
gas jar with a lid
KSh250.00 Original price was: KSh250.00.KSh150.00Current price is: KSh150.00.
Glass tubbing cutter wheel type
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,500.00Current price is: KSh1,500.00.
Glass stirring rod
KSh250.00 Original price was: KSh250.00.KSh200.00Current price is: KSh200.00.
Whatsapp Order
A stirring rod, also known as a glass rod, is a slender, cylindrical piece of solid glass used for mixing chemicals and liquids in laboratory settings. Its smooth, inert surface makes it ideal for stirring solutions without reacting with the substances. The rod is typically about 20–30 cm in length, providing enough reach to mix in beakers, flasks, or other containers. Due to its heat-resistant properties, it can also be used to stir hot liquids without breaking or melting.
SKU:
ACS86322CHEM0
Category: LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
Description
Uses
- Stirring solutions: Glass rods are primarily used to stir mixtures or solutions, ensuring even distribution of solutes.
- Decanting liquids: When pouring liquids from one container to another, the glass rod helps guide the liquid along its surface to prevent splashing.
- Spreading liquids: In microbiology labs, glass rods (specifically bent into a “hockey stick” shape) are used to spread cultures on agar plates.
- Inducing crystallization: A glass rod can be used to scratch the inside of a container, inducing crystallization in supersaturated solutions.
- Testing for acidity: Glass rods can be used to transfer small drops of liquid onto pH indicator papers for acidity testing.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Glass stirring rod” Cancel reply
Related products
bar and gauge apparatus
KSh0.01
Barometer tubes
KSh0.01
A barometer tube is a slender, sealed, and typically transparent tube used in barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. It is usually filled with a liquid, often mercury, but sometimes water or another fluid, which rises or falls within the tube in response to changes in atmospheric pressure. The height of the liquid column in the tube serves as an indicator of the current atmospheric pressure, with higher pressure causing the liquid to fall and lower pressure causing it to rise. This measurement helps in predicting weather changes and understanding atmospheric conditions.
Beaker Plastic
KSh0.01
A plastic beaker is a laboratory container made from plastic material, typically featuring a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a spout or pouring lip. It is used for holding, measuring, and mixing liquids or substances during various scientific experiments, research, or educational activities. Plastic beakers come in a range of sizes and are designed to withstand various chemicals and temperatures, making them versatile tools in laboratory settings.
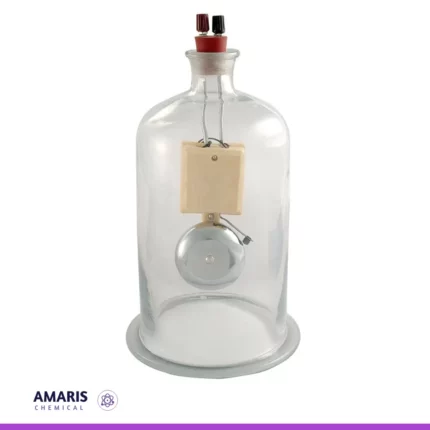
bell in vacuum
KSh0.01
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
bell in vacuum with air pump with plate
KSh0.01
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
Bernoulli Tube Apparatus
KSh0.01
The Bernoulli tube apparatus, also known as a Venturi tube apparatus, is a scientific device used to demonstrate the principles of fluid dynamics, particularly the Bernoulli's principle. It consists of a specially shaped tube with a constricted region, often referred to as a Venturi section. When fluid (liquid or gas) flows through the tube, the constricted section leads to changes in pressure and velocity according to Bernoulli's principle, which states that as the velocity of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases and vice versa. This apparatus is commonly used in educational settings to visually illustrate how the flow of a fluid can affect its pressure, helping to explain various phenomena like lift in aircraft wings, fluid flow through pipes, and more.



 LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.