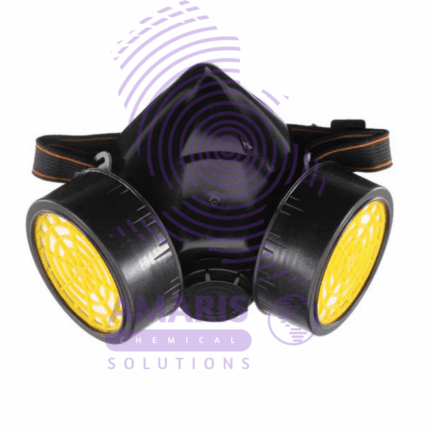
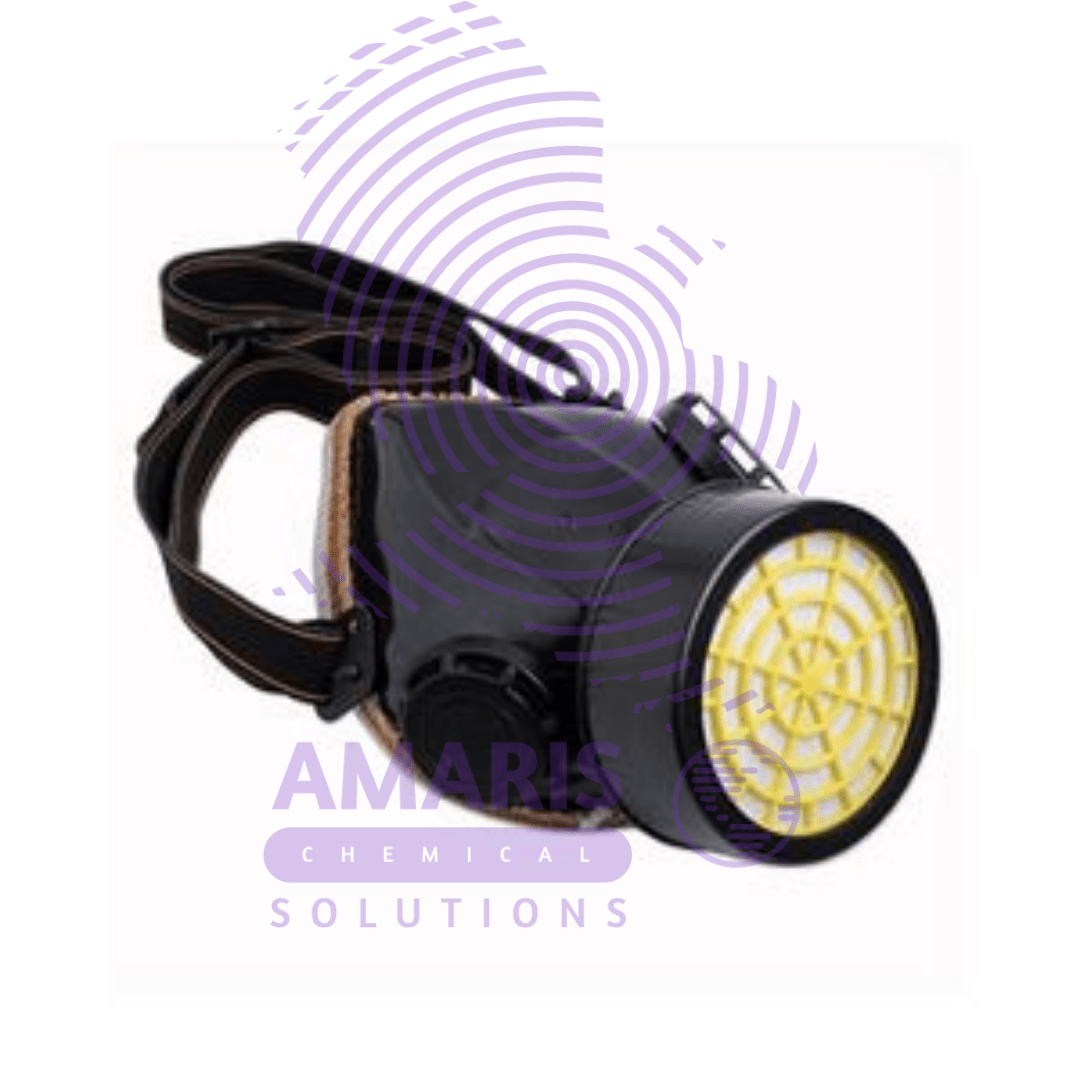
Single Gas Mask
KSh3,000.00 Original price was: KSh3,000.00.KSh2,500.00Current price is: KSh2,500.00.
