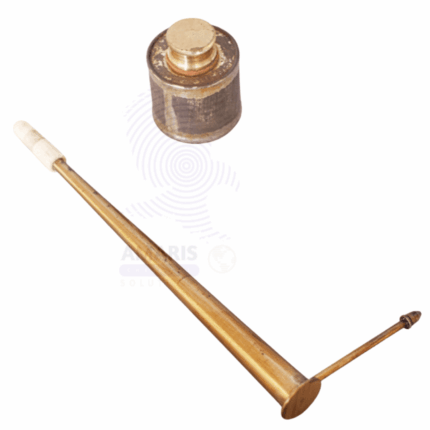
Blow pipes
A blow pipe is a versatile laboratory tool designed for producing a controlled flame through the combustion of a gas, typically using a fuel source like propane or natural gas. It consists of a long, slender tube with an open end that allows the user to blow air into the gas stream, intensifying the flame.
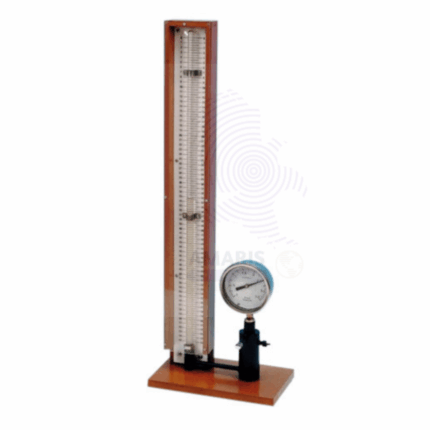
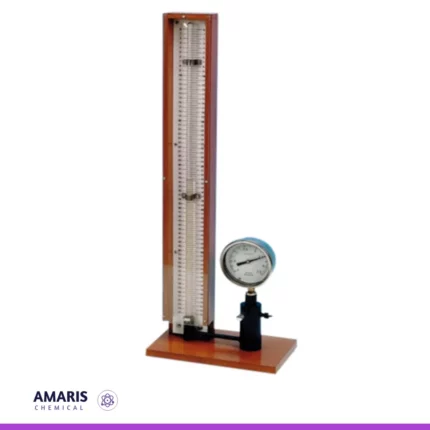
Boyles law apparatus
The Boyle's Law apparatus is a laboratory device designed to illustrate the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It typically features a sealed transparent container or cylinder that holds the gas, allowing for visual observation of any changes in volume. Attached to the container is a pressure measurement device, such as a manometer or pressure gauge, which accurately records the gas's pressure. The apparatus includes a volume adjustment mechanism, often in the form of a movable piston, enabling the user to compress or expand the gas and observe the corresponding pressure changes. Some setups may also incorporate temperature control to maintain constant conditions during experiments. Graduated scales on the apparatus facilitate precise measurements of gas volume. Overall, this apparatus serves as an essential educational tool, providing a hands-on experience for students to explore and understand Boyle's Law, which states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
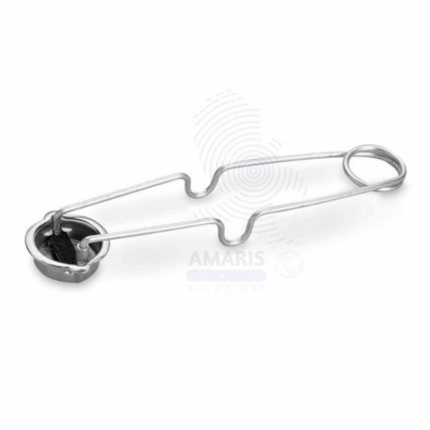
Bunsen burner lighter
A Bunsen burner lighter is a laboratory tool designed for safely igniting a Bunsen burner. It typically consists of a long, slender metal body with a flint or electronic igniter at one end and a nozzle to direct the flame. The device is lightweight and portable, making it easy to use in various laboratory settings.
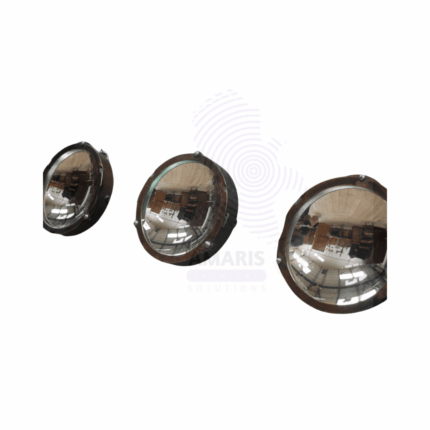
Concave mirrors
Concave mirrors are essential optical components, characterized by their inward curvature, ability to focus light, and versatile applications in various fields, from scientific research to everyday items. Their unique properties make them invaluable in any setting that requires precise light manipulation and image formation.
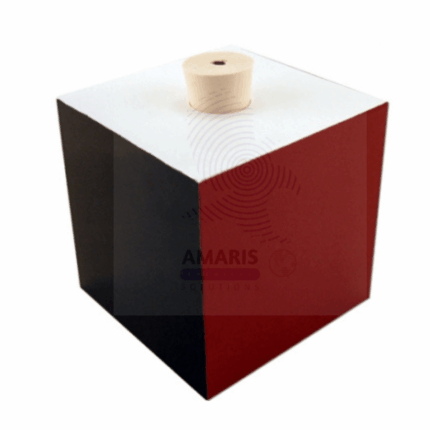
Leslie cubes
A Leslie cube is a hollow, metallic cube, usually filled with hot water, used to study heat radiation and thermal emissivity. Each of its four vertical sides has a different surface finish—typically polished metal, matte black, white, and a rough or textured surface—allowing direct comparison of how various surfaces emit infrared radiation. The cube is an excellent tool for demonstrating that darker, rougher surfaces emit more thermal radiation than lighter, polished surfaces. It is commonly used in physics and thermodynamics experiments to explore concepts of heat transfer and radiation efficiency.
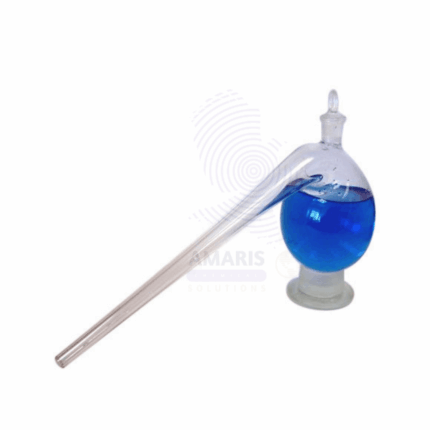
Retort flask
A retort flask is a heat-resistant, pear-shaped glass vessel with a long, downward-pointing neck, designed primarily for distillation processes. Its unique shape allows for efficient collection and condensation of vapors, making it ideal for separating substances based on their boiling points. The wide base provides stability and facilitates uniform heating, while the long neck helps direct vapors into a receiving container. It is commonly used in chemical laboratories for tasks such as distillation, refluxing, and crystallization, offering precise control over heating and vapor condensation in various experimental setups.
U tube lab glass with side arms
A U-tube lab glass with side arms is a specialized piece of laboratory glassware characterized by its U-shaped design, which allows for versatile applications in chemical experiments. The main body of the U-tube features two vertical arms connected at the bottom, with additional side arms that extend horizontally. These side arms are typically fitted with ground glass joints or stoppers, enabling easy connection to other apparatus.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters