A beehive-shelf in a laboratory typically refers to a specialized type of shelving unit designed to accommodate a large number of small containers or samples, resembling the structure of a beehive with its hexagonal compartments. These shelves are commonly used in research labs, especially in fields like biology, chemistry, or pharmaceuticals, where there is a need to organize and store numerous small items such as vials, test tubes, or microplates.
The design of beehive-shelves allows for efficient use of space while providing easy access to individual containers. This type of shelving system is often made of durable materials like plastic or metal, and the compartments may have adjustable dividers to accommodate different sizes of containers.
In laboratory settings, organization and easy access to samples are crucial for efficient workflow and accurate experimentation, making beehive-shelves a popular choice for storage solutions. They help researchers keep their samples orderly and accessible, reducing the risk of misplacement or contamination
Absorption Tower
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
Absorption tower
An absorption tower, also known as an absorption column or scrubber, is a vertical cylindrical vessel designed for efficient mass transfer between gas and liquid phases. Typically constructed from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or glass, the tower is filled with packing materials or trays that maximize surface area, facilitating optimal interaction between the gas and liquid. As the gas flows upward through the column, it encounters a downward flow of liquid solvent that absorbs specific gases or vapors, effectively removing pollutants or desired components from the gas stream. Widely utilized in various industries and laboratory settings, absorption towers play a crucial role in applications such as gas scrubbing, air purification, chemical separation, and solvent recovery, contributing significantly to pollution control and resource recycling. Their versatile design allows for both continuous and batch operation, making them essential for enhancing the efficiency of numerous chemical and environmental processes.
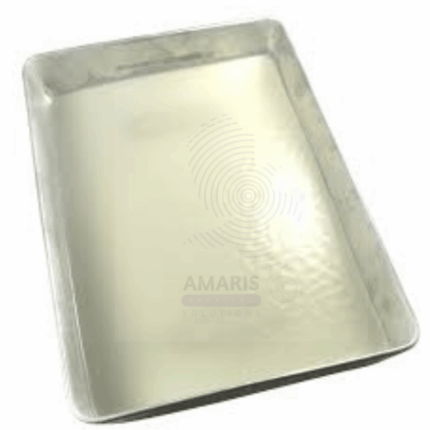
Aluminum Dissecting Pan with wax
A laboratory aluminum dissecting pan with wax is a specialized tool used in scientific and educational settings, particularly in biology and anatomy laboratories. It typically consists of a shallow, rectangular or oval-shaped pan made of aluminum, and the surface of the pan is coated with a layer of wax.
The main purpose of this pan is to provide a convenient and controlled surface for dissecting biological specimens. The wax-coated surface allows for easy pinning and securing of specimens during dissection procedures. The wax also helps to prevent the specimens from slipping or moving around, making it easier for students or researchers to work with precision.
These pans are commonly used for various dissection exercises, where students or researchers can study the internal structures of organisms and learn about their anatomical features. The aluminum construction makes the pan durable and easy to clean, ensuring it can withstand repeated use.
Overall, a laboratory aluminum dissecting pan with wax is an essential tool that enhances the learning and research experience by providing a stable and secure platform for dissecting and examining biological specimens.
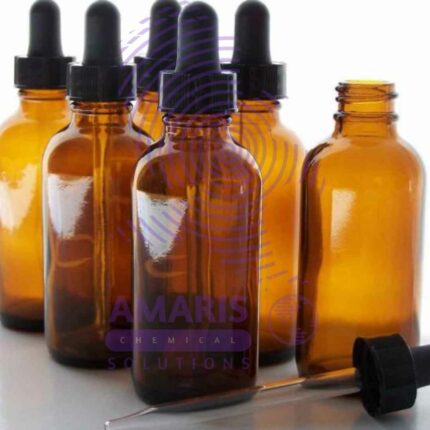
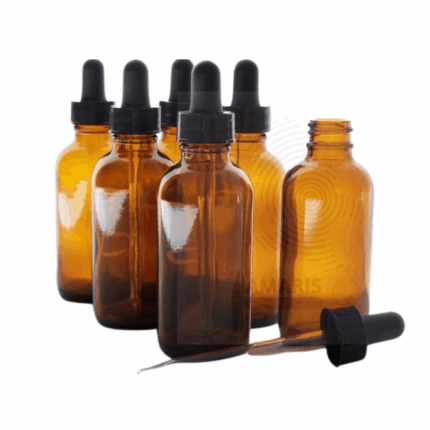
Amber Bottles Polystop
A laboratory glass amber bottle is a specialized container commonly used in laboratories to store and protect light-sensitive substances, chemicals, or solutions. These bottles are made from amber-colored glass, which provides protection against ultraviolet (UV) and visible light radiation. The amber glass helps to minimize the degradation and decomposition of light-sensitive contents by blocking a significant portion of the light spectrum.
The amber color of the glass is achieved by adding iron, sulfur, and other compounds during the glass manufacturing process. This coloration is what gives the bottles their distinctive amber or brown appearance.
Laboratory glass amber bottles typically come in various sizes, ranging from small volumes of a few milliliters to large capacities of several liters. They often have a screw-on or snap-on cap, providing a secure and airtight seal to prevent spills, evaporation, and contamination.
Due to their ability to protect light-sensitive substances, laboratory glass amber bottles are widely used in chemistry, biology, pharmaceuticals, and other scientific fields where sample integrity and stability are crucial.
Amber bottles polystop
Amber bottles with polystop closures are designed for optimal storage and protection of light-sensitive chemicals and reagents. Crafted from durable materials such as glass or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), these bottles provide excellent UV protection, preventing degradation of sensitive compounds. The polystop closure ensures a secure, airtight seal, minimizing the risk of contamination and evaporation. Ideal for storing solvents, pharmaceuticals, and biological samples, these bottles offer convenient dispensing options while maintaining the integrity of their contents. Their opaque design allows for clear labeling, making them essential tools in any laboratory setting
Amber laboratory reagent bottles
Amber laboratory reagent bottles are specialized containers designed to store and protect light-sensitive chemicals and samples. Made from high-quality glass, these bottles feature a distinctive amber color that effectively blocks harmful ultraviolet (UV) light, preventing photodegradation and ensuring the stability of sensitive substances.
Typically available in various sizes, amber reagent bottles come with tightly sealing lids to minimize exposure to air and contaminants. They are ideal for storing a range of laboratory materials, including organic solvents, biological samples, and pharmaceuticals. Their durable construction ensures safe handling and long-term storage, making them essential tools in chemical, biological, and environmental laboratories.
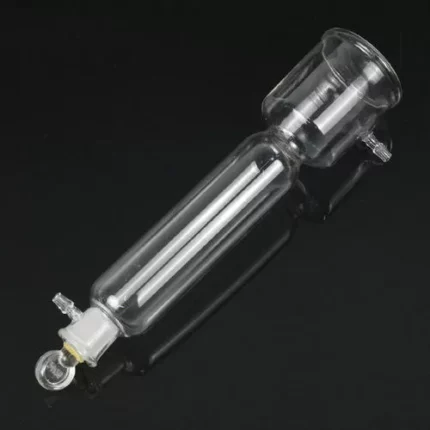
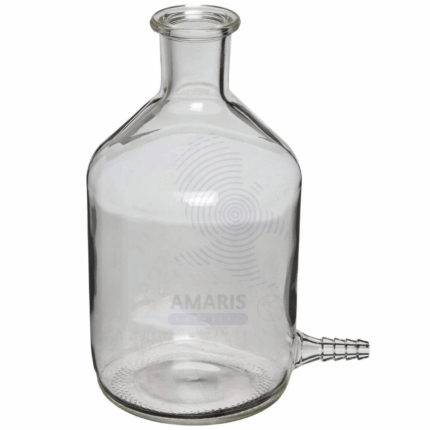
Aspirator Bottle Glass
A laboratory aspirator glass bottle, also known as a vacuum aspirator bottle or a vacuum filtration flask, is a specialized glass container used in scientific laboratories for various applications. It is designed to create a vacuum or negative pressure, which allows the filtration of liquids through a porous medium like a filter paper or a membrane.
The bottle typically has a conical or pear-shaped body with a sidearm or neck near the top. This neck is where a rubber or silicone stopper is inserted, allowing for the attachment of tubing or a hose to connect to a vacuum source or water aspirator. (Available in 2.5l,5l,10l,)
Laboratory aspirator glass bottles are commonly used in vacuum filtration processes to separate a solid precipitate from a liquid solution. When connected to a vacuum source, the air inside the bottle is removed, creating a pressure difference that draws the liquid through the filter, leaving the solid behind on the filter paper.
These bottles come in various sizes to accommodate different filtration needs and are an essential tool in many research, analytical, and quality control laboratories for tasks like separating particulate matter, sterilizing solutions, and performing various filtration techniques. They are often made of durable borosilicate glass to withstand the pressure changes and chemical interactions that may occur during laboratory operations.
Aspirator bottle glass
An aspirator bottle is a specialized glass container designed for use in laboratory settings. Typically made from high-quality borosilicate glass, these bottles are resistant to thermal shock and a wide range of chemicals. They feature a wide mouth for easy filling and cleaning and often come with a ground glass or plastic stopper to ensure airtight sealing.
Aspirator bottles are equipped with an inlet for a vacuum line, allowing them to create a vacuum inside the bottle for applications like vacuum filtration or degassing liquids. Their design may include graduated markings for accurate measurement and a robust base to prevent tipping. Ideal for storing solvents, acids, and other laboratory liquids, aspirator bottles provide a safe and efficient means of handling and dispensing fluids while minimizing contamination risk.
Atomic Model Set
A lab atomic model set is a collection of physical models and materials designed to represent the structure of atoms and molecules. It is commonly used in educational and scientific laboratory settings to visually demonstrate the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom, as well as the bonding patterns between atoms in molecules. These sets typically include colored balls of various sizes representing different types of atoms, as well as connectors or magnets to simulate chemical bonds between them. The purpose of these sets is to help students and researchers better understand the principles of atomic and molecular structure in a tangible and interactive way.
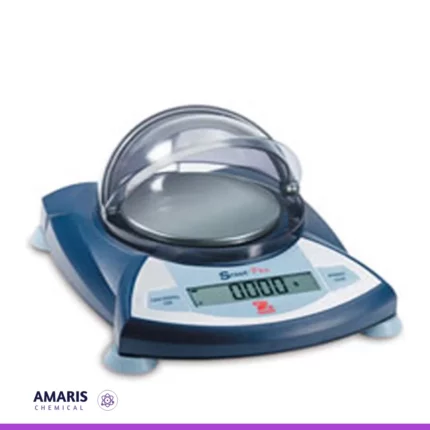
Balance bathroom scale
A balance bathroom scale is a mechanical or digital device used to measure body weight or the mass of larger objects. It typically consists of a flat platform where the object or person stands, and it displays the weight either via an analog dial or a digital screen. Unlike precision laboratory balances, it is designed for general-use purposes where fine accuracy is not required, making it suitable for personal or approximate weight measurements. This type of scale is commonly found in homes or commercial settings and is robust enough to handle heavier loads
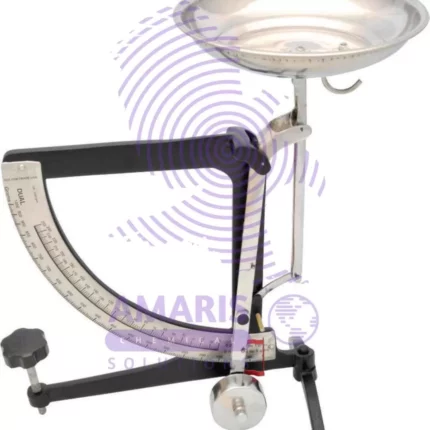
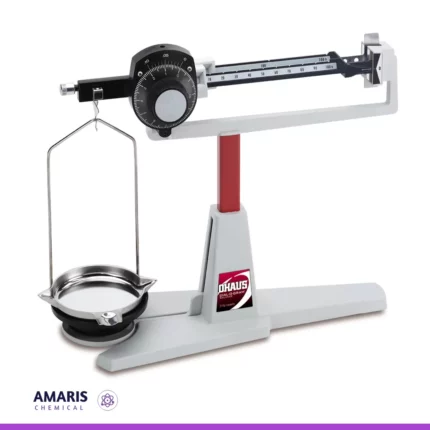
Balance lever
The best definition of a balance lever is a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or beam that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. It is used to compare the weights or forces of two objects and determine if they are in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the other (unbalanced).
The balance lever operates on the principle of torque, where the torque (rotational force) exerted on one side of the fulcrum is equal to the torque on the other side when the system is in equilibrium. This principle is expressed by the formula: Torque = Force × Distance from fulcrum.
By placing known masses or weights on one side of the lever and an unknown weight on the other side, the balance lever can be used as a weighing scale. When the lever is in balance, the two sides are equal in weight or force. This concept has been widely used in various applications, from traditional weighing scales to more complex systems like seesaws or construction equipment.
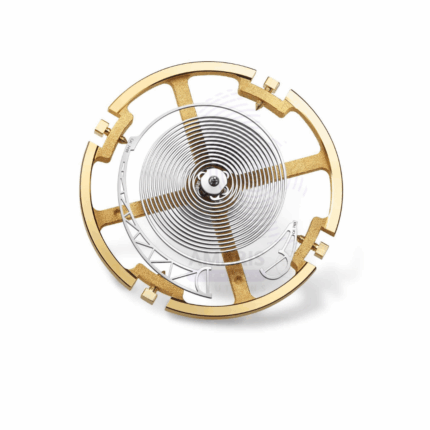
Balance spring
A balance spring, also known as a hairspring, is a fine, tightly coiled spring used in precision instruments, particularly in mechanical balances and watches, to control the oscillation of a balance wheel. In laboratory balances, it provides a restoring force that helps maintain equilibrium and ensures highly accurate measurements. The spring's flexibility and precision help in damping vibrations and stabilizing the balance, allowing the instrument to return to its zero position after disturbances. This makes the balance spring vital for precise and stable mass measurements, especially in analytical applications
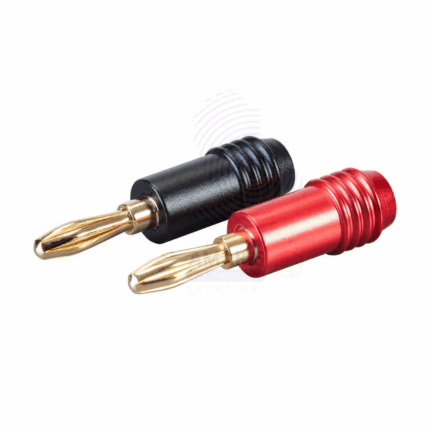
Banana plug
A banana plug is a type of electrical connector commonly used in audio and electronic devices. It is designed to securely connect wires to binding posts or jacks found on audio equipment, speakers, amplifiers, and test instruments.
The name "banana plug" comes from its distinctive shape, resembling a curved banana. These plugs typically have a cylindrical metal body with a spring-loaded prong or pin that can be inserted into a corresponding socket or binding post. The plug's design allows for easy and quick connection and disconnection of wires without the need for soldering, making it a convenient choice for frequently changing connections.
Banana plugs are favored for their reliable contact and low resistance, which helps maintain good audio signal quality. They are commonly used in home audio setups, speaker systems, and test and measurement applications where a secure and durable electrical connection is essential.
Bar and gauge apparatus
The bar and gauge apparatus are essential instruments used in laboratories to measure pressure in various systems, whether it be atmospheric pressure or the pressure of gases and liquids in closed systems. The barometer, often referred to as the bar apparatus, is primarily used to measure atmospheric pressure, playing a critical role in experiments involving gas laws and environmental studies. On the other hand, pressure gauges are used to monitor and control the pressure within containers, pipelines, or reactors, ensuring precise pressure management. These devices are vital for maintaining safety and achieving accurate experimental results, particularly in setups involving pressurized gases or liquids
Bar breaking apparatus
The bar breaking apparatus is a precision laboratory instrument designed to evaluate the mechanical strength of materials, specifically their ability to resist breaking under stress. It typically measures tensile strength, flexural strength, or break resistance by applying controlled force to bar-shaped specimens until they fracture. The device is essential in quality control, material testing, and research, offering precise data for materials such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Its robust design allows for consistent and repeatable testing, ensuring the reliability of the material's mechanical properties.
Barlows wheel apparatus
The Barlow's wheel apparatus is an experimental device used to demonstrate the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic principles. It consists of a horizontal wheel or disk with radial metal spokes attached to its center. The wheel is mounted on an axle, allowing it to rotate freely.
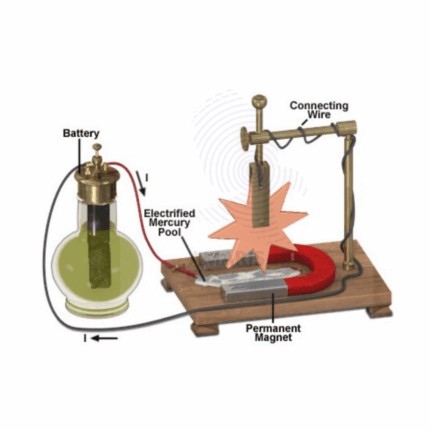
Barlows wheel apparatus
Barlow's wheel, named after the English mathematician and physicist Peter Barlow, is an early demonstration of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a simple apparatus used to generate electricity by rotating a copper disc between the poles of a magnet. When the disc spins, it cuts across the magnetic field lines, inducing an electric current in the disc due to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
The apparatus typically consists of a horizontal axle with a copper disc mounted on it, positioned between the poles of a magnet. The copper disc is connected to a circuit, and when it rotates, an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the disc, causing electric current to flow through the circuit.
Barlow's wheel is a classic demonstration in physics education to illustrate the principles of electromagnetic induction and the generation of electric current. It played a significant role in the development of electrical machinery and the understanding of electromagnetism.
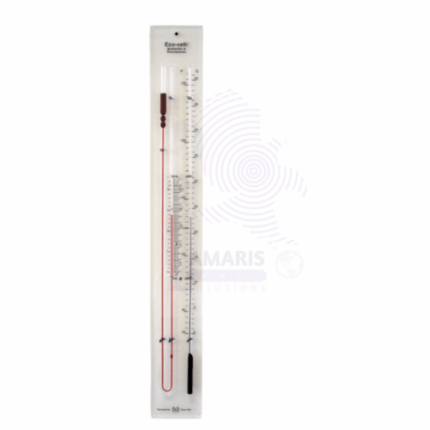
Barometer tubes
A barometer tube is a slender, sealed, and typically transparent tube used in barometers to measure atmospheric pressure. It is usually filled with a liquid, often mercury, but sometimes water or another fluid, which rises or falls within the tube in response to changes in atmospheric pressure. The height of the liquid column in the tube serves as an indicator of the current atmospheric pressure, with higher pressure causing the liquid to fall and lower pressure causing it to rise. This measurement helps in predicting weather changes and understanding atmospheric conditions.
Barometer tubes
A barometer tube is a long, sealed glass or metal tube used to measure atmospheric pressure. It is typically filled with a liquid, such as mercury, with one end sealed and the other submerged in a reservoir of the same liquid. The atmospheric pressure pushes on the reservoir, causing the liquid level in the tube to rise or fall. The height of the liquid column reflects the current atmospheric pressure, allowing for precise readings. Barometer tubes are commonly used in meteorology, physics, and laboratory experiments to observe pressure changes and calibrate instruments.
beaker hysil
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Beaker hysil
A Hysil beaker is a type of laboratory glassware known for its high chemical resistance and durability. Made from borosilicate glass, it can withstand high temperatures and sudden temperature changes, making it ideal for various laboratory applications. The beaker features a wide mouth for easy pouring and stirring, with graduated markings on the side for approximate volume measurement. Its transparent nature allows for easy observation of the contents, while its flat bottom ensures stability on laboratory surfaces. Hysil beakers are commonly used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids, as well as conducting chemical reactions, making them an essential tool in scientific research and educational laboratories
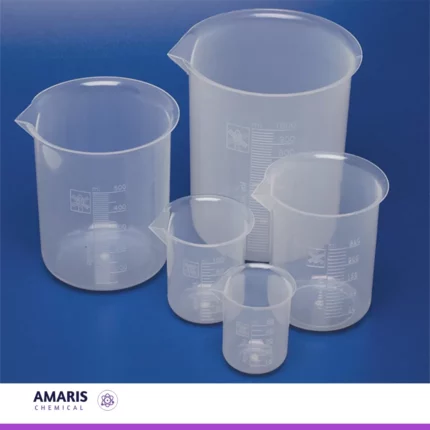
Beaker Plastic
A plastic beaker is a laboratory container made from plastic material, typically featuring a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a spout or pouring lip. It is used for holding, measuring, and mixing liquids or substances during various scientific experiments, research, or educational activities. Plastic beakers come in a range of sizes and are designed to withstand various chemicals and temperatures, making them versatile tools in laboratory settings.