A gas mask used in laboratories is typically designed to protect against various hazardous substances, including chemicals, biological agents, and radioactive particles. These masks usually feature a tight seal around the face to prevent contaminants from entering. Here’s a basic overview of the components and considerations:
- Facepiece: The main part of the mask that covers the nose, mouth, and sometimes the eyes. It’s usually made of rubber or silicone for flexibility and a proper seal.
- Filter Cartridges: These cartridges are attached to the mask and contain various filter materials to purify the air. They can be specific to certain types of contaminants or provide broader protection.
- Straps: Adjustable straps secure the mask to the wearer’s face, ensuring a snug fit.
- Exhalation Valve: This valve allows the wearer to exhale air without letting outside air in, maintaining a closed system for breathing.
- Visibility: Some masks feature transparent facepieces or additional eyepieces to ensure proper vision while wearing the mask.
- Comfort Features: Some masks include features like padding or adjustable nose bridges for added comfort during extended wear
Uses of Single gas mask
Chemical Protection:
Laboratories often handle a wide range of chemicals, some of which can be toxic, corrosive, or irritating to the respiratory system. Gas masks with appropriate filter cartridges can safeguard against inhaling these chemicals.
Biological Protection:
In laboratories working with biological agents such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, there’s a risk of exposure to airborne pathogens. Gas masks with suitable filters can help prevent inhalation of biological contaminants.
Radiological Protection:
Laboratories dealing with radioactive materials or isotopes need protection from inhaling radioactive particles. Gas masks with specialized filters designed to capture radioactive particles can mitigate this risk.
Emergency Situations:
In the event of a laboratory accident involving the release of hazardous gasses or vapors, a gas mask can provide immediate protection to laboratory personnel until the area is evacuated or the situation is controlled.
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE):
Gas masks are part of the personal protective equipment (PPE) ensemble used in laboratory settings where respiratory protection is necessary. They complement other PPE such as gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles to ensure overall safety.
Field Research or Sampling:
Scientists conducting fieldwork or sampling in environments with unknown or potentially hazardous airborne substances may use gas masks as a precautionary measure.
Training and Preparedness:
Gas masks are also used in laboratory safety training and emergency preparedness drills to familiarize personnel with their use and ensure they know how to don and doff them correctly in case of an emergency.
Related products
Gas Jar Lid
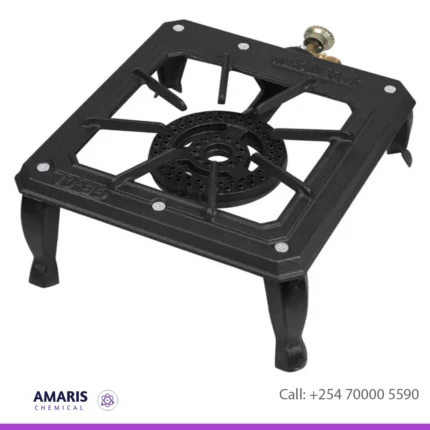
Gas Stove Portable
Hoffman Voltameter
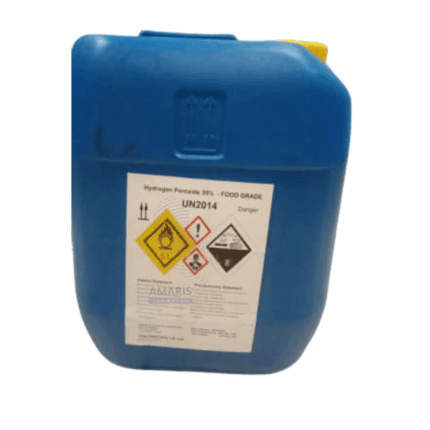
Hydrogen peroxide 35% food grade
Melamine 25kg
Rectangular Glass Block
- Windows: In laboratory buildings, rectangular glass blocks are often used as windows to allow natural light into the space while maintaining safety and privacy.
- Partition Walls: Glass blocks can be used to construct partition walls within the laboratory, separating different work areas while still allowing visibility and light transmission.
- Observation Windows: In controlled environments such as cleanrooms or containment labs, rectangular glass blocks may be installed as observation windows, allowing researchers to monitor experiments or processes from outside the controlled area.
- Fume Hood Windows: Glass blocks are sometimes used as windows in fume hoods, providing a transparent barrier between the user and hazardous chemicals or fumes while still allowing observation of experiments.
- Light Transmission: Glass blocks can also be used in experimental setups where controlled light transmission is required, such as in optical experiments or photobiology studies.
- Decorative Elements: In some cases, glass blocks are used for aesthetic purposes in laboratory design, adding visual interest to the space while still providing functional benefits like light transmission and visibility.