Back to products


Distilled Monoglycerides Remosoft
$ 0.45 Original price was: $ 0.45.$ 0.33Current price is: $ 0.33.
Disperse Black
Whatsapp Order
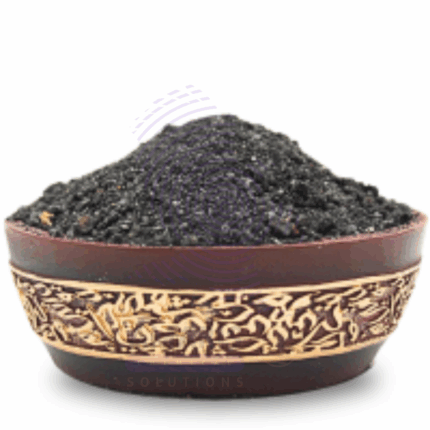
Disperse Black is a synthetic dye belonging to the class of disperse dyes, primarily used for dyeing hydrophobic fibers such as polyester, nylon, acetate, and other synthetic textiles. It is characterized by its fine particle size, high tinctorial strength, excellent fastness properties (wash, light, and rubbing), and ability to produce deep, uniform black shades. Disperse Black dyes are water-insoluble and applied in aqueous dispersion form during high-temperature dyeing processes. These dyes are favored in the textile industry for their vibrant colors and durability.
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle
Disperse Black
Primary Uses
- Textile Industry
- Used extensively for dyeing polyester fibers, which constitute a large segment of synthetic textiles.
- Employed in dyeing nylon, acetate, and blends containing synthetic fibers.
- Provides deep, rich black shades with excellent colorfastness properties, ideal for garments, upholstery, and technical textiles.
- Utilized in high-temperature and carrier dyeing processes, allowing uniform penetration and dye uptake.
- Applied in batch dyeing, continuous dyeing, and jet dyeing methods.
- Used for printing applications on synthetic fabrics when incorporated into disperse dye inks.Technical & Industrial Textiles
- Used for dyeing fabrics in automotive textiles, industrial filters, and outdoor fabrics that require color durability and resistance to environmental conditions.
- Suitable for high-performance textiles needing resistance to washing, light exposure, and abrasion.
Secondary Uses
- Ink Manufacturing
- Incorporated into disperse dye inks for textile printing and specialized industrial printing applications.Research & Development
- Used as a model dye for testing dyeing methods, colorfastness evaluations, and textile finishing processes.Polymer & Plastic Coloring
- Occasionally used to color synthetic polymers and plastics where deep black coloration is required, although less common than in textile dyeing.
KEY PRODUCT FEATURES
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name: Typically a proprietary mixture of disperse azo and anthraquinone dyes designed to yield black color
- Common/Trade Name: Disperse Black
- CAS Number: Varies based on specific dye composition (common disperse blacks include CAS numbers like 12225-21-7 for Disperse Black 9)
- HS Code: 3204.19.00
- Molecular Formula: Varies by specific dye components (commonly azo, anthraquinone derivatives)
- Synonyms:
- Disperse Black dye
- Synthetic disperse dye black
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Fine powder or granules
- Color: Deep black
- Odor: Odorless
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; dispersible in aqueous medium with surfactants or dispersing agents
- Particle Size: Typically nano- to micron-scale for optimal dispersion
- Stability: Stable under normal storage; sensitive to strong acids and bases
- Fastness Properties: High resistance to washing, light, perspiration, and rubbing
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Hazard Class (GHS): May be classified as hazardous depending on composition; potential skin sensitizer or irritant
- Toxicity: Low to moderate; some disperse dyes may cause allergic reactions or sensitization
- Exposure Limits: Follow occupational exposure limits for dyes and powders
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture
- Container Type: Sealed bags or drums, often polyethylene-lined to prevent moisture ingress
- Shelf Life: Typically 2–3 years if stored properly
- Handling Precautions: Avoid dust generation; use PPE to prevent inhalation and skin/eye contact
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Compliance with textile and consumer safety regulations (OEKO-TEX, REACH, etc.) depends on dye purity and formulation
- Restricted use in some regions due to potential allergenic or environmental impact; verify specific dye regulatory status
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Ecotoxicity: Some disperse dyes may have moderate aquatic toxicity; proper wastewater treatment essential
- Persistence: Variable; some components may be persistent in the environment
- Bioaccumulation: Generally low potential
- Carcinogenicity/Mutagenicity: Some disperse dyes have been studied for carcinogenicity, but Disperse Black dyes commonly used have limited evidence; handling precautions recommended
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Handling Precautions
PPE Required:
- Dust mask or respirator (to avoid inhalation of dye powders)
- Safety goggles
- Gloves (nitrile or latex)
- Protective clothing or apron
Handling Guidelines:
- Use in well-ventilated areas or with dust extraction systems
- Avoid generating dust clouds during transfer or mixing
- Prevent contact with skin and eyes
- Follow good industrial hygiene practices
Storage Measures:
- Keep containers tightly closed
- Store away from moisture and incompatible materials such as strong oxidizers or acids
- Avoid exposure to high humidity and temperature fluctuations
Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke in the handling area
- Maintain cleanliness to prevent contamination
First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move affected person to fresh air; seek medical attention if respiratory irritation occurs
- Skin Contact: Wash affected area with soap and water; seek medical advice if irritation or sensitization develops
- Eye Contact: Rinse immediately with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes; consult physician if irritation persists
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth; do not induce vomiting; seek medical advice immediately
Firefighting Measures
- Fire Hazards: Non-flammable; powder form may pose dust explosion hazard under specific conditions
- Extinguishing Media: Use water spray, foam, dry chemical, or CO₂ as appropriate for surrounding fire
- Special Precautions: Avoid dust clouds; use protective equipment for firefighters
- Decomposition Products: May release toxic fumes such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and carbon monoxide upon combustion
Related products
Acid Black 2 Powder
Acid Black 2 Powder is a synthetic anionic disazo dye belonging to the acid dye class, specifically formulated for intense black coloration with excellent light and wash fastness properties. This high-purity powder (100% active) exhibits superior solubility in aqueous solutions, making it particularly suitable for dyeing protein-based fibers like wool, silk, and nylon under acidic conditions. As a chromium-complex dye, it delivers enhanced color depth and improved fastness characteristics compared to non-metalized acid dyes. The powder form ensures precise dosing, consistent batch-to-batch reproducibility, and long-term stability when stored properly. Its molecular structure features sulfonic acid groups that facilitate strong ionic bonding with amino groups in fibers, resulting in vibrant, penetration-rich coloration with minimal bleeding.
Acid Black 210
Acid Black 210 is a high-performance, metal-complex acid dye specifically engineered for deep black shades with exceptional wet fastness properties. This chromium-based dye belongs to the 1:2 metal complex dye class, offering superior molecular stability and fiber affinity. The powder formulation delivers consistent, vibrant coloration for synthetic polyamide fibers and protein-based textiles, with optimized characteristics for industrial dyeing processes. Its molecular structure features multiple sulfonic acid groups that ensure excellent water solubility and penetration, while the metal complex formation provides enhanced light and wash fastness compared to non-metalized acid dyes.
Apple Green Dye
Apple Green Dye is a synthetic or natural colorant that imparts a vibrant, bright green hue resembling the skin of a fresh green apple. It is available in various forms including powders, liquids, and granules, and can be water-soluble or oil-dispersible depending on its chemical base. This dye is widely used across multiple industries including cosmetics, food and beverage, textiles, and industrial applications to achieve consistent and stable green coloration.
It offers excellent light and heat stability, and when formulated correctly, maintains its brightness across a range of pH levels. Apple Green Dye can be derived from certified colorants for safe use in consumables or from synthetic sources for industrial applications.
Black 5
Black 5, also known as Acid Black 5 or CI 20470, is a synthetic dye commonly used in various industries for its deep, rich black to bluish-black color. It belongs to the azo dye family and is typically supplied as a fine powder or granules in industrial packaging, such as 25kg bags. Black 5 is water-soluble and exhibits excellent stability in acidic conditions, making it ideal for applications in textiles, personal care, and some food and pharmaceutical formulations where permitted.
This dye offers high tinctorial strength, consistent batch-to-batch quality, and compatibility with other dyes for custom blends. It is used both for its standalone dark color and to darken or tone other dye shades.
Black Jawi
Black Jawi is a natural, mineral-rich volcanic sand or powder, traditionally harvested from volcanic regions. Its high content of silica, iron oxides, magnesium, and trace minerals makes it a versatile material for agriculture, construction, cosmetics, and industrial applications. Packaged in 30kg bulk quantities, it is ideal for large-scale projects requiring durability, soil enhancement, or therapeutic properties.
Green Pigment
Green Pigment is a concentrated dispersion of green pigment particles in a suitable carrier, designed for use in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. Known for its vivid green color and excellent stability, this pigment offers good resistance to heat, light, and chemicals. It is widely employed in plastics, coatings, inks, and other manufacturing processes where vibrant, durable green coloration is required.
Printofix Black H-TR
Printofix Black H-TR is a high-quality black textile printing paste designed for use in screen printing applications. It provides excellent color strength, fastness, and adhesion on a variety of fabrics including cotton, polyester, and blended textiles. The formulation ensures sharp, vibrant prints with good wash and rub resistance, making it ideal for industrial and fashion textile printing.
Tomato Red Dye
Tomato Red Dye is a synthetic azo dye prized for its vibrant, bright red coloration and excellent water solubility. It delivers consistent, vivid red shades that are stable under a variety of environmental conditions, including exposure to light, heat, and washing. This dye is extensively used across multiple industries including food and beverage, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and textiles. In food applications, it enhances the visual appeal of products such as beverages, confectionery, sauces, and baked goods. Its compatibility with different formulation types and regulatory approvals make it a reliable choice for cosmetic products like lipsticks, blushes, and nail polishes, as well as pharmaceutical tablets and syrups for identification and aesthetic purposes. The dye's superior performance, combined with strict adherence to safety and quality standards, ensures that it meets the requirements of manufacturers and regulatory bodies worldwide.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders