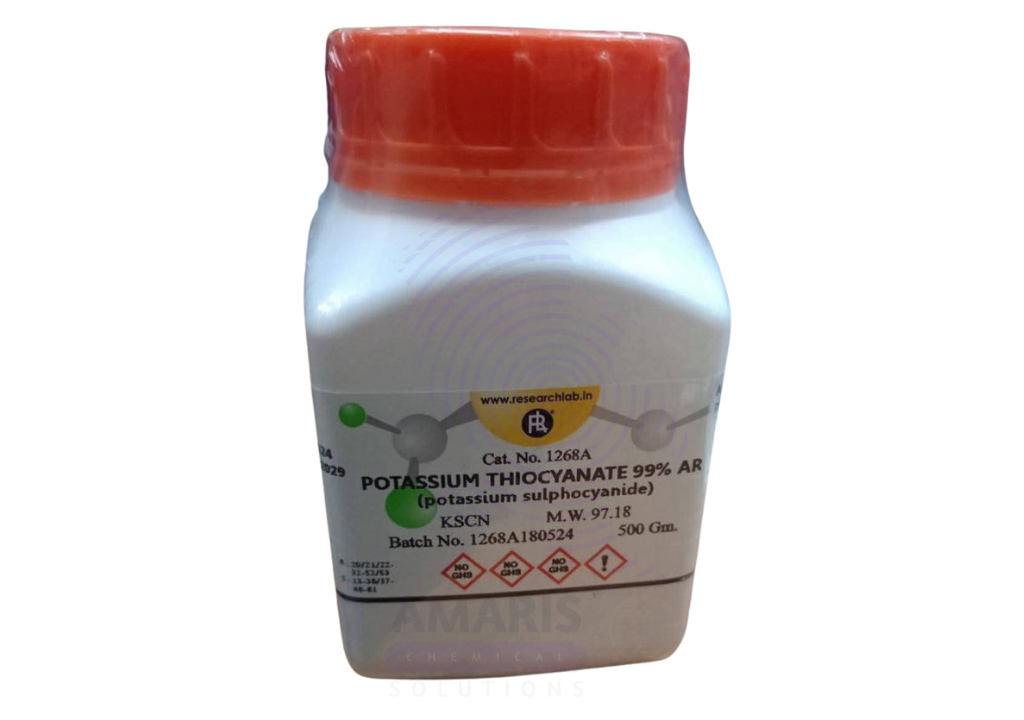
Potassium Thiocyanate Extra Pure
$ 18.00 Original price was: $ 18.00.$ 17.78Current price is: $ 17.78.
Potassium Thiocyanate Extra Pure is a high-purity crystalline compound commonly used in analytical chemistry, forensic science, and complexometric titrations. Known for forming deeply colored complexes with iron and other metal ions, it is frequently employed as a qualitative reagent for detecting ferric ions. In laboratory environments, it also plays a role in spectrophotometric analysis, chemical synthesis, and photographic processing. Its extra pure grade ensures exceptional clarity and consistency in results, making it suitable for precision applications where reagent-grade chemicals are not sufficient.
Potassium Thiocyanate Extra Pure
PRIMARY USES
- Analytical Chemistry
- Used in iron(III) thiocyanate tests to detect Fe³⁺ ions (deep red complex formation).
- Common reagent for colorimetric and spectrophotometric analysis of various metal ions.
- Applied in gravimetric and titrimetric
- Forensic & Toxicological Analysis
- Plays a role in blood and saliva analysis due to its ability to react with specific ions.
- Used in chemical detection kits and trace residue identification.
- Photographic Industry
- Acts as a fixing agent and stabilizer in photographic emulsions.
- Assists in complexation and removal of unreacted silver halides.
SECONDARY USES
- Chemical Synthesis
- Intermediate in preparing thiocyanate complexes, organosulfur compounds, and catalysts.
- Used in the formation of transition metal coordination compounds.
- Biochemical Applications
- Employed in protein denaturation studies and enzyme activity assays as a chaotropic agent.
- Facilitates membrane permeability studies in controlled environments.
- Educational Laboratories
- Demonstrates coordination chemistry, redox reactions, and ligand exchange principles in classrooms.
- Suitable for color reaction demonstrations and reagent preparation.
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name: Potassium Thiocyanate
- CAS Number: 333-20-0
- HS Code: 2842.90.90
- Molecular Formula: KSCN
- Synonyms:
- Potassium rhodanide
- Thiocyanic acid, potassium salt
- KSCN
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Solid (crystalline powder or granules)
- Color & Odor: Colorless to white crystals; faint bitter or sulfur-like odor
- Boiling Point & Melting Point:
- Melting Point: ~173 °C
- Decomposes before boiling
- Density/Specific Gravity: ~1.89 g/cm³
- Solubility:
- Soluble in water (highly soluble)
- Soluble in ethanol and acetone
- pH Level: ~6–8 (1% aqueous solution)
- Vapor Pressure & Volatility: Negligible vapor pressure
- Flash Point: Not flammable
- Autoignition Temperature: Not applicable
- Viscosity: Not applicable (solid)
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Hazard Class (GHS Classification):
- Acute Toxicity (Oral, Category 4)
- Eye Irritation (Category 2A)
- NFPA Ratings:
- Health: 2
- Flammability: 0
- Reactivity: 1
- Exposure Limits:
- No specific OSHA PEL or ACGIH TLV established
- Reactivity:
- Incompatible with strong acids, oxidizers, and nitrates
- May release toxic gases (e.g., hydrogen cyanide) when heated or acidified
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place
- Protect from light and moisture
- Incompatible Materials:
- Acids, strong oxidizing agents, nitrates
- Container Type:
- Airtight plastic or glass containers
- Shelf Life & Expiration Date:
- Stable under recommended conditions; check every 2–3 years
- Special Handling Requirements:
- Use gloves and safety goggles
- Work in a fume hood if handling powders or solutions extensively
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Regulatory Status:
- Listed under TSCA and REACH
- Hazard Symbols (GHS Pictograms):
- ⚠️ Warning (Acute toxicity, eye irritation)
- Transportation Restrictions:
- Not regulated as a hazardous material by DOT/ADR
- No UN number
- Waste Disposal Method:
- Dispose as hazardous waste
- Must comply with local, state, and national environmental regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.)
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Ecotoxicity:
- Toxic to aquatic organisms in high concentrations
- Persistence in Environment:
- Can degrade slowly; may persist in water if not treated
- Carcinogenicity/Mutagenicity:
- Not classified as carcinogenic by IARC, NTP, or OSHA
- Biodegradability:
- Not readily biodegradable; inorganic salt
- Not readily biodegradable; inorganic salt
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Chemical-resistant lab coat
- Nitrile gloves (check for integrity before use)
- Safety goggles or chemical splash face shield
- Dust mask or respirator in case of inadequate ventilation
Handling:
- Handle with care in a well-ventilated area
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing
- Do not inhale dust or vapors
- Prevent release into the environment
- Avoid mixing with acids — may release toxic hydrogen cyanide gas
Storage:
- Store tightly sealed in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
- Protect from moisture and light
- Keep away from incompatible materials such as acids, strong oxidizers, and metals
- Label properly and keep away from food and drink
FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation:
- Remove victim to fresh air immediately
- Keep at rest and warm
- Provide oxygen if breathing is difficult
- Seek immediate medical attention
Skin Contact:
- Immediately wash skin with soap and plenty of water
- Remove contaminated clothing
- Seek medical advice if irritation develops or persists
Eye Contact:
- Rinse cautiously with water for at least 15 minutes
- Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do
- Seek urgent medical attention
Ingestion:
- Rinse mouth with water (only if person is conscious)
- Do not induce vomiting
- Seek emergency medical help immediately — cyanide poisoning possible
FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES
Flammability:
- Not highly flammable but may decompose on heating
Extinguishing Media:
- Use dry chemical, CO₂, or alcohol-resistant foam
- Water spray may be used to cool containers, not for direct extinguishment
Hazardous Combustion Products:
- Hydrogen cyanide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, potassium oxides
Firefighter Protection:
- Full protective gear with self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA)
- Approach fire with caution — toxic gases may be released
- Control runoff to prevent environmental contamination


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders