Glass Rod for Static Electricity
KSh0.01
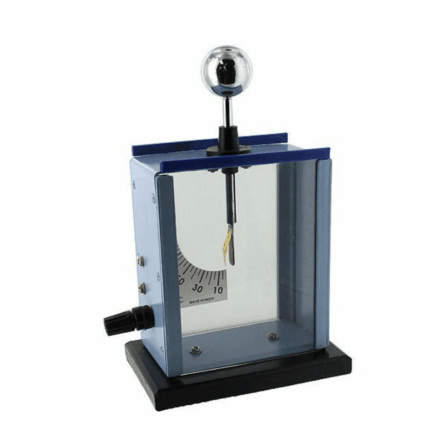

Gold Leaf Electroscope
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,700.00Current price is: KSh1,700.00.
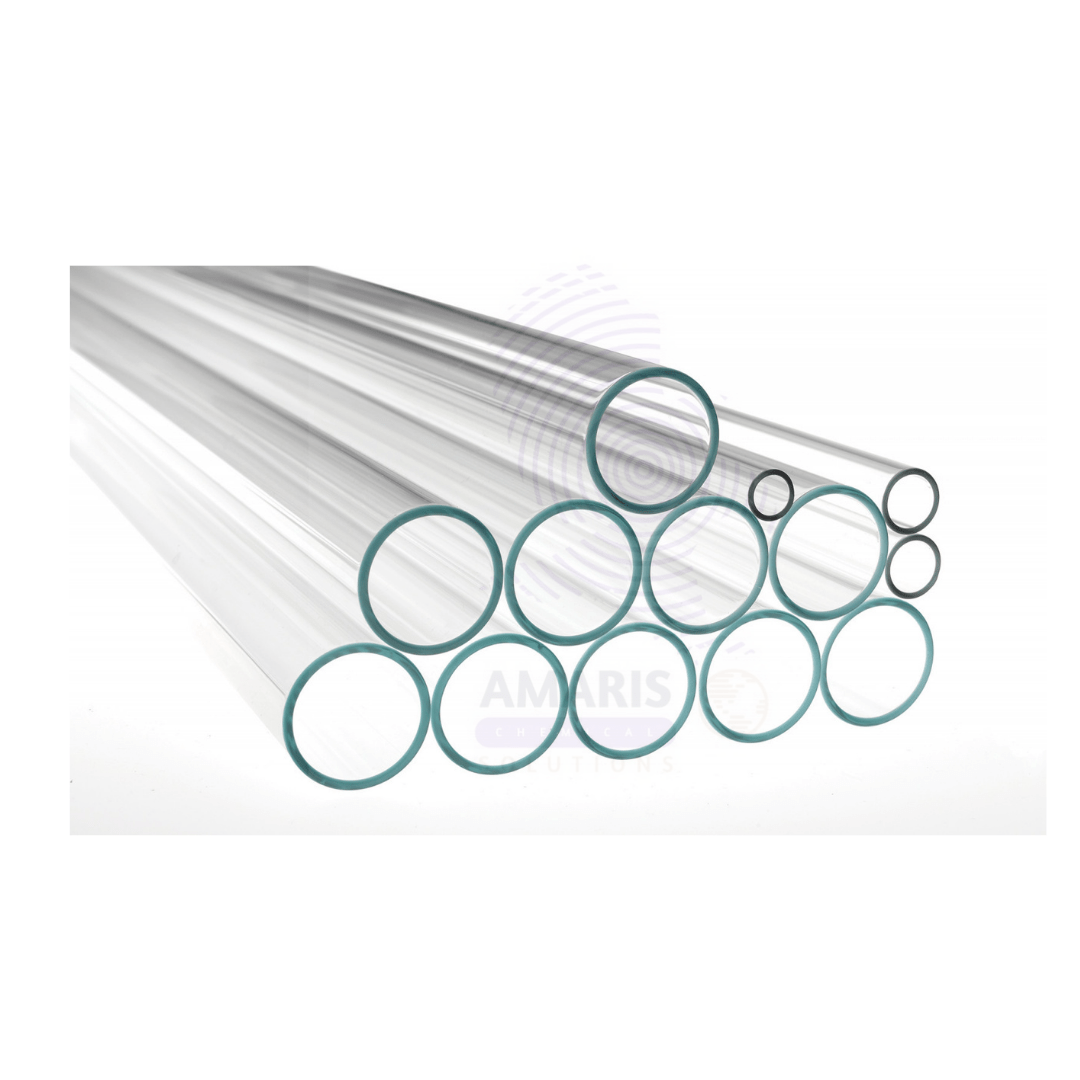
Glass Tubing
KSh500.00 Original price was: KSh500.00.KSh400.00Current price is: KSh400.00.
Glass tubing is a versatile material commonly used in various scientific, industrial, and decorative applications. It is typically made from borosilicate glass, which is known for its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for laboratory use.
SKU:
ACS29438CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Glass tubing
1. Manufacture of Laboratory Apparatus
- Test Tubes: Glass tubing is cut and shaped into test tubes, which are essential for holding, mixing, and heating chemical substances.
- Pipettes: Used for transferring precise volumes of liquids, glass pipettes are made from drawn glass tubing.
- Burettes: Graduated glass tubes with a stopcock at one end, used for titrations.
- Condensers: Glass tubing is used to make condensers for cooling vapor in distillation processes.
2. Fluid Transfer and Flow Systems
- Connecting Tubes: Used to connect various pieces of lab equipment, allowing the transfer of gases or liquids between them.
- Capillary Tubes: Very fine glass tubes used for tasks such as drawing small quantities of fluids or for chromatography.
3. Reactions and Heating
- Reaction Tubes: Glass tubing can be used to construct reaction tubes for carrying out small-scale chemical reactions.
- Heating Elements: Glass tubing can be used to hold and heat samples in controlled conditions due to its resistance to thermal shock.
4. Measurement Instruments
- Manometers: U-shaped glass tubes filled with liquid (such as mercury or water) used to measure pressure differences.
- Gas Syringes: Glass syringes connected via glass tubing are used to measure and manipulate gases.
5. Gas Handling and Sampling
- Gas Collection: Glass tubing is often used in setups for collecting and analyzing gases produced in reactions.
- Gas Sampling Tubes: Used to capture and analyze gaseous samples from various environments or reactions.
6. Distillation and Separation
- Distillation Columns: Made from glass tubing, these columns are essential for separating mixtures based on different boiling points.
- Fractionating Columns: Used in fractional distillation to improve the separation of mixtures.
7. Chromatography
- Chromatography Columns: Glass tubing is used to make columns for liquid chromatography, which are used to separate chemical mixtures.
8. Protective and Insulating Uses
- Sheaths for Thermocouples: Glass tubing can encase thermocouples, protecting them from corrosive substances.
- Insulating Tubes: Used to insulate wires or other components in high-temperature environments.
9. Specialized Uses
- Optical Systems: Sometimes glass tubing is used in optical instruments for its clarity and purity.
- Spectroscopy: Glass tubing can be part of setups for spectroscopic analysis, where it helps guide and contain light or samples.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Balance Bathroom Scale
KSh0.01
beaker pyrex
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
bell in vacuum with air pump with plate
KSh0.01
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
Blotting paper
KSh0.01
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent and thin sheet of paper, typically made from materials like cotton, linen, or other plant fibers. It is designed to quickly absorb excess liquids, such as ink, oil, or moisture, from various surfaces without smudging or smearing the substances. Blotting paper is commonly used to remove excess ink from a freshly written page, absorb oil from the skin without disturbing makeup, or dry wet items. It is often found in office settings, art studios, and cosmetic applications due to its efficient absorption properties.
blow pipes
KSh0.01
A blowpipe apparatus is a scientific instrument used in analytical chemistry and mineralogy for conducting various tests, particularly flame tests and microchemical reactions. It typically consists of a small tube or pipette through which a controlled stream of air or oxygen is blown onto a sample being heated. This stream of air or oxygen enhances the combustion of the sample, allowing the observation of characteristic colors emitted by different elements when they are vaporized and excited by the heat. The blowpipe apparatus is often used to identify and differentiate between different elements and compounds based on their unique emission spectra and reactions.