a vacuum or negative pressure, which allows the filtration of liquids through a porous medium like a filter paper or a membrane.
The bottle typically has a conical or pear-shaped body with a sidearm or neck near the top. This neck is where a rubber or silicone stopper is inserted, allowing for the attachment of tubing or a hose to connect to a vacuum source or water aspirator. (Available in 2.5l,5l,10l,)
Laboratory aspirator glass bottles are commonly used in vacuum filtration processes to separate a solid precipitate from a liquid solution. When connected to a vacuum source, the air inside the bottle is removed, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the filter, leaving the solid behind on the filter paper.
These bottles come in various sizes to accommodate different filtration needs and are an essential tool in many research, analytical, and quality control laboratories for tasks like separating particulate matter, sterilizing solutions, and performing various filtration techniques. They are often made of durable borosilicate glass to withstand the pressure changes and chemical interactions that may occur during laboratory operations.
Uses of Aspiratory bottles
1. Vacuum Filtration
- Application : Aspiratory bottles are essential for vacuum filtration processes where solids are separated from liquids.
- How it works : The bottle is connected to a vacuum source, and the liquid is drawn through a filter paper or membrane, leaving the solid residue on the filter.
2. Sample Collection Under Vacuum
- Application : These bottles are used to collect samples under reduced pressure, such as gases or volatile liquids.
- How it works : The vacuum created inside the bottle helps draw the sample into the container without contamination or loss.
3. Distillation and Evaporation
- Application : In distillation setups, aspiratory bottles can be used to collect condensed vapors or to facilitate the evaporation of solvents under vacuum.
- How it works : The vacuum reduces the boiling point of the solvent, allowing for more efficient evaporation at lower temperatures.
4. Chromatography
- Application : In some chromatographic techniques, aspiratory bottles are used to collect eluents or fractions under vacuum.
- How it works : The vacuum assists in speeding up the separation process by enhancing the flow of the mobile phase through the stationary phase.
5. Liquid Waste Collection
- Application : Aspiratory bottles are often used to collect liquid waste generated during experiments, especially when working with hazardous or toxic substances.
- How it works : The vacuum ensures that the waste is safely contained within the bottle, minimizing exposure to the user.
6. Cell Culture and Biological Applications
- Application : In biological labs, aspiratory bottles are used to remove media or other liquids from cell cultures without disturbing the cells.
- How it works : The gentle vacuum action prevents damage to delicate cells while effectively removing unwanted liquids.
7. Drying Samples
- Application : Aspiratory bottles can be part of a setup used to dry samples by applying vacuum to remove moisture or solvents.
- How it works : The vacuum lowers the vapor pressure, accelerating the drying process.
8. Gas Handling
- Application : These bottles are sometimes used in gas handling systems to trap or collect specific gases during chemical reactions.
- How it works : The vacuum helps direct the flow of gases into the bottle for collection or analysis.
9. Pressure Equalization
- Application : In certain experiments, aspiratory bottles help maintain pressure equilibrium between different parts of a system.
- How it works : By connecting the bottle to the system, it acts as a buffer to absorb pressure changes.
10. Chemical Synthesis
- Application : During synthesis reactions, aspiratory bottles may be used to collect by-products or to control the reaction environment under vacuum.
- How it works : The vacuum can drive the reaction forward by removing products as they form, shifting the equilibrium.
Characteristics of Glass Aspiratory Bottles:
- Durability : Glass is resistant to breakage under normal laboratory conditions.
- Chemical Resistance : It does not react with most chemicals, ensuring the integrity of the samples or reagents.
- Transparency : Allows visual monitoring of the contents during experiments.
- Heat Resistance : Can withstand temperature fluctuations often encountered in lab procedures.