Concave and convex lens
Convex lenses are thicker at the center and thinner at the edges, causing parallel light rays to converge towards a focal point, which allows them to produce real or virtual images depending on the object's distance. They are widely used in applications such as microscopes, cameras, and projectors for magnification and image projection. In contrast, concave lenses are thinner at the center and thicker at the edges, causing parallel light rays to diverge, resulting in virtual images that are always upright. They are commonly employed in glasses for nearsightedness, laser beam expanders, and optical instruments to correct aberrations. Together, concave and convex lenses play crucial roles in various optical experiments and applications, enhancing light manipulation and analysis in laboratory settings.
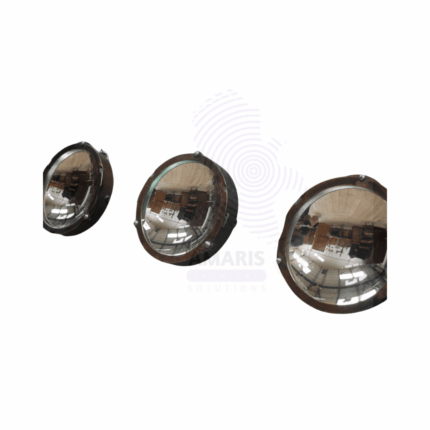
Concave mirrors
Concave mirrors are essential optical components, characterized by their inward curvature, ability to focus light, and versatile applications in various fields, from scientific research to everyday items. Their unique properties make them invaluable in any setting that requires precise light manipulation and image formation.
Microscope cover slips
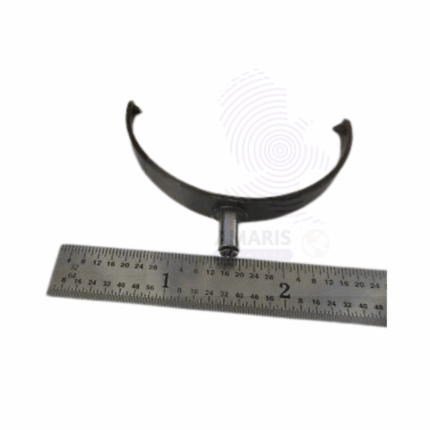
Microscope mirror holder
A microscope mirror holder is a precision mechanism designed to secure and position the reflective mirror in traditional microscopes. It allows for adjustable angling of the mirror, enabling users to direct and focus light from external sources onto the specimen for optimal illumination. This component is essential in models without built-in lighting, providing flexibility in light control and enhancing the clarity of the observed specimen.
Microtone hand type
The microtone hand type, commonly known as a microtome, is a precision instrument used in laboratories for slicing extremely thin sections of biological specimens, typically ranging from 1 to 100 micrometers. Designed for manual operation, it features a handwheel that allows users to finely adjust the thickness of the cuts, ensuring consistent and accurate sectioning. Equipped with a sharp, adjustable blade made from stainless steel or glass, the microtome securely holds tissue samples in place, minimizing vibrations that could affect slice quality. Its stable base and ergonomic design make it user-friendly for individuals of varying skill levels. Microtomes are essential in histology and pathology for preparing samples for microscopic examination, aiding in disease diagnosis and research. Additionally, they are widely used in educational settings to teach tissue preparation techniques, making them a versatile and invaluable tool in biological sciences.
Smoke cell
A smoke cell is a specialized laboratory apparatus designed to capture and observe smoke particles generated from combustion or pyrolysis processes. Typically made of transparent glass, it allows researchers to study the physical and chemical properties of smoke in a controlled environment. Smoke cells are often used for analyzing particle size, distribution, and composition, as well as for examining light scattering and absorption behaviors. They play a crucial role in fields like atmospheric science, environmental chemistry, and material safety, enabling experiments that simulate real-world smoke interactions with air and light. Their transparent design facilitates direct observation and measurement, making them an invaluable tool for understanding smoke behavior and its implications.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters