

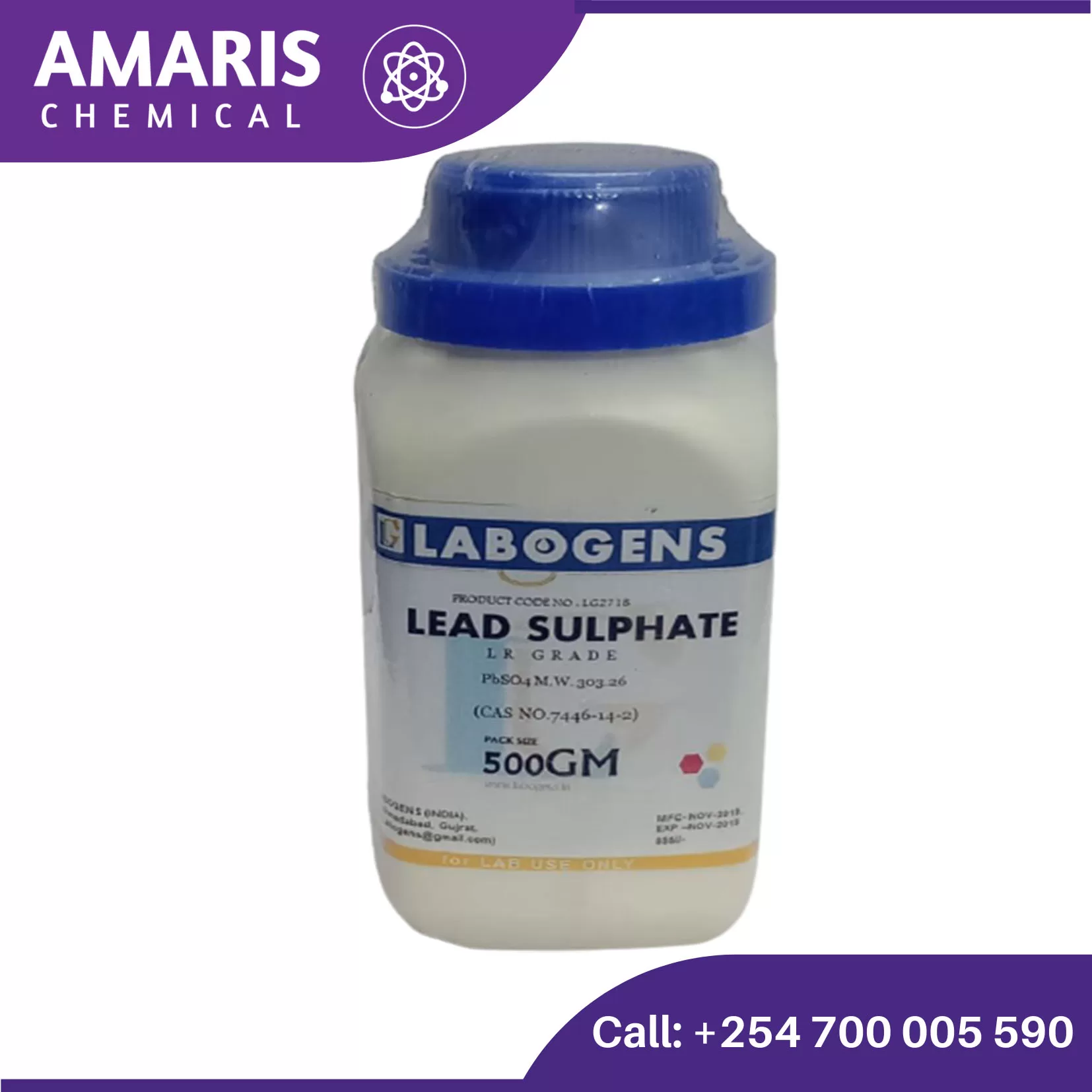
Lead Sulphate 500gm
KSh2,500.00 Original price was: KSh2,500.00.KSh2,300.00Current price is: KSh2,300.00.
Lead sulfate (PbSO4) is an inorganic compound that is a white crystalline solid. It is insoluble in water and commonly occurs as a mineral in nature, known as anglesite. Lead sulfate is formed by the reaction of lead(II) ions with sulfate ions. It has various industrial applications, including its use as a pigment in paints, as a component in batteries (though its use has decreased due to environmental concerns), and as a material in the production of certain types of glass and ceramics. However, it’s important to note that lead sulfate is toxic, and exposure to it can lead to lead poisoning, which can have serious health effects. Therefore, proper handling and disposal procedures are necessary when working with lead sulfate or products containing it.
Uses of Lead Sulphate
Precipitation Reactions:
Lead sulfate can be used in precipitation reactions to isolate or detect sulfate ions in solution. When a solution containing lead(II) ions (Pb^2+) is mixed with a solution containing sulfate ions (SO4^2-), lead sulfate precipitates out as a white solid.
Electrochemistry:
Lead sulfate has been used historically in lead-acid batteries, though its use in this application has decreased due to environmental concerns. In laboratory settings, lead sulfate may still be used in experiments related to electrochemistry, such as in the study of battery chemistry or corrosion processes.
Analytical Chemistry:
Lead sulfate can be employed in analytical chemistry techniques for the quantification or separation of certain analytes. For example, it may be used as a matrix material in X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy for elemental analysis.
Catalysis:
Lead sulfate has been investigated for its catalytic properties in various reactions, although its use in this capacity is less common compared to other catalysts due to its toxicity.
Reference Materials:
Lead sulfate may be used as a reference material or standard in certain analytical techniques, such as in X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis for calibration purposes
Related products
Acetaldehyde
- Chemical Structure: Acetaldehyde consists of two carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and four hydrogen atoms. Its structure is CH3CHO, where the carbon atom in the middle is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom and singly bonded to a hydrogen atom and a methyl group (CH3).
- Occurrence: Acetaldehyde can be found naturally in various ripe fruits, coffee, and heated milk. It is also produced by the oxidation of ethanol (alcohol) by enzymes in the liver and other tissues in humans, making it an intermediate product in alcohol metabolism.
Aceto Carmine 100 ml
Properties
- Color: Red to purplish-red.
- Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol.
- Staining Characteristics: Stains chromatin and cytoplasmic components, providing contrast for better visualization under a microscope.
Preparation
- Ingredients:
- Carmine dye: A natural red dye extracted from the cochineal insect.
- Acetic acid: A colorless liquid organic compound with a pungent smell.
- Procedure:
- Dissolve a specific amount of carmine powder in hot distilled water.
- Add glacial acetic acid to the solution.
- Filter the mixture to remove any undissolved particles.


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.