beaker pyrex
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Beaker Simax
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
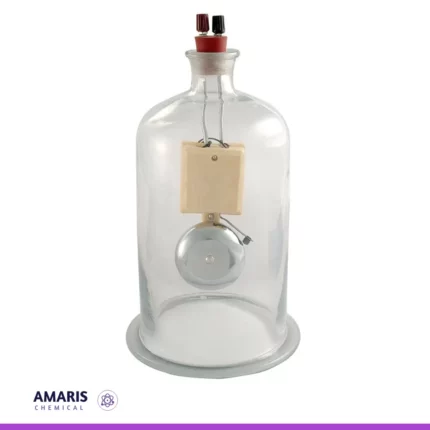
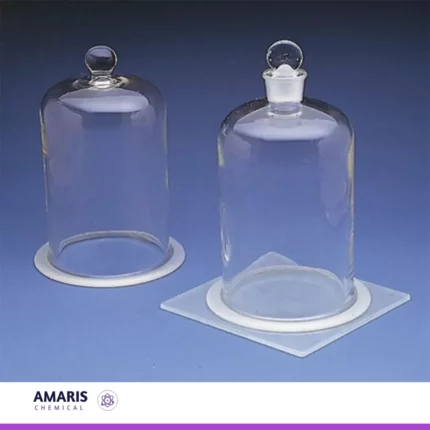
bell in vacuum
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
Bell in vacuum
A bell jar is a cylindrical glass or plastic container with a bell-shaped top, designed to create a vacuum environment when placed over a base. Its smooth, transparent walls allow for easy observation of the contents inside. Typically used in laboratory settings, the bell jar can be connected to a vacuum pump to remove air and lower the pressure inside, making it ideal for experiments that require the absence of air or specific atmospheric conditions.
The bell jar's applications include conducting vacuum experiments, studying chemical reactions, performing dehydration studies, and observing the effects of reduced pressure on various materials. Its design ensures a secure seal, enabling scientists to manipulate environmental variables effectively and safely.
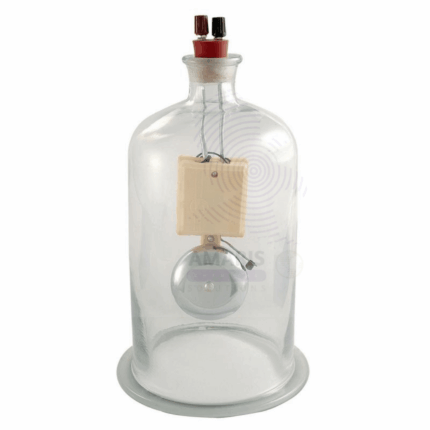
bell in vacuum with air pump with plate
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
Bell in vacuum with air pump with plate
In a laboratory setting, a bell is positioned inside a clear vacuum chamber mounted on a sturdy plate. The vacuum chamber is connected to an air pump that allows for the controlled removal of air. When the bell is struck, it produces sound waves that normally propagate through the air. As the air is gradually pumped out of the chamber, the intensity of the sound decreases, demonstrating the principle that sound requires a medium, such as air, to travel. This visual and auditory demonstration effectively illustrates the concepts of sound transmission, pressure changes, and the properties of a vacuum, making it an excellent educational tool for exploring fundamental physics principles.
This setup enables students to witness firsthand how sound fades in a vacuum and encourages discussions about the relationship between sound and the medium through which it travels.
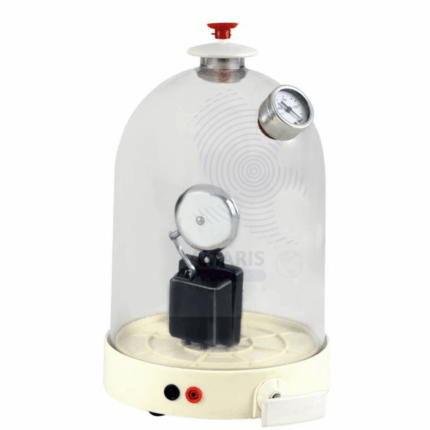
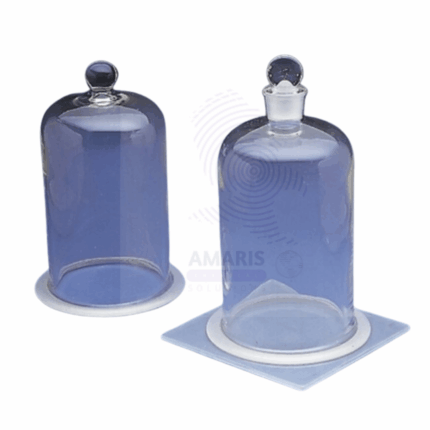
Bell Jar with knob
The best definition of a bell jar apparatus is a scientific instrument used in laboratories to create a controlled environment for various experimental purposes, such as studying the behavior of gases, conducting vacuum experiments, or demonstrating principles of physics and chemistry. It consists of a glass or transparent plastic container shaped like a bell, which can be sealed to create a vacuum chamber. The apparatus allows researchers to manipulate and observe the interactions of substances or objects within the vacuum or controlled atmosphere, often enabling investigations that wouldn't be possible under standard atmospheric conditions.
Bell jar with knob
A bell jar with a knob is a transparent, dome-shaped container typically made of glass or clear plastic. It features a wide base and a tapered top, allowing for a secure fit on various surfaces. The knob at the top facilitates easy handling and movement, enabling quick access to the interior. This jar is designed to create a sealed environment, making it ideal for experiments involving vacuum, gas containment, and pressure control. Its clear material allows for easy observation of the contents, making it a valuable tool in both educational and research settings for demonstrating scientific principles and conducting various experiments.
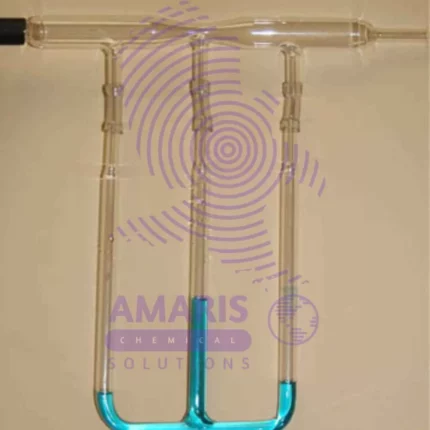
Bernoulli Tube Apparatus
The Bernoulli tube apparatus, also known as a Venturi tube apparatus, is a scientific device used to demonstrate the principles of fluid dynamics, particularly the Bernoulli's principle. It consists of a specially shaped tube with a constricted region, often referred to as a Venturi section. When fluid (liquid or gas) flows through the tube, the constricted section leads to changes in pressure and velocity according to Bernoulli's principle, which states that as the velocity of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases and vice versa. This apparatus is commonly used in educational settings to visually illustrate how the flow of a fluid can affect its pressure, helping to explain various phenomena like lift in aircraft wings, fluid flow through pipes, and more.
Blotting paper
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent and thin sheet of paper, typically made from materials like cotton, linen, or other plant fibers. It is designed to quickly absorb excess liquids, such as ink, oil, or moisture, from various surfaces without smudging or smearing the substances. Blotting paper is commonly used to remove excess ink from a freshly written page, absorb oil from the skin without disturbing makeup, or dry wet items. It is often found in office settings, art studios, and cosmetic applications due to its efficient absorption properties.
Blotting paper
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent, porous paper designed to absorb liquids and retain solid substances. Typically made from cotton or cellulose fibers, it is characterized by its smooth texture and high wicking ability, allowing it to efficiently draw in moisture. In laboratory settings, it is widely used for tasks such as absorbing excess liquids, facilitating chromatography, transferring samples, and preparing biological specimens. Its versatility makes it an essential tool in various scientific applications, including molecular biology, histology, and general laboratory work.
blow pipes
A blowpipe apparatus is a scientific instrument used in analytical chemistry and mineralogy for conducting various tests, particularly flame tests and microchemical reactions. It typically consists of a small tube or pipette through which a controlled stream of air or oxygen is blown onto a sample being heated. This stream of air or oxygen enhances the combustion of the sample, allowing the observation of characteristic colors emitted by different elements when they are vaporized and excited by the heat. The blowpipe apparatus is often used to identify and differentiate between different elements and compounds based on their unique emission spectra and reactions.
Blow pipes
A blow pipe is a versatile laboratory tool designed for producing a controlled flame through the combustion of a gas, typically using a fuel source like propane or natural gas. It consists of a long, slender tube with an open end that allows the user to blow air into the gas stream, intensifying the flame.
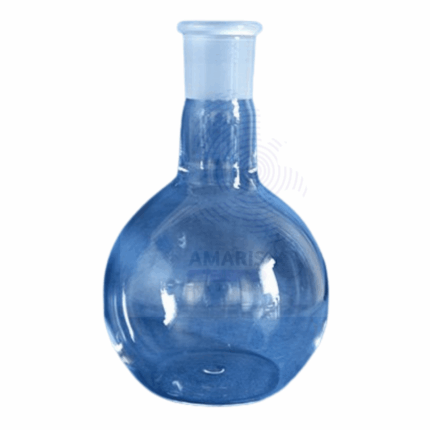
Boiling Flask Flat Bottom
A boiling flask apparatus, also known as a distillation setup or distillation apparatus, is a laboratory equipment arrangement used for separating and purifying components of a liquid mixture based on their differing boiling points. It typically consists of a round-bottomed flask (boiling flask) connected to a condenser, often with a heating source beneath the boiling flask. As the mixture in the boiling flask is heated, the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first, rises into the condenser where it cools and condenses back into liquid, and is then collected as a separate fraction. This allows scientists to isolate and collect different components of a mixture, such as liquids with distinct boiling points, enabling various applications in chemistry, research, and industry.
Boiling flask flat bottom
A flat-bottom boiling flask is a type of laboratory glassware characterized by its round body and flat base, designed for efficient heating and mixing of liquids. Made typically from borosilicate glass, which withstands high temperatures and thermal shock, it features a wide opening for easy access and the addition of materials. The flat bottom provides stability on flat surfaces, making it suitable for use on hot plates or in various chemical processes.
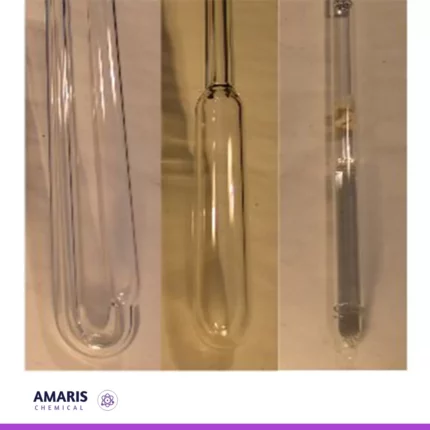
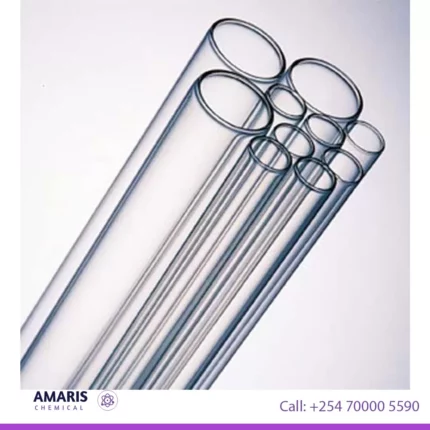
Borosilicate Glass Tubings
Borosilicate glass tubings are specialized glass tubes composed of a type of glass that primarily contains boron trioxide and silica as its main components. This glass composition gives borosilicate glass its unique properties, such as high thermal resistance, excellent chemical durability, and low coefficient of thermal expansion. These characteristics make borosilicate glass tubings particularly suitable for applications that involve high temperatures, rapid temperature changes, and exposure to corrosive chemicals, making them widely used in laboratory equipment, industrial processes, and various scientific and technical applications.
Borosilicate glass tubings
Borosilicate glass tubing is a high-performance glass made primarily from silica and boron trioxide, known for its excellent thermal and chemical resistance. It has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, allowing it to withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking. This makes it ideal for laboratory applications where heat fluctuations occur, such as in heating and cooling processes.
The glass is clear and transparent, providing excellent visibility for monitoring experiments and processes. It is also non-reactive, ensuring that it does not interfere with the substances it comes into contact with, making it suitable for storing and handling chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and biological samples.
Borosilicate glass tubing is versatile and can be easily fabricated into various shapes and sizes, allowing it to be used in everything from laboratory glassware to custom experimental setups. Its durability and reliability make it a preferred choice for scientists and researchers in a wide range of fields.