Back to products


Combustion Boat
$ 8.20 Original price was: $ 8.20.$ 8.09Current price is: $ 8.09.
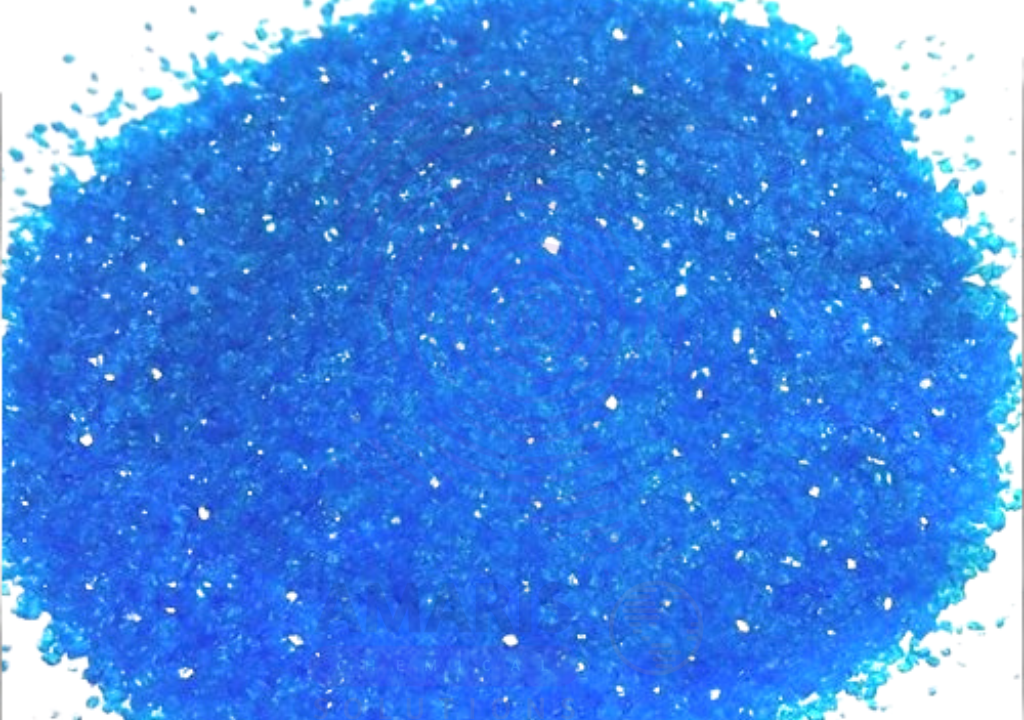
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate
Whatsapp Order
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate (Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate) is a bright blue crystalline solid with the chemical formula CuSO₄·5H₂O. It is the hydrated form of copper sulfate and is highly soluble in water. This compound is widely used in agriculture, chemical manufacturing, and laboratory applications due to its fungicidal, algicidal, and micronutrient properties. The pentahydrate form is the most common and commercially available, known for its vivid blue color and versatile reactivity.
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate Uses
Primary Uses
- Agriculture
- Widely used as a fungicide to control fungal diseases such as downy mildew, blight, and leaf spots in fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
- Acts as a copper micronutrient fertilizer to prevent and correct copper deficiency in soil and plants, essential for enzyme function and photosynthesis.
- Employed as a bactericide and algaecide in irrigation water and water reservoirs.
- Chemical & Industrial Applications
- Used as a raw material for producing other copper salts, catalysts, and chemicals.
- Utilized in analytical chemistry for Fehling’s and Benedict’s tests to detect reducing sugars.
- Functions as a mordant in textile dyeing and printing processes to fix dyes.
- Applied in electroplating baths for copper deposition.
Secondary Uses
- Water Treatment
- Used to control algae growth in ponds, reservoirs, and water treatment facilities, helping maintain water quality.
- Veterinary Medicine
- Included in trace mineral premixes for livestock feed to prevent copper deficiency and support overall animal health.
- Pigment and Paint Industry
- Serves as a pigment in ceramics, paints, and inks due to its distinctive blue color.
- Laboratory Reagent
- Used in research and educational labs for qualitative and quantitative analysis of chemicals.
KEY PRODUCT FEATURES
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name (IUPAC): Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
- Common/Trade Name: Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate, Blue Vitriol
- CAS Number: 7758-99-8
- HS Code: 2833.21.00
- Molecular Formula: CuSO₄·5H₂O
- Synonyms:
- Copper sulfate pentahydrate
- Blue vitriol
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Crystalline solid
- Color & Odor: Bright blue; odorless
- Melting Point: Decomposes at 110°C (loses water molecules)
- Boiling Point: Not applicable (decomposes before boiling)
- Density: ~2.28 g/cm³
- Solubility:
- Highly soluble in water (approx. 316 g/L at 20°C)
- Insoluble in ethanol and other organic solvents
- Stability: Stable under normal conditions; hygroscopic
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Hazard Class (GHS): Harmful if swallowed; hazardous to aquatic life
- NFPA Ratings:
- Health: 2
- Flammability: 0
- Reactivity: 0
- Exposure Limits: OSHA PEL = 1 mg/m³ (as Cu)
- Toxicity: Can cause irritation to eyes, skin, and respiratory tract; toxic if ingested in large amounts
- Reactivity: Stable; reacts with strong reducing agents
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances such as strong acids and bases. Keep containers tightly closed.
- Container Type: Polyethylene or glass containers recommended.
- Shelf Life: 3-5 years if stored properly.
- Special Handling: Use PPE to avoid dust inhalation and skin contact; avoid moisture exposure to prevent caking.
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- FDA Status: Not approved for direct food contact; agricultural uses regulated.
- REACH Status: Registered and regulated under EU chemical safety laws.
- Transportation: Classified as hazardous material (Class 6.1 toxic substance) with appropriate labeling.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose in accordance with local hazardous waste regulations; avoid environmental contamination.
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Ecotoxicity: Highly toxic to aquatic organisms; avoid discharge into water bodies.
- Persistence: Copper ions may persist and accumulate in sediments.
- Bioaccumulation: Possible bioaccumulation in aquatic life.
- Carcinogenicity/Mutagenicity: Not classified as carcinogenic; toxicity primarily from copper ions.
- Biodegradability: Inorganic compound; not biodegradable but can be immobilized.
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Handling Precautions
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Protective gloves
- Safety goggles
- Dust mask or respirator when handling powder
Handling Measures:
- Avoid inhaling dust and prevent skin and eye contact
- Use in well-ventilated areas
- Prevent spills and moisture exposure
Storage Measures:
- Keep container sealed and dry
- Store away from incompatible materials such as strong reducing agents
Hygiene Practices:
- Wash hands after handling
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling the product
First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if breathing is difficult.
- Skin Contact: Wash thoroughly with water; seek medical care if irritation develops.
- Eye Contact: Rinse eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes; seek immediate medical help.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth; do not induce vomiting; seek emergency medical assistance.
Firefighting Measures
- Fire Hazards: Non-flammable; decomposition produces toxic fumes when heated.
- Extinguishing Media: Use water spray, foam, dry chemical, or CO₂.
- Special Precautions: Firefighters should wear protective clothing and breathing apparatus.
- Decomposition Products: Copper oxides, sulfur oxides, and toxic fumes.
Related products
Ammonium Cupric Chloride
Ammonium Cupric Chloride is a blue-green crystalline inorganic compound composed of copper, ammonium, and chloride ions. It is widely used as a source of copper in agricultural fungicides and bactericides, as well as in electroplating, chemical synthesis, and textile dyeing. Its antimicrobial properties make it valuable for controlling fungal and bacterial infections in plants. Additionally, it serves as a precursor in various industrial and laboratory applications.
Bentonite Powder
Bentonite powder is a naturally occurring absorbent clay primarily composed of montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay mineral. It exhibits excellent swelling and water absorption properties, making it highly versatile in industrial and commercial applications. Bentonite forms a gel-like substance when mixed with water, which imparts viscosity and plasticity. It is used extensively for its binding, sealing, and adsorptive characteristics. Its fine powder form allows for easy incorporation in various processes including drilling, foundry, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate (CuSO₄·5H₂O) is a bright blue crystalline solid widely used as a chemical reagent, agricultural fungicide, and analytical reagent. It consists of copper, sulfur, oxygen, and water molecules, forming a distinctive pentahydrate structure. This inorganic salt is highly soluble in water, exhibiting antifungal, algaecidal, and bactericidal properties. Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate is extensively employed in agriculture, industry, and laboratory applications due to its effectiveness, affordability, and well-understood chemistry.
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous (Copper(II) sulfate, anhydrous form) is a blue to green crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It is an inorganic compound consisting of copper, sulfur, and oxygen with the formula CuSO₄. Unlike its hydrated counterpart (CuSO₄·5H₂O), the anhydrous form contains no water molecules. It is widely used in agriculture, industry, and chemical manufacturing due to its fungicidal, algicidal, and chemical reactivity properties. The compound serves as a precursor to many copper salts and catalysts.
DL-Methionine Feed Grade
DL-Methionine Feed Grade is a synthetic, racemic mixture of the amino acid methionine, consisting of equal parts D- and L-isomers. It is an essential sulfur-containing amino acid widely used as a nutritional supplement in animal feed formulations. DL-Methionine plays a critical role in protein synthesis, growth, and metabolic functions in livestock and poultry. This feed-grade quality ensures high purity (minimum 99%) and suitability for inclusion in feed blends to enhance growth performance, improve feed efficiency, and prevent methionine deficiency-related disorders.
Guanidine Carbonate
Guanidine Carbonate is a white crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, with strong basicity and high nitrogen content. It’s a versatile chemical intermediate widely used in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, polymer chemistry, textiles, and laboratory research. Its buffering properties and reactivity make it valuable in synthesis, pH regulation, and as a nitrogen source.
L-Lysine HCL Feed Grade
L-Lysine HCL Feed Grade is a highly pure form of the essential amino acid lysine combined with hydrochloric acid to improve its stability and solubility. It appears as a white crystalline powder and is widely used as a dietary supplement in animal feed to enhance growth, improve feed efficiency, and balance amino acid profiles. L-Lysine HCL is critical in poultry, swine, and aquaculture nutrition, helping to meet animals’ lysine requirements for protein synthesis and overall health.
Zinc chloride
Zinc Chloride is a highly versatile, white crystalline inorganic compound known for its strong hygroscopic nature and high solubility in water. It serves multiple industrial roles including fluxing, dehydrating, catalysis, and preservation. With applications across metallurgy, pharmaceuticals, textiles, water treatment, and chemical synthesis, Zinc Chloride is valued for its reactivity and binding properties.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders