“Beaker Plastic” has been added to your cart. View cart


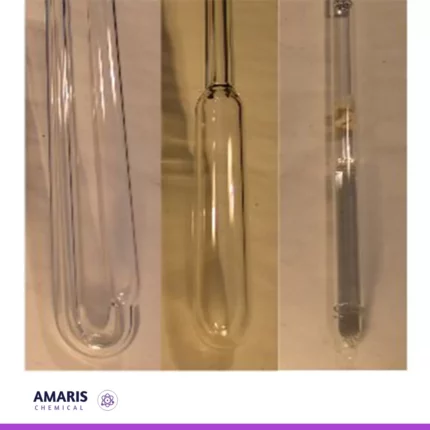
Glass tubing cutter file
$1,500.00 Original price was: $1,500.00.$1,400.00Current price is: $1,400.00.

Hoffman Voltameter
$500.00 Original price was: $500.00.$450.00Current price is: $450.00.
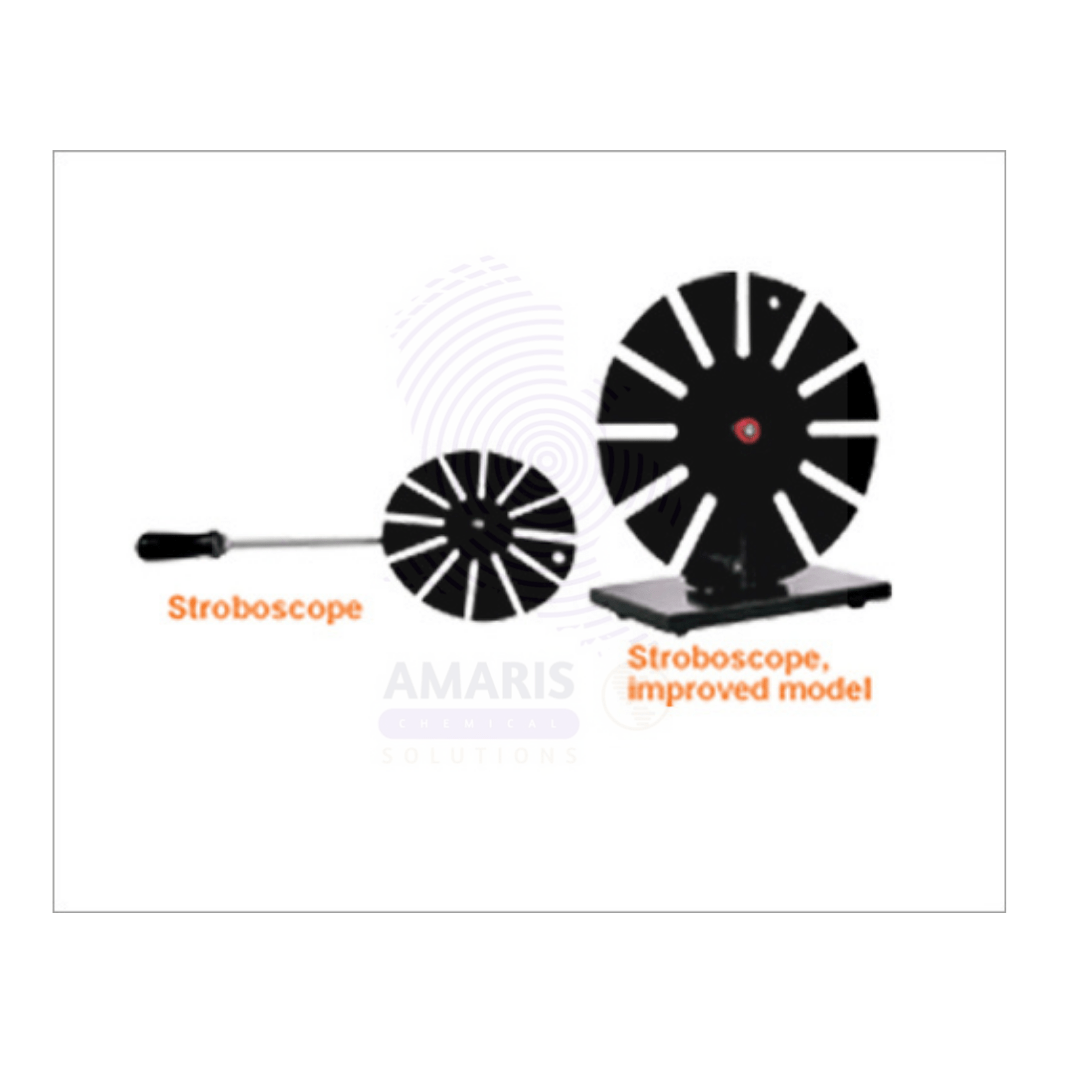
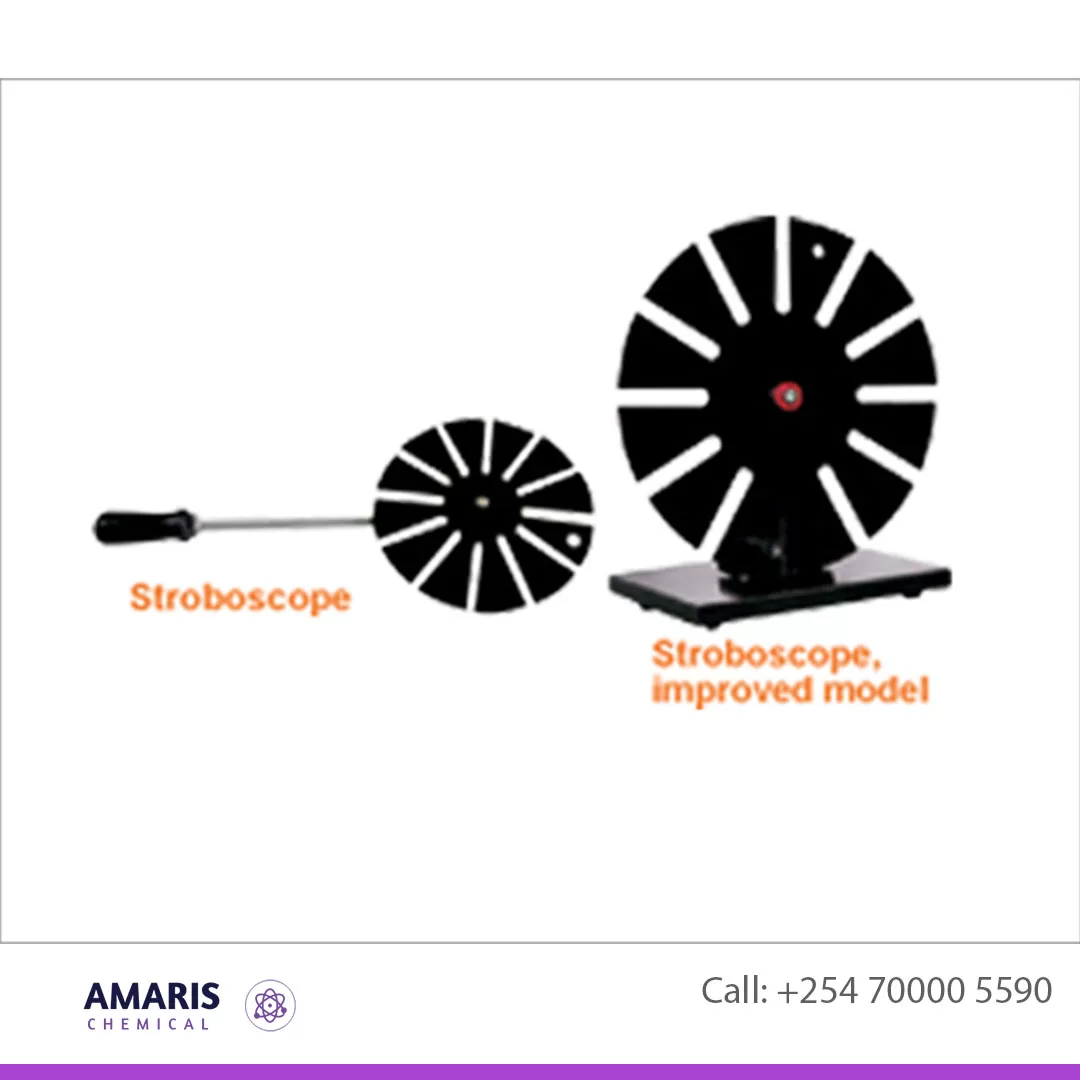
Hand Stroboscope
$850.00 Original price was: $850.00.$800.00Current price is: $800.00.
Whatsapp Order
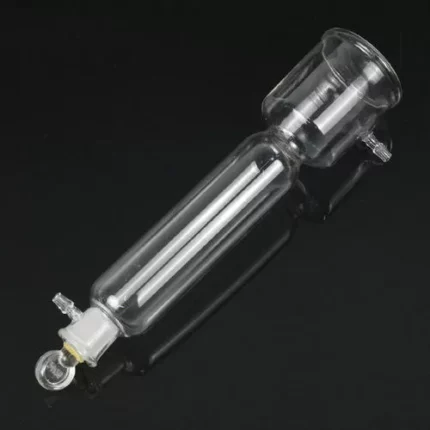
Hare’s Apparatus is a device used in laboratories to compare the densities of two liquids. It consists of two glass tubes connected at the bottom by a piece of flexible tubing and attached to a stand to keep the setup stable and upright.
SKU:
ACS35236CHEM0
Category: LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
Description
Uses of Hand stroboscope
- Density Comparison:
- Educational Demonstrations: Hare’s Apparatus is used in classrooms and laboratories to visually demonstrate the concept of density and how it affects the height of liquid columns.
- Experimental Determination: It allows students and researchers to determine the relative densities of two immiscible liquids by comparing the heights of the liquid columns in the two connected tubes.
- Hydrostatic Pressure Studies:
- Principle of Hydrostatic Pressure: The apparatus helps illustrate how different liquids exert different pressures at the same height due to their varying densities.
- Pascal’s Law: Demonstrates Pascal’s principle by showing how pressure applied to a fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
- Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle:
- Understanding Buoyancy: By comparing the densities of different liquids, students can better understand the concept of buoyancy and why objects float or sink in different liquids.
- Viscosity Studies:
- Flow and Viscosity: While primarily used for density comparison, Hare’s Apparatus can be adapted to observe the flow characteristics of different liquids, providing insights into their viscosities.
- Material Science:
- Solubility and Miscibility: It can be used to study the miscibility of different liquids and their solubility properties, which is important in material science and chemical engineering.
- Thermodynamic Studies:
- Temperature Effects on Density: By conducting experiments at different temperatures, students can observe how temperature changes affect the density of liquids, linking to concepts in thermodynamics.
- Calibration and Verification:
- Instrument Calibration: It serves as a simple tool for calibrating other instruments that measure liquid density, by providing a straightforward method for density comparison.
- Quality Control: In industrial laboratories, it can be used for quick quality control checks to ensure the consistency of liquid densities in processes such as food and beverage production.
- Chemical Analysis:
- Purity Testing: The apparatus can help in assessing the purity of liquids, as impurities often alter the density of a liquid.
Related products
Absorption Tower
$0.01
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
Balance lever
$0.01
The best definition of a balance lever is a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or beam that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. It is used to compare the weights or forces of two objects and determine if they are in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the other (unbalanced).
The balance lever operates on the principle of torque, where the torque (rotational force) exerted on one side of the fulcrum is equal to the torque on the other side when the system is in equilibrium. This principle is expressed by the formula: Torque = Force × Distance from fulcrum.
By placing known masses or weights on one side of the lever and an unknown weight on the other side, the balance lever can be used as a weighing scale. When the lever is in balance, the two sides are equal in weight or force. This concept has been widely used in various applications, from traditional weighing scales to more complex systems like seesaws or construction equipment.
balance spring
$0.01
Barometer tubes
$0.01
A barometer tube is a slender, sealed, and typically transparent tube used in barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. It is usually filled with a liquid, often mercury, but sometimes water or another fluid, which rises or falls within the tube in response to changes in atmospheric pressure. The height of the liquid column in the tube serves as an indicator of the current atmospheric pressure, with higher pressure causing the liquid to fall and lower pressure causing it to rise. This measurement helps in predicting weather changes and understanding atmospheric conditions.
Beaker Plastic
$0.01
A plastic beaker is a laboratory container made from plastic material, typically featuring a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a spout or pouring lip. It is used for holding, measuring, and mixing liquids or substances during various scientific experiments, research, or educational activities. Plastic beakers come in a range of sizes and are designed to withstand various chemicals and temperatures, making them versatile tools in laboratory settings.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters