Balance bathroom scale
A balance bathroom scale is a mechanical or digital device used to measure body weight or the mass of larger objects. It typically consists of a flat platform where the object or person stands, and it displays the weight either via an analog dial or a digital screen. Unlike precision laboratory balances, it is designed for general-use purposes where fine accuracy is not required, making it suitable for personal or approximate weight measurements. This type of scale is commonly found in homes or commercial settings and is robust enough to handle heavier loads
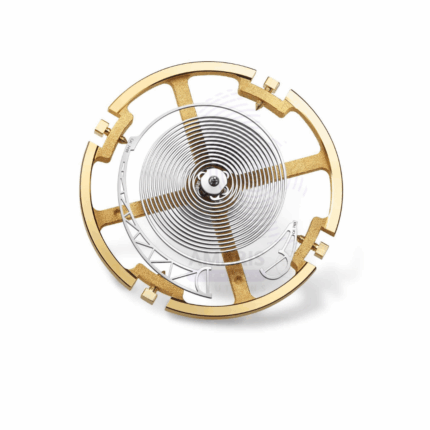
Balance spring
A balance spring, also known as a hairspring, is a fine, tightly coiled spring used in precision instruments, particularly in mechanical balances and watches, to control the oscillation of a balance wheel. In laboratory balances, it provides a restoring force that helps maintain equilibrium and ensures highly accurate measurements. The spring's flexibility and precision help in damping vibrations and stabilizing the balance, allowing the instrument to return to its zero position after disturbances. This makes the balance spring vital for precise and stable mass measurements, especially in analytical applications
Bar breaking apparatus
The bar breaking apparatus is a precision laboratory instrument designed to evaluate the mechanical strength of materials, specifically their ability to resist breaking under stress. It typically measures tensile strength, flexural strength, or break resistance by applying controlled force to bar-shaped specimens until they fracture. The device is essential in quality control, material testing, and research, offering precise data for materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Its robust design allows for consistent and repeatable testing, ensuring the reliability of the material's mechanical properties.
Barometer tubes
A barometer tube is a long, sealed glass or metal tube used to measure atmospheric pressure. It is typically filled with a liquid, such as mercury, with one end sealed and the other submerged in a reservoir of the same liquid. The atmospheric pressure pushes on the reservoir, causing the liquid level in the tube to rise or fall. The height of the liquid column reflects the current atmospheric pressure, allowing for precise readings. Barometer tubes are commonly used in meteorology, physics, and laboratory experiments to observe pressure changes and calibrate instruments.
Beaker hysil
A Hysil beaker is a type of laboratory glassware known for its high chemical resistance and durability. Made from borosilicate glass, it can withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes, making it ideal for various laboratory applications. The beaker features a wide mouth for easy pouring and stirring, with graduated markings on the side for approximate volume measurement. Its transparent nature allows for easy observation of the contents, while its flat bottom ensures stability on laboratory surfaces. Hysil beakers are commonly used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids, as well as conducting chemical reactions, making them an essential tool in scientific research and educational laboratories
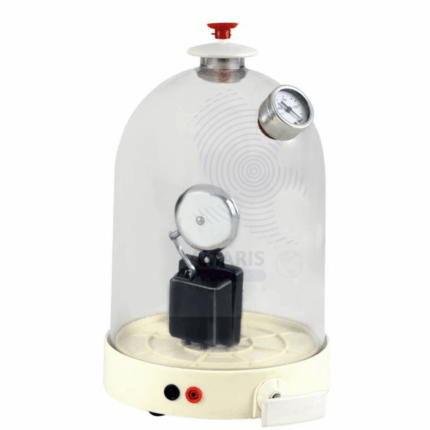
Bell in vacuum with air pump with plate
In a laboratory setting, a bell is positioned inside a clear vacuum chamber mounted on a sturdy plate. The vacuum chamber is connected to an air pump that allows for the controlled removal of air. When the bell is struck, it produces sound waves that normally propagate through the air. As the air is gradually pumped out of the chamber, the intensity of the sound decreases, demonstrating the principle that sound requires a medium, such as air, to travel. This visual and auditory demonstration effectively illustrates the concepts of sound transmission, pressure changes, and the properties of a vacuum, making it an excellent educational tool for exploring fundamental physics principles.
This setup enables students to witness firsthand how sound fades in a vacuum and encourages discussions about the relationship between sound and the medium through which it travels.
Bottle weighing plastic
Bottle weighing plastics, also known as weighing bottles or weigh boats, are lightweight containers specifically designed for laboratory use. They are made from durable, chemical-resistant plastic, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of substances. The smooth surfaces allow for easy cleaning and prevent sample contamination. These containers feature a wide mouth for convenient filling and transferring of solids and powders, promoting accurate and efficient weighing processes. Their lightweight design minimizes any impact on balance readings, making them ideal for precise measurements. Available in various sizes, bottle weighing plastics offer versatility for different laboratory applications, including sample storage, chemical reactions, and moisture-sensitive materials. Their transparent construction enables easy visibility of contents, facilitating quick identification and monitoring.
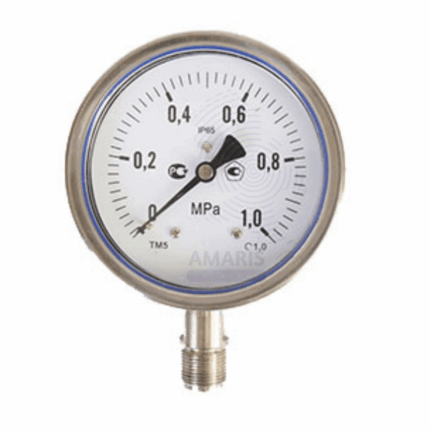
Bourdan gauge
A Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device used to measure pressure, typically of gases or liquids, with high accuracy and reliability. It consists of a curved, flexible tube (the Bourdon tube) that straightens as pressure increases. This movement is translated into a dial reading via a pointer, allowing users to easily gauge the pressure level.
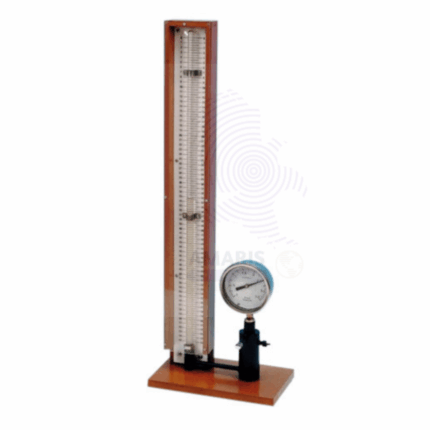
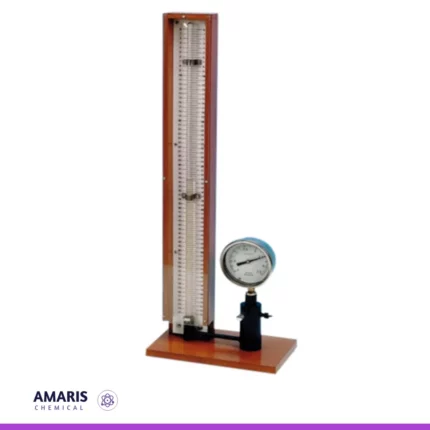
Boyles law apparatus
The Boyle's Law apparatus is a laboratory device designed to illustrate the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It typically features a sealed transparent container or cylinder that holds the gas, allowing for visual observation of any changes in volume. Attached to the container is a pressure measurement device, such as a manometer or pressure gauge, which accurately records the gas's pressure. The apparatus includes a volume adjustment mechanism, often in the form of a movable piston, enabling the user to compress or expand the gas and observe the corresponding pressure changes. Some setups may also incorporate temperature control to maintain constant conditions during experiments. Graduated scales on the apparatus facilitate precise measurements of gas volume. Overall, this apparatus serves as an essential educational tool, providing a hands-on experience for students to explore and understand Boyle's Law, which states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
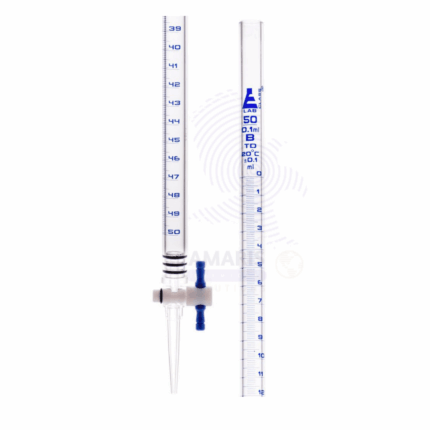
Burette acrylic
An acrylic burette is a precision laboratory instrument designed for accurate measurement and dispensing of liquid volumes. Constructed from durable, transparent acrylic, it allows for clear visibility of the liquid inside while being lightweight and resistant to breakage. The burette typically features a graduated scale for easy reading of volumes and a precision stopcock that enables controlled dispensing of liquids. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for use with a wide range of reagents, including acids and bases. Ideal for titration experiments and various analytical procedures, the acrylic burette combines functionality with safety, making it a valuable tool in both educational and professional laboratory settings.
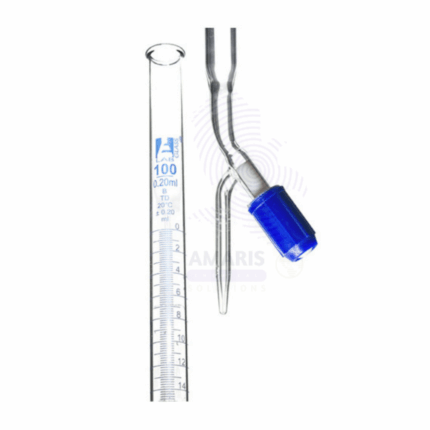
Burette rotaflow
The burette rotaflow is a precision laboratory instrument designed for accurate liquid dispensing and titration. It features a graduated glass or plastic tube with a rotating stopcock at its base, allowing for controlled flow and easy adjustment of liquid volume. The rotaflow mechanism enables a smooth, continuous release of liquid, making it ideal for applications requiring precise measurements.
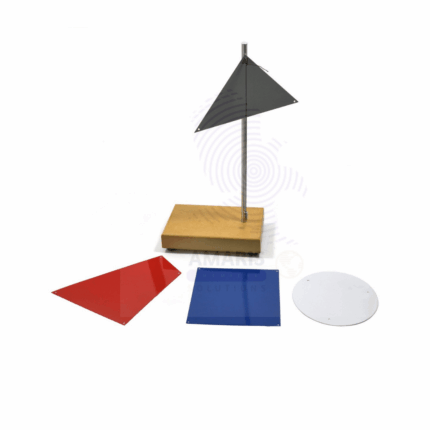
Centre of gravity apparatus
The center of gravity apparatus is a specialized tool used in physics and engineering to study the principles of balance, stability, and weight distribution. Typically consisting of a base platform with adjustable arms and a support for various objects, the apparatus allows users to precisely determine the center of gravity of different shapes and materials. By placing an object on the apparatus and adjusting weights or changing its orientation, users can visually and practically observe how the center of gravity influences stability. This hands-on experience facilitates a deeper understanding of equilibrium conditions, showcasing how an object's design affects its performance in real-world applications, such as in architecture or vehicle design. As an educational tool, the center of gravity apparatus effectively demonstrates key concepts in mechanics, making abstract theories tangible and accessible to students and researchers alike.
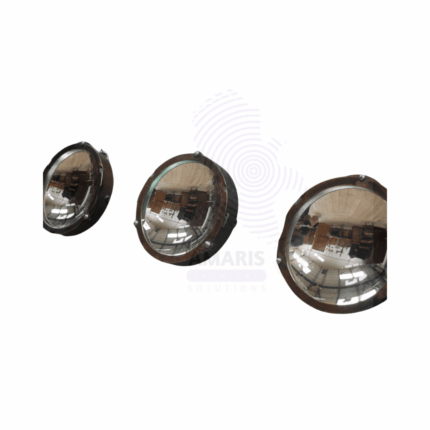
Concave mirrors
Concave mirrors are essential optical components, characterized by their inward curvature, ability to focus light, and versatile applications in various fields, from scientific research to everyday items. Their unique properties make them invaluable in any setting that requires precise light manipulation and image formation.
Magnetic needle on stand
A magnetic needle on a stand is a precision tool consisting of a lightweight, magnetized needle that pivots freely on a central point, typically mounted on a vertical stand. The needle aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field, pointing toward the magnetic north-south direction. The stand provides stability, allowing for clear and accurate readings.
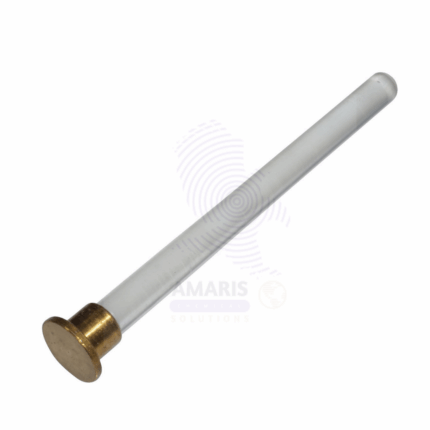
Proof Plane
A proof plane is a small, flat, conductive disk, typically made of metal, that is used in electrostatics experiments to sample electric charge from a surface. It serves as a tool to study charge distribution and behavior on conductors and insulators. When the proof plane makes contact with a charged object, it collects a small amount of charge, which can then be transferred to an electroscope or electrometer for measurement. This allows researchers to analyze electric fields, verify polarization, and demonstrate principles of electrostatics, such as charge conservation and transfer. Its design facilitates precise interactions with charged surfaces, making it essential for educational and experimental applications in physics.
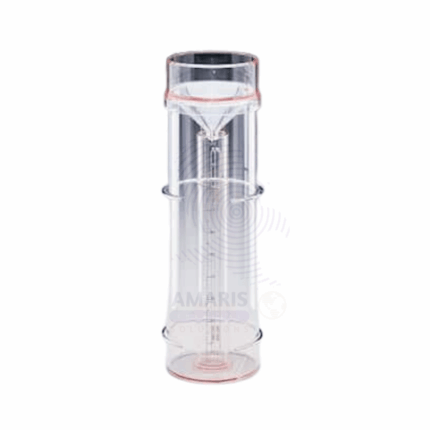
Rain gauge
A rain gauge is a simple yet effective instrument used to measure the amount of rainfall in a specific area over a set period. Typically consisting of a cylindrical container with a funnel at the top that directs rainwater into a measuring tube, it accurately collects and displays precipitation levels. Rain gauges can be made from various materials, including plastic or metal, and are often marked with measurement units (millimeters or inches) for easy reading. They can be manually checked or connected to digital sensors for automatic data recording, making them essential tools for meteorologists, gardeners, and anyone interested in tracking weather patterns.
Resistance box plug type
Resistance coil
A resistance coil is a length of conductive wire, typically made from high-resistance materials like nichrome, designed to convert electrical energy into heat through the process of resistive heating. When an electric current passes through the coil, the resistance of the wire generates heat, making it ideal for applications requiring controlled heating. Resistance coils are commonly used in laboratory equipment such as furnaces, ovens, and incubators to achieve precise temperature control for various scientific processes. Their durability and efficiency make them essential for consistent, reliable heating in research and experimental setups.
Smoke cell
A smoke cell is a specialized laboratory apparatus designed to capture and observe smoke particles generated from combustion or pyrolysis processes. Typically made of transparent glass, it allows researchers to study the physical and chemical properties of smoke in a controlled environment. Smoke cells are often used for analyzing particle size, distribution, and composition, as well as for examining light scattering and absorption behaviors. They play a crucial role in fields like atmospheric science, environmental chemistry, and material safety, enabling experiments that simulate real-world smoke interactions with air and light. Their transparent design facilitates direct observation and measurement, making them an invaluable tool for understanding smoke behavior and its implications.
Thermocouple
A thermocouple is a temperature-sensing device that converts heat into an electrical signal. It consists of two different metal wires joined at one end, forming a junction. When this junction experiences a change in temperature, a voltage is generated that is proportional to the temperature difference between the junction and a reference point. Thermocouples are known for their wide temperature range, fast response time, and durability, making them ideal for various industrial and laboratory applications. They are commonly used to monitor and control temperatures in processes requiring precision and reliability.
Tuning fork
This high-quality tuning fork set includes eight precision-tuned forks, each crafted from durable aluminum for optimal resonance and clarity. Each fork is meticulously tuned to specific frequencies, ranging from low to high pitches, making it an essential tool for sound experiments, musical applications, and educational demonstrations. Ideal for studying sound waves, resonance, and interference patterns, this set is perfect for laboratory use, music classrooms, and audiology tests. The included storage case ensures easy organization and portability, making it a practical choice for both professionals and students.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters