Glass Rod for Static Electricity
KSh0.01
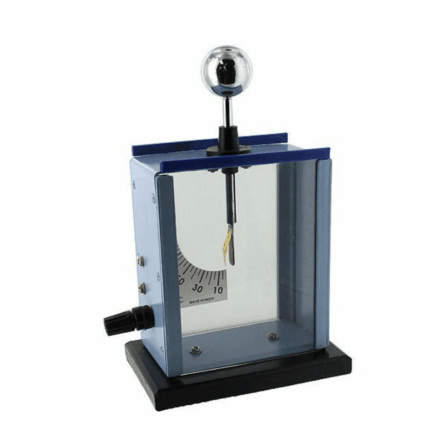

Gold Leaf Electroscope
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,700.00Current price is: KSh1,700.00.
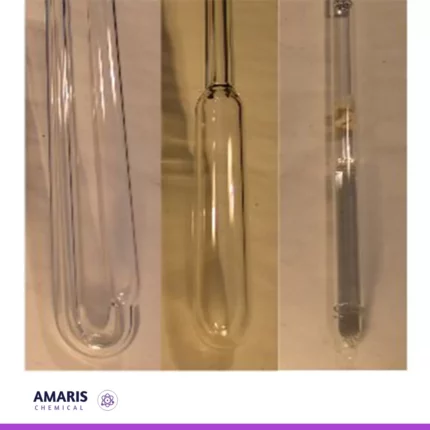
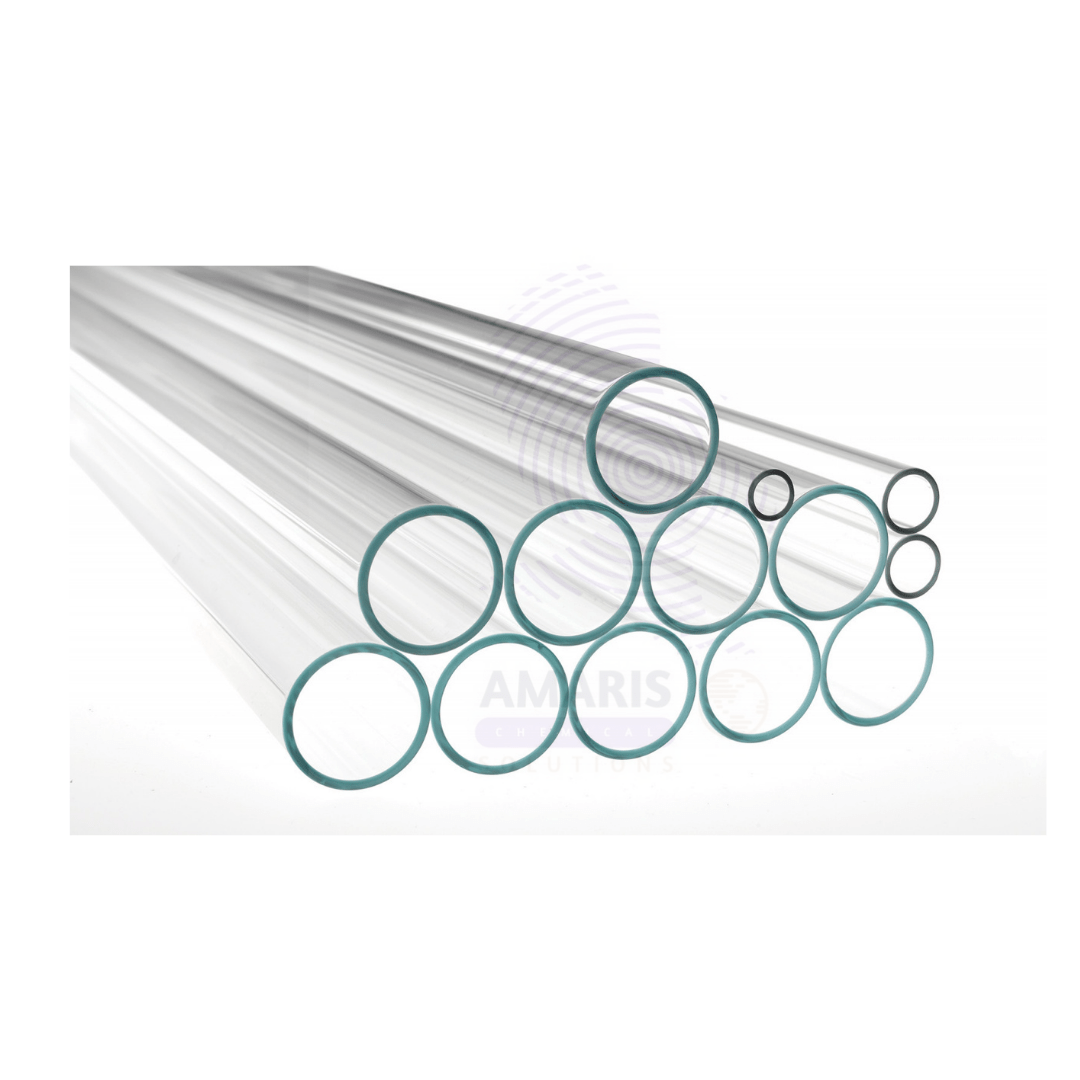
Glass Tubing
KSh500.00 Original price was: KSh500.00.KSh400.00Current price is: KSh400.00.
Glass tubing is a versatile material commonly used in various scientific, industrial, and decorative applications. It is typically made from borosilicate glass, which is known for its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for laboratory use.
SKU:
ACS29438CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Glass tubing
1. Manufacture of Laboratory Apparatus
- Test Tubes: Glass tubing is cut and shaped into test tubes, which are essential for holding, mixing, and heating chemical substances.
- Pipettes: Used for transferring precise volumes of liquids, glass pipettes are made from drawn glass tubing.
- Burettes: Graduated glass tubes with a stopcock at one end, used for titrations.
- Condensers: Glass tubing is used to make condensers for cooling vapor in distillation processes.
2. Fluid Transfer and Flow Systems
- Connecting Tubes: Used to connect various pieces of lab equipment, allowing the transfer of gases or liquids between them.
- Capillary Tubes: Very fine glass tubes used for tasks such as drawing small quantities of fluids or for chromatography.
3. Reactions and Heating
- Reaction Tubes: Glass tubing can be used to construct reaction tubes for carrying out small-scale chemical reactions.
- Heating Elements: Glass tubing can be used to hold and heat samples in controlled conditions due to its resistance to thermal shock.
4. Measurement Instruments
- Manometers: U-shaped glass tubes filled with liquid (such as mercury or water) used to measure pressure differences.
- Gas Syringes: Glass syringes connected via glass tubing are used to measure and manipulate gases.
5. Gas Handling and Sampling
- Gas Collection: Glass tubing is often used in setups for collecting and analyzing gases produced in reactions.
- Gas Sampling Tubes: Used to capture and analyze gaseous samples from various environments or reactions.
6. Distillation and Separation
- Distillation Columns: Made from glass tubing, these columns are essential for separating mixtures based on different boiling points.
- Fractionating Columns: Used in fractional distillation to improve the separation of mixtures.
7. Chromatography
- Chromatography Columns: Glass tubing is used to make columns for liquid chromatography, which are used to separate chemical mixtures.
8. Protective and Insulating Uses
- Sheaths for Thermocouples: Glass tubing can encase thermocouples, protecting them from corrosive substances.
- Insulating Tubes: Used to insulate wires or other components in high-temperature environments.
9. Specialized Uses
- Optical Systems: Sometimes glass tubing is used in optical instruments for its clarity and purity.
- Spectroscopy: Glass tubing can be part of setups for spectroscopic analysis, where it helps guide and contain light or samples.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Aspirator Bottle Glass
A laboratory aspirator glass bottle, also known as a vacuum aspirator bottle or a vacuum filtration flask, is a specialized glass container used in scientific laboratories for various applications. It is designed to create a vacuum or negative pressure, which allows the filtration of liquids through a porous medium like a filter paper or a membrane.
The bottle typically has a conical or pear-shaped body with a sidearm or neck near the top. This neck is where a rubber or silicone stopper is inserted, allowing for the attachment of tubing or a hose to connect to a vacuum source or water aspirator. (Available in 2.5l,5l,10l,)
Laboratory aspirator glass bottles are commonly used in vacuum filtration processes to separate a solid precipitate from a liquid solution. When connected to a vacuum source, the air inside the bottle is removed, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the filter, leaving the solid behind on the filter paper.
These bottles come in various sizes to accommodate different filtration needs and are an essential tool in many research, analytical, and quality control laboratories for tasks like separating particulate matter, sterilizing solutions, and performing various filtration techniques. They are often made of durable borosilicate glass to withstand the pressure changes and chemical interactions that may occur during laboratory operations.
Balance Bathroom Scale
KSh0.01
bar and gauge apparatus
KSh0.01
Barometer tubes
KSh0.01
A barometer tube is a slender, sealed, and typically transparent tube used in barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. It is usually filled with a liquid, often mercury, but sometimes water or another fluid, which rises or falls within the tube in response to changes in atmospheric pressure. The height of the liquid column in the tube serves as an indicator of the current atmospheric pressure, with higher pressure causing the liquid to fall and lower pressure causing it to rise. This measurement helps in predicting weather changes and understanding atmospheric conditions.
beaker hysil
KSh0.01
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
beaker pyrex
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.