Solvents are liquid chemicals designed to dissolve, suspend, or extract grease, oils, adhesives, and other stubborn contaminants without damaging surfaces. They are widely used in industrial, automotive, and household cleaning applications due to their fast-evaporating and degreasing properties.
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is a simple organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CHO. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, fruity odor. Here are some key points about acetaldehyde:
- Chemical Structure: Acetaldehyde consists of two carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and four hydrogen atoms. Its structure is CH3CHO, where the carbon atom in the middle is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom and singly bonded to a hydrogen atom and a methyl group (CH3).
- Occurrence: Acetaldehyde can be found naturally in various ripe fruits, coffee, and heated milk. It is also produced by the oxidation of ethanol (alcohol) by enzymes in the liver and other tissues in humans, making it an intermediate product in alcohol metabolism.
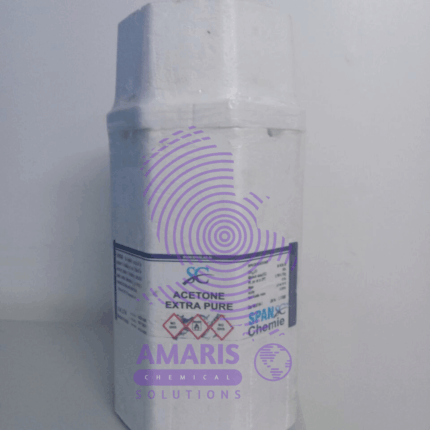
Acetone Extra Pure
Acetone Extra Pure
Acetone is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. It is a common organic solvent that is widely used in the production of plastics, fibers, drugs, and other chemical compounds. Acetone is also commonly used as a cleaning agent and a nail polish remover. Chemically, it is the simplest ketone and is represented by the formula CH3COCH3.
Dichloromethane 270kg
Dichloromethane, also known as methylene chloride, is a volatile organic compound and a colorless, sweet-smelling chemical compound with the chemical formula CH2Cl2. It is a widely used solvent in various industrial applications and laboratory processes. Dichloromethane is characterized by its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic and inorganic substances, making it valuable in tasks such as paint stripping, degreasing, and as a solvent in chemical reactions. However, it should be handled with care as it can pose health and environmental risks due to its potential toxicity and volatility.
Diethyl Glycol (DEG)
Diethyl glycol (DEG) is a colorless, low-volatility liquid with a slightly sweet odor. It is a clear, water-soluble liquid that is commonly used as a solvent in the production of lacquers, varnishes, and resins. DEG is also used in the manufacture of plasticizers, lubricants, and brake fluids. It is a member of the ethylene glycol family of compounds and has the chemical formula C4H10O2. However, it is important to note that DEG can be toxic if ingested, and appropriate safety measures should be taken when handling this substance.
Ethyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate is a widely used organic compound with the chemical formula C₄H₈O₂, known for its pleasant, fruity odor and excellent solvent properties. As a fast-evaporating ester, it serves as a key ingredient in industries such as paints, coatings, and printing inks, where it acts as a low-toxicity thinner and drying agent. In the pharmaceutical sector, it is utilized for drug extraction and tablet coatings, while the food industry employs it as a flavoring agent to impart fruity notes in candies and beverages. Its effectiveness as a degreaser makes it valuable in electronics and metal cleaning. Additionally, ethyl acetate finds applications in cosmetics, adhesives, and even as a biodegradable alternative in decaffeination processes. Despite its advantages—such as being relatively non-toxic and environmentally friendly—it is highly flammable and requires careful handling. Overall, ethyl acetate's versatility, mild odor, and solvent efficiency make it indispensable across multiple industrial and commercial applications.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters