Pharmaceutical Grade refers to the highest quality and purity level of chemicals and ingredients used in the production of medicines and healthcare products. .
Pharmaceutical Grade materials are used in:
Formulation of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
Production of excipients such as binders, fillers, disintegrants, and preservatives
Injectables, tablets, capsules, creams, and syrups
Biotech and vaccine manufacturing
Clinical research and drug development
Acesulfame K
Acesulfame K
Acesulfame K, also known as Acesulfame Potassium or Ace-K, is a high-intensity artificial sweetener that is commonly used as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products. It is a white, odorless powder that is about 200 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar), but it has no caloric value and does not affect blood sugar levels. Acesulfame K is chemically stable and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for use in baked goods and other heat-processed products. It is often found in sugar-free or low-calorie products, such as diet sodas, sugar-free chewing gums, desserts, and tabletop sweeteners.
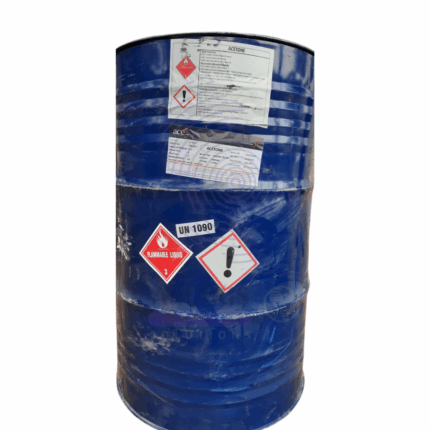
Acetone
Acetone
Acetone is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. It is a common organic solvent that is widely used in the production of plastics, fibers, drugs, and other chemical compounds. Acetone is also commonly used as a cleaning agent and a nail polish remover. Chemically, it is the simplest ketone and is represented by the formula CH3COCH3.
Amphoteric
Amphoteric refers to a substance or compound that has the ability to react as both an acid and a base. In other words, it can either accept a proton (H+) to act as a base or donate a proton to act as an acid, depending on the conditions of the reaction. The term "amphoteric" is often used in the context of chemistry to describe species that exhibit this dual nature of reactivity.
Bleaching Earth
Bleaching earth is a vital industrial adsorbent that purifies oils, fats, and fuels by removing impurities, improving quality, and ensuring stability. Its effectiveness, versatility, and cost-efficiency make it indispensable in food processing, biofuels, petrochemicals, and environmental applications.
Calcium carbonate (Coated)
Calcium Carbonate (coated) refers to a form of calcium carbonate in which the individual particles of the mineral are coated or encapsulated with a layer of a different material. This layer can be composed of various substances, such as stearic acid, fatty acids, or other polymers. The purpose of the coating is to modify the surface properties of the calcium carbonate particles, such as their hydrophobicity or compatibility with other materials, making them more suitable for specific applications. Coated calcium carbonate is widely used in industries such as plastics, paper, paints, and coatings, where it can improve the properties of the final product, such as brightness, whiteness, and durability.
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CaCl2. It is a salt composed of calcium and chlorine ions and is highly soluble in water. Calcium chloride is commonly used as a desiccant, de-icer, and in various industrial processes. It is also used in food and beverage applications as a firming agent, and in medicine as a source of calcium for people with calcium deficiencies.
Calcium propionate
Calcium propionate is a food additive that is commonly used as a preservative to prevent the growth of mold and other microorganisms in various food products. It is the calcium salt of propionic acid and is often referred to by its chemical formula, Ca(C2H5COO)2. Calcium propionate is white crystalline powder or granules that are easily soluble in water. When added to food, it helps extend its shelf life by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and molds, thereby preventing spoilage. It is commonly used in baked goods, dairy products, processed meats, and other foods where mold and bacterial growth are a concern.



 LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances