Description
Provides the suck in force that enables a dropper to hold liquid while transferring to new containers.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
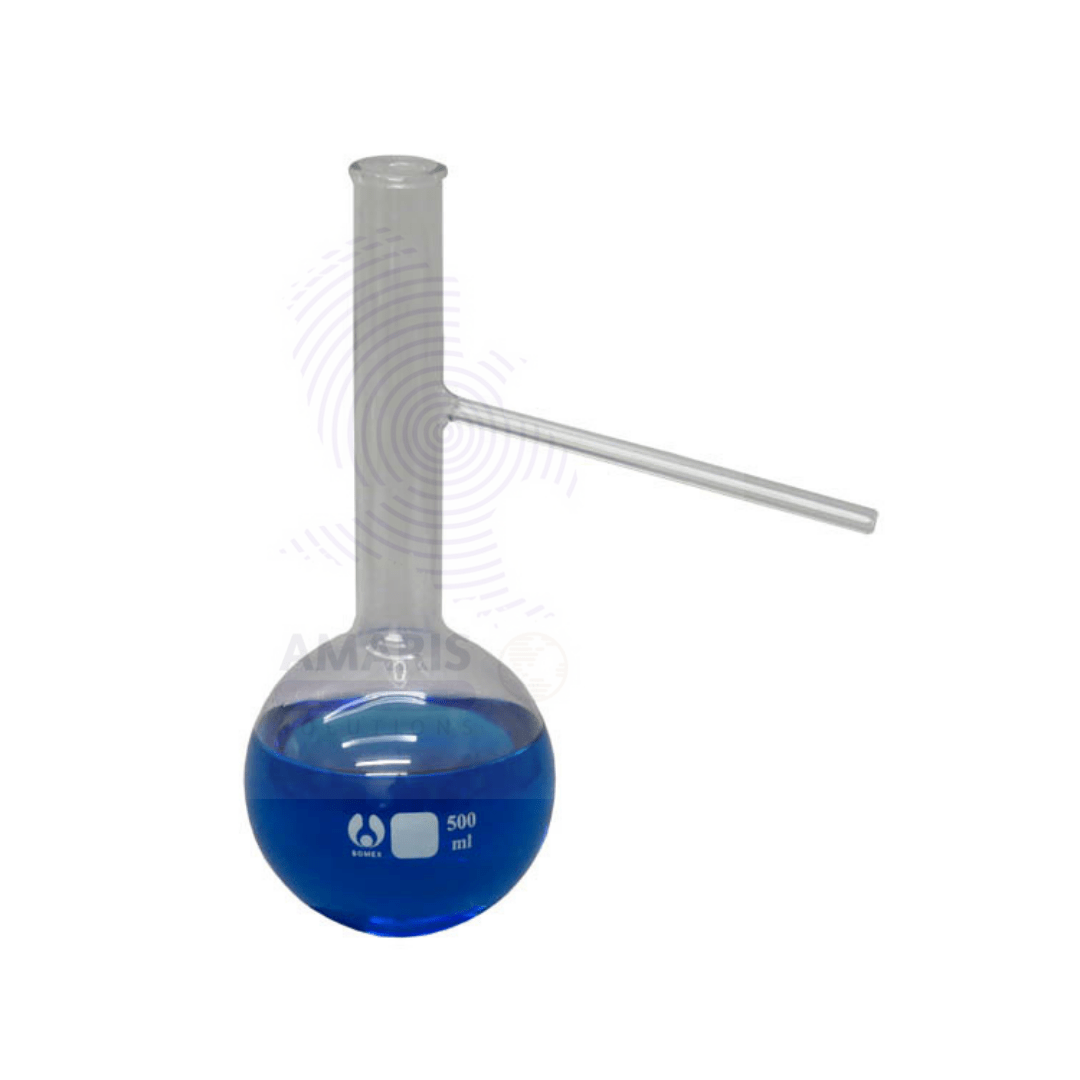
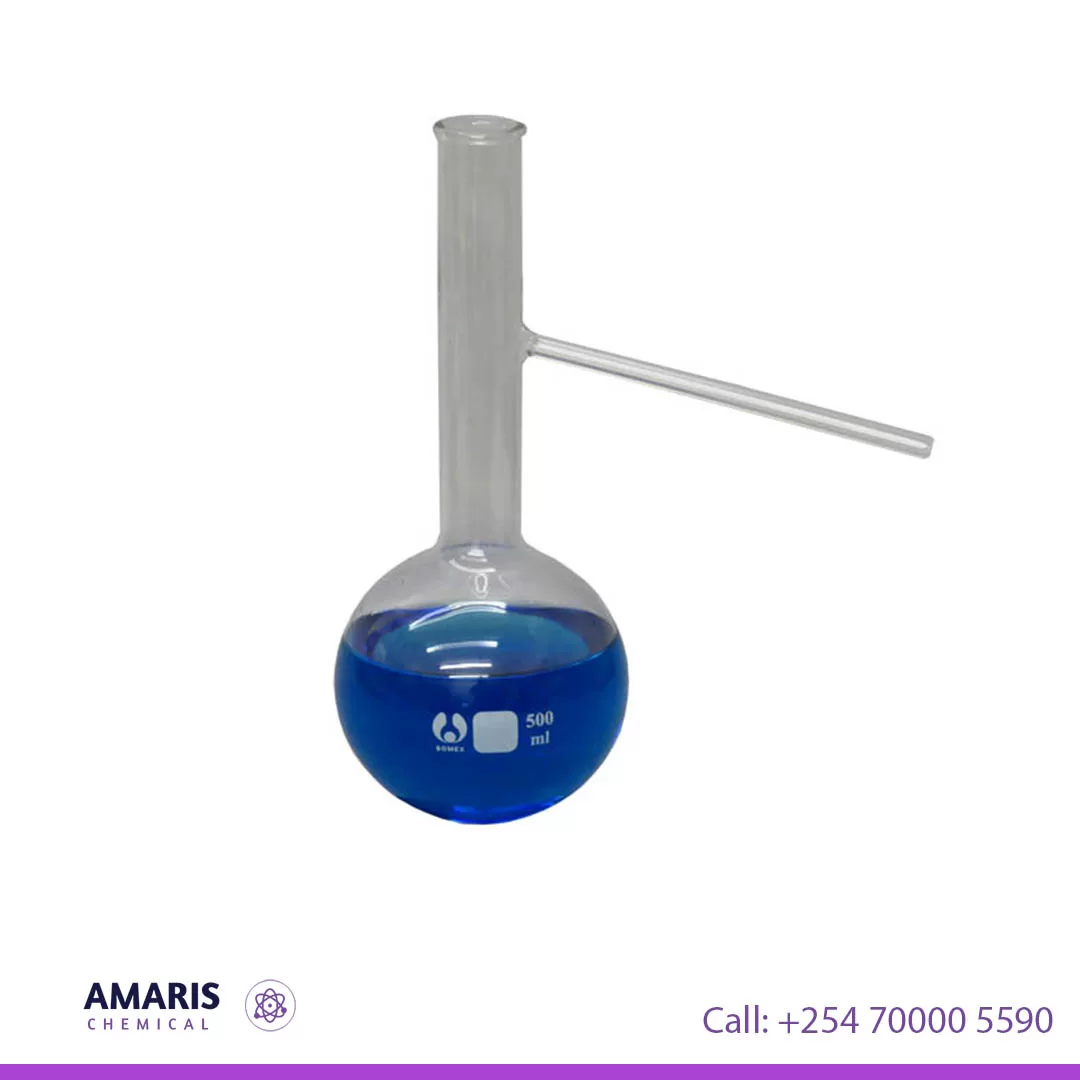
Aspirator Bottle Glass
A laboratory aspirator glass bottle, also known as a vacuum aspirator bottle or a vacuum filtration flask, is a specialized glass container used in scientific laboratories for various applications. It is designed to create a vacuum or negative pressure, which allows the filtration of liquids through a porous medium like a filter paper or a membrane.
The bottle typically has a conical or pear-shaped body with a sidearm or neck near the top. This neck is where a rubber or silicone stopper is inserted, allowing for the attachment of tubing or a hose to connect to a vacuum source or water aspirator. (Available in 2.5l,5l,10l,)
Laboratory aspirator glass bottles are commonly used in vacuum filtration processes to separate a solid precipitate from a liquid solution. When connected to a vacuum source, the air inside the bottle is removed, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the filter, leaving the solid behind on the filter paper.
These bottles come in various sizes to accommodate different filtration needs and are an essential tool in many research, analytical, and quality control laboratories for tasks like separating particulate matter, sterilizing solutions, and performing various filtration techniques. They are often made of durable borosilicate glass to withstand the pressure changes and chemical interactions that may occur during laboratory operations.
Atomic Model Set
KSh0.01
A lab atomic model set is a collection of physical models and materials designed to represent the structure of atoms and molecules. It is commonly used in educational and scientific laboratory settings to visually demonstrate the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, as well as the bonding patterns between atoms in molecules. These sets typically include colored balls of various sizes representing different types of atoms, as well as connectors or magnets to simulate chemical bonds between them. The purpose of these sets is to help students and researchers better understand the principles of atomic and molecular structure in a tangible and interactive way.
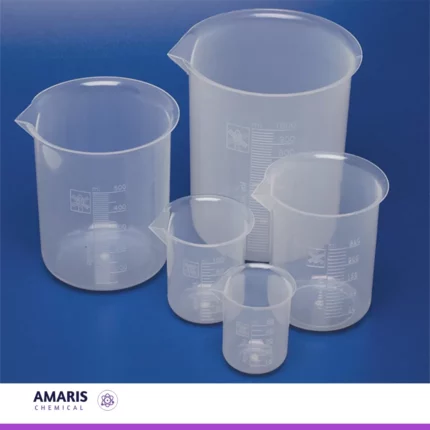
Beaker Plastic
KSh0.01
A plastic beaker is a laboratory container made from plastic material, typically featuring a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a spout or pouring lip. It is used for holding, measuring, and mixing liquids or substances during various scientific experiments, research, or educational activities. Plastic beakers come in a range of sizes and are designed to withstand various chemicals and temperatures, making them versatile tools in laboratory settings.
Beaker Simax
KSh0.01
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Blotting paper
KSh0.01
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent and thin sheet of paper, typically made from materials like cotton, linen, or other plant fibers. It is designed to quickly absorb excess liquids, such as ink, oil, or moisture, from various surfaces without smudging or smearing the substances. Blotting paper is commonly used to remove excess ink from a freshly written page, absorb oil from the skin without disturbing makeup, or dry wet items. It is often found in office settings, art studios, and cosmetic applications due to its efficient absorption properties.
blow pipes
KSh0.01
A blowpipe apparatus is a scientific instrument used in analytical chemistry and mineralogy for conducting various tests, particularly flame tests and microchemical reactions. It typically consists of a small tube or pipette through which a controlled stream of air or oxygen is blown onto a sample being heated. This stream of air or oxygen enhances the combustion of the sample, allowing the observation of characteristic colors emitted by different elements when they are vaporized and excited by the heat. The blowpipe apparatus is often used to identify and differentiate between different elements and compounds based on their unique emission spectra and reactions.