Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate 500gm
Disodium phosphate, also known as sodium hydrogen phosphate or disodium hydrogen phosphate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2HPO4. It is a white, crystalline powder or granular solid that is highly soluble in water.
In terms of its chemical composition, disodium phosphate consists of two sodium (Na+) ions and one phosphate (PO43-) ion. It is derived from phosphoric acid and is commonly used as a food additive, pH buffer, and a source of phosphorus in various industries.
As a food additive, disodium phosphate is primarily used as a texturizer, emulsifier, and stabilizer in processed foods and beverages. It helps improve the texture, increase shelf life, and prevent the separation of ingredients. Additionally, it can act as a pH regulator in certain food products.
In summary, disodium phosphate is an inorganic compound that serves various purposes in food and industrial applications, primarily as a food additive and pH buffer.
Distilled Water 20 liters
Distilled water is water that has been purified through a process of distillation. Distillation involves boiling water and then condensing the steam back into liquid form, leaving behind impurities and contaminants. This process removes minerals, salts, and other substances, resulting in water that is nearly pure H2O. Distilled water is commonly used in laboratory settings, in medical procedures, and in some household appliances such as steam irons and humidifiers. It's also often used in automotive cooling systems and in certain types of aquariums. However, because it lacks minerals that are beneficial to health, long-term consumption of distilled water may not be ideal for human consumption.
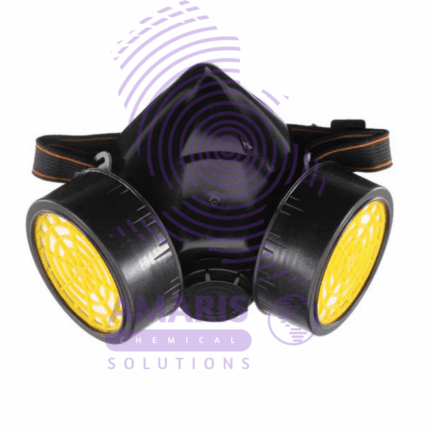
Double Gas Mask
A double gas mask, also known as a dual cartridge respirator, is commonly used in laboratories and industrial settings where there's a risk of exposure to hazardous gases, vapors, or particulates.
Here's how it works:
- Dual Cartridges: The mask has two cartridges, one on each side of the mask, which contain filters to purify the air. These cartridges are usually filled with activated charcoal or other filtering materials designed to absorb or neutralize specific chemicals or particulates.
- Seal: A proper seal between the mask and the wearer's face is crucial to ensure that no contaminated air can leak in. This seal is typically achieved through adjustable straps that secure the mask snugly against the face.
- Exhalation Valve: Most masks have an exhalation valve to allow the wearer to exhale easily without causing a buildup of moisture or CO2 inside the mask.
- Visibility: The mask is designed to provide adequate visibility while still offering protection. Some models have anti-fog features to prevent the visor from fogging up during use.
- Compatibility: Depending on the specific hazards in the environment, different types of cartridges can be used with the mask. These cartridges are often color-coded for easy identification.
- Fit Testing: It's essential for users to undergo fit testing to ensure that the mask provides an effective seal. Fit testing involves performing various exercises to check for any leaks around the mask's edges.
EDTA Disodium Salt 500gm
Tetra sodium EDTA, also known as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt, is a chemical compound commonly used in various industrial and commercial applications. It is a chelating agent, meaning it has the ability to bind and capture metal ions, thus preventing them from reacting with other substances or causing unwanted effects.
A concise definition of tetra sodium EDTA would be:
"Tetra sodium EDTA is a water-soluble salt derived from ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, used as a chelating agent to bind and sequester metal ions, serving purposes such as metal complexation, stabilization, and preventing undesired chemical reactions."
Egg Albumen
Egg albumen refers to the clear, viscous substance found within an egg's shell, commonly known as egg white. It's composed mainly of water and proteins, including albumin, globulins, and mucoproteins. Egg albumen serves various purposes in cooking and baking, providing structure, leavening, moisture, and binding properties to a wide range of dishes, from meringues to soufflés. Additionally, it's a good source of protein and is often used as a dietary supplement or in various skincare products due to its purported benefits for skin health.
Fehling Solution 1 and 2
Fehling's solution is used in chemistry to detect the presence of reducing sugars. It is composed of two separate solutions that are mixed in equal volumes just before use.
Fehling's Solution 1
- Composition: This solution contains copper(II) sulfate (CuSO₄).
- Appearance: It is a deep blue solution.
- Preparation: Typically prepared by dissolving copper(II) sulfate in water.
Fehling's Solution 2
- Composition: This solution contains a mixture of potassium sodium tartrate (Rochelle salt) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Appearance: It is a clear, colorless solution.
- Preparation: Potassium sodium tartrate and sodium hydroxide are dissolved in water.
Ferric Chloride anhydrous 500gm
Ferric chloride anhydrous is a dark brown, crystalline solid with the chemical formula FeCl3. It is an inorganic compound that is highly soluble in water and has a strong acidic odor. Ferric chloride anhydrous is a powerful oxidizing agent and is commonly used as a coagulant in water treatment, as a catalyst in chemical reactions, and as a etchant in the electronics industry. It is also used in the production of dyes, pigments, and other chemicals. Ferric chloride anhydrous is a corrosive substance that should be handled with care, as it can cause skin and eye irritation and can be harmful if ingested or inhaled
Ferric Nitrate 500gm
Ferric nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Fe(NO3)3. It is an inorganic salt that is typically found as a purple crystalline solid in its hydrated form. Here are some key points about ferric nitrate:
- Chemical Formula: Fe(NO3)3
- Appearance: Purple crystals in its hydrated form, and it is soluble in water.
Field Stain A and B 25gm
Field Stain A and B are used in a staining technique for blood films, particularly for the rapid identification of malaria parasites and other hematological purposes. The staining method is known as Field's stain, and it is a type of Romanowsky stain.
Field Stain A
- Composition: Field Stain A is typically an aqueous solution of methylene blue, which stains the nuclei of cells blue.
- Function: It primarily stains the acidic components of the cell, including DNA and RNA. This makes the nuclei and certain cytoplasmic components appear blue.
Field Stain B
- Composition: Field Stain B is usually an aqueous solution of eosin, which stains the basic components of the cell pink.
- Function: It stains the cytoplasm and extracellular components pink to red. Eosinophilic structures, such as red blood cells and certain granules, are highlighted by this stain.
Usage
- Procedure:
- Prepare the blood smear: A drop of blood is spread thinly on a glass slide and allowed to air dry.
- Apply Field Stain A: The dried smear is immersed in Field Stain A for a short duration, typically around 5-10 seconds.
- Rinse: The slide is briefly rinsed in water to remove excess stain.
- Apply Field Stain B: The smear is then immersed in Field Stain B for another short duration, around 5-10 seconds.
- Rinse and dry: The slide is rinsed again in water and allowed to air dry.
- Outcome: The resulting stained smear allows for the differentiation of various cell components, making it easier to identify and analyze blood cells and any parasitic infections like malaria.