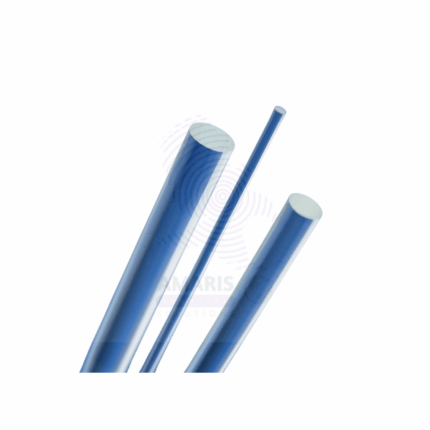
Glass Rod for Static Electricity
KSh0.01

Gold Leaf Electroscope
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,700.00Current price is: KSh1,700.00.
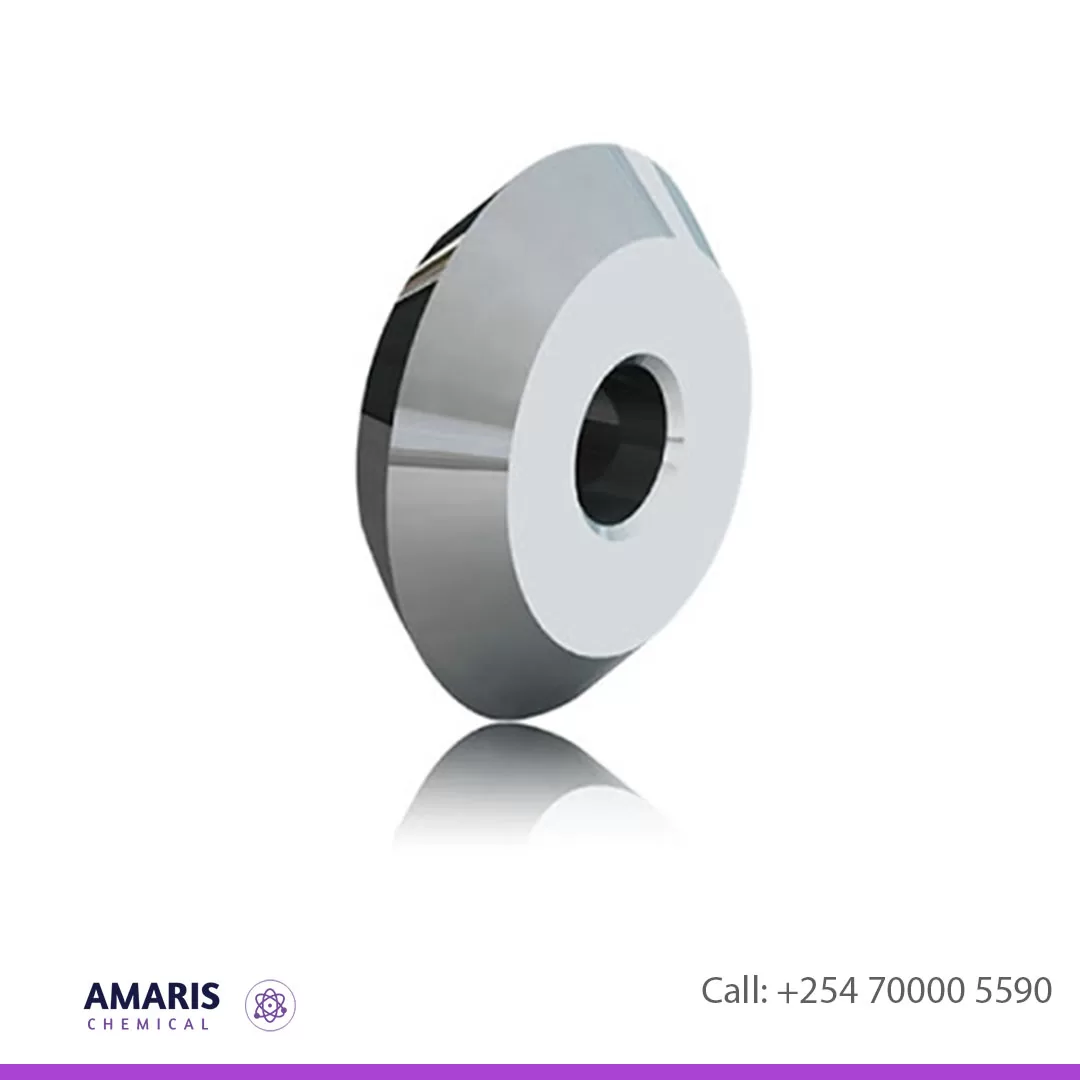
Glass Tubing Cutter Wheel Type
KSh900.00 Original price was: KSh900.00.KSh800.00Current price is: KSh800.00.
A glass tubing cutter with a wheel type design is a commonly used tool in laboratories for precisely cutting glass tubing. These cutters are preferred for their ability to make clean and smooth cuts with minimal effort and risk of breaking the glass unevenly.
SKU:
ACS54332CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Glass Tubing Cutter Wheel Type
1. Preparing Custom Glassware
- Cutting Glass Tubing to Size: Customizing the length of glass tubing to create specific pieces of glassware such as pipettes, burettes, and condensers.
- Crafting Specialized Apparatus: Making precise cuts for specialized glass apparatus required in unique experimental setups.
2. Modifying Existing Glassware
- Trimming Glass Pieces: Adjusting the length of glass tubing in pre-made laboratory setups for optimal fit and function.
- Creating Openings: Making openings or notches in glassware for connections or modifications.
3. Chemical and Biological Experiments
- Setting Up Reactions: Preparing glass tubing for use in various chemical reactions, ensuring the tubing fits properly into reaction setups.
- Biological Sampling: Creating customized glass tools for sampling and handling biological materials.
4. Instrumentation Assembly
- Assembling Glass Instruments: Constructing and modifying glass components in instruments like gas chromatography setups, distillation columns, and other analytical equipment.
- Repair and Maintenance: Repairing damaged glass parts of laboratory instruments to ensure they function correctly.
5. Educational Demonstrations
- Teaching Tool: Demonstrating proper glass cutting techniques in educational settings to train students and laboratory personnel.
- Hands-On Learning: Allowing students to practice cutting glass tubing as part of their laboratory skills development.
6. Creating Joints and Connectors
- Fabricating Glass Joints: Making precise cuts to form joints and connectors between different glass components, ensuring airtight and secure connections.
- Connecting Tubes: Customizing glass tubing to create smooth connections in complex glassware assemblies.
7. Smoothing Edges and Preparing Ends
- Deburring Edges: After cutting, the edges can be sharp; the cutter helps in making clean cuts that are easier to smooth with minimal additional work.
- Preparing Ends for Sealing: Ensuring the cut ends of the glass tubing are smooth and even, making them easier to seal with heat or to attach to other components.
8. Safety Enhancements
- Reducing Breakage Risk: By making clean, precise cuts, the cutter helps reduce the risk of glass breakage and associated hazards during experiments.
- Minimizing Injuries: Proper use of the cutter minimizes the likelihood of injuries that can occur from jagged or improperly cut glass.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Absorption Tower
KSh0.01
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
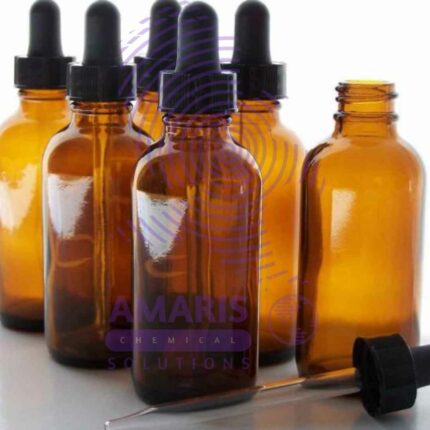
Amber Bottles Polystop
KSh0.01
A laboratory glass amber bottle is a specialized container commonly used in laboratories to store and protect light-sensitive substances, chemicals, or solutions. These bottles are made from amber-colored glass, which provides protection against ultraviolet (UV) and visible light radiation. The amber glass helps to minimize the degradation and decomposition of light-sensitive contents by blocking a significant portion of the light spectrum.
The amber color of the glass is achieved by adding iron, sulfur, and other compounds during the glass manufacturing process. This coloration is what gives the bottles their distinctive amber or brown appearance.
Laboratory glass amber bottles typically come in various sizes, ranging from small volumes of a few milliliters to large capacities of several liters. They often have a screw-on or snap-on cap, providing a secure and airtight seal to prevent spills, evaporation, and contamination.
Due to their ability to protect light-sensitive substances, laboratory glass amber bottles are widely used in chemistry, biology, pharmaceuticals, and other scientific fields where sample integrity and stability are crucial.
Aspirator Bottle Glass
A laboratory aspirator glass bottle, also known as a vacuum aspirator bottle or a vacuum filtration flask, is a specialized glass container used in scientific laboratories for various applications. It is designed to create a vacuum or negative pressure, which allows the filtration of liquids through a porous medium like a filter paper or a membrane.
The bottle typically has a conical or pear-shaped body with a sidearm or neck near the top. This neck is where a rubber or silicone stopper is inserted, allowing for the attachment of tubing or a hose to connect to a vacuum source or water aspirator. (Available in 2.5l,5l,10l,)
Laboratory aspirator glass bottles are commonly used in vacuum filtration processes to separate a solid precipitate from a liquid solution. When connected to a vacuum source, the air inside the bottle is removed, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the filter, leaving the solid behind on the filter paper.
These bottles come in various sizes to accommodate different filtration needs and are an essential tool in many research, analytical, and quality control laboratories for tasks like separating particulate matter, sterilizing solutions, and performing various filtration techniques. They are often made of durable borosilicate glass to withstand the pressure changes and chemical interactions that may occur during laboratory operations.
Atomic Model Set
KSh0.01
A lab atomic model set is a collection of physical models and materials designed to represent the structure of atoms and molecules. It is commonly used in educational and scientific laboratory settings to visually demonstrate the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, as well as the bonding patterns between atoms in molecules. These sets typically include colored balls of various sizes representing different types of atoms, as well as connectors or magnets to simulate chemical bonds between them. The purpose of these sets is to help students and researchers better understand the principles of atomic and molecular structure in a tangible and interactive way.
balance spring
KSh0.01
beaker hysil
KSh0.01
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.