Glass Rod for Static Electricity
KSh0.01
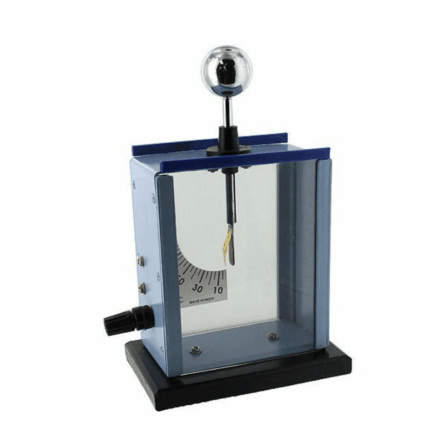

Gold Leaf Electroscope
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,700.00Current price is: KSh1,700.00.
Glass Tubing Cutter Wheel Type
KSh900.00 Original price was: KSh900.00.KSh800.00Current price is: KSh800.00.
A glass tubing cutter with a wheel type design is a commonly used tool in laboratories for precisely cutting glass tubing. These cutters are preferred for their ability to make clean and smooth cuts with minimal effort and risk of breaking the glass unevenly.
SKU:
ACS54332CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Glass Tubing Cutter Wheel Type
1. Preparing Custom Glassware
- Cutting Glass Tubing to Size: Customizing the length of glass tubing to create specific pieces of glassware such as pipettes, burettes, and condensers.
- Crafting Specialized Apparatus: Making precise cuts for specialized glass apparatus required in unique experimental setups.
2. Modifying Existing Glassware
- Trimming Glass Pieces: Adjusting the length of glass tubing in pre-made laboratory setups for optimal fit and function.
- Creating Openings: Making openings or notches in glassware for connections or modifications.
3. Chemical and Biological Experiments
- Setting Up Reactions: Preparing glass tubing for use in various chemical reactions, ensuring the tubing fits properly into reaction setups.
- Biological Sampling: Creating customized glass tools for sampling and handling biological materials.
4. Instrumentation Assembly
- Assembling Glass Instruments: Constructing and modifying glass components in instruments like gas chromatography setups, distillation columns, and other analytical equipment.
- Repair and Maintenance: Repairing damaged glass parts of laboratory instruments to ensure they function correctly.
5. Educational Demonstrations
- Teaching Tool: Demonstrating proper glass cutting techniques in educational settings to train students and laboratory personnel.
- Hands-On Learning: Allowing students to practice cutting glass tubing as part of their laboratory skills development.
6. Creating Joints and Connectors
- Fabricating Glass Joints: Making precise cuts to form joints and connectors between different glass components, ensuring airtight and secure connections.
- Connecting Tubes: Customizing glass tubing to create smooth connections in complex glassware assemblies.
7. Smoothing Edges and Preparing Ends
- Deburring Edges: After cutting, the edges can be sharp; the cutter helps in making clean cuts that are easier to smooth with minimal additional work.
- Preparing Ends for Sealing: Ensuring the cut ends of the glass tubing are smooth and even, making them easier to seal with heat or to attach to other components.
8. Safety Enhancements
- Reducing Breakage Risk: By making clean, precise cuts, the cutter helps reduce the risk of glass breakage and associated hazards during experiments.
- Minimizing Injuries: Proper use of the cutter minimizes the likelihood of injuries that can occur from jagged or improperly cut glass.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Balance Bathroom Scale
KSh0.01
Balance lever
KSh0.01
The best definition of a balance lever is a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or beam that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. It is used to compare the weights or forces of two objects and determine if they are in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the other (unbalanced).
The balance lever operates on the principle of torque, where the torque (rotational force) exerted on one side of the fulcrum is equal to the torque on the other side when the system is in equilibrium. This principle is expressed by the formula: Torque = Force × Distance from fulcrum.
By placing known masses or weights on one side of the lever and an unknown weight on the other side, the balance lever can be used as a weighing scale. When the lever is in balance, the two sides are equal in weight or force. This concept has been widely used in various applications, from traditional weighing scales to more complex systems like seesaws or construction equipment.
bare enamelled copper wire
KSh0.01
Barlows wheel apparatus
KSh0.01
The Barlow's wheel apparatus is an experimental device used to demonstrate the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic principles. It consists of a horizontal wheel or disk with radial metal spokes attached to its center. The wheel is mounted on an axle, allowing it to rotate freely.
Beaker Plastic
KSh0.01
A plastic beaker is a laboratory container made from plastic material, typically featuring a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a spout or pouring lip. It is used for holding, measuring, and mixing liquids or substances during various scientific experiments, research, or educational activities. Plastic beakers come in a range of sizes and are designed to withstand various chemicals and temperatures, making them versatile tools in laboratory settings.
Beaker Simax
KSh0.01
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Boyles Law apparatus
KSh0.01