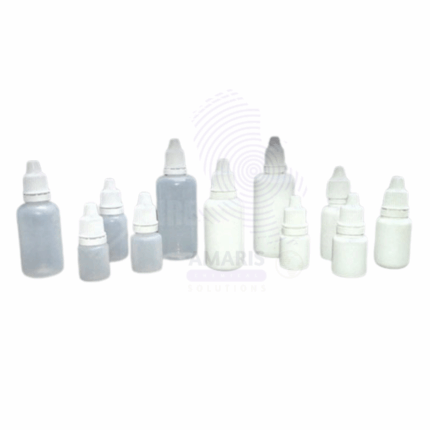
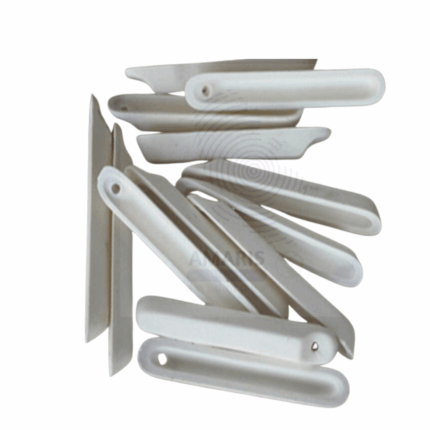
Bottle dropper rabbit type plastic
A rabbit-type plastic bottle dropper is a small, squeezable container made from durable, lightweight plastic, featuring a long, slender dropper tip. Its design typically includes a rounded body for easy grip and a secure cap to prevent leakage. The dropper tip allows for precise dispensing of liquids, making it ideal for controlled application of reagents, samples, or solutions in laboratory, clinical, and household settings. These droppers are often used for transferring small volumes of liquid, conducting experiments, or administering medications, and are valued for their accuracy and convenience. The material is typically resistant to chemicals, ensuring compatibility with various solutions.
Bottle Dropper Rabbit type plastic 60ml
Bottle Dropper Rabbit type plastic 60ml , also known as a dropper bottle or dropper pipette, is a common laboratory tool used to dispense small amounts of liquid with precision. It consists of a bottle with a dropper tip attached to its cap. The dropper tip usually has a rubber bulb or squeeze mechanism at the top that allows the user to draw liquid into the dropper by squeezing and then dispense it in controlled drops by releasing pressure.
These dropper bottles are commonly used in chemistry, biology, and medical laboratories for tasks such as titration, adding reagents to reactions, and dispensing solutions in small volumes. They provide a convenient and accurate way to add liquids drop by drop, which is often necessary for experiments requiring precise measurements or control over the amount of liquid added.
Bottle weighing plastic
Bottle weighing plastics, also known as weighing bottles or weigh boats, are lightweight containers specifically designed for laboratory use. They are made from durable, chemical-resistant plastic, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of substances. The smooth surfaces allow for easy cleaning and prevent sample contamination. These containers feature a wide mouth for convenient filling and transferring of solids and powders, promoting accurate and efficient weighing processes. Their lightweight design minimizes any impact on balance readings, making them ideal for precise measurements. Available in various sizes, bottle weighing plastics offer versatility for different laboratory applications, including sample storage, chemical reactions, and moisture-sensitive materials. Their transparent construction enables easy visibility of contents, facilitating quick identification and monitoring.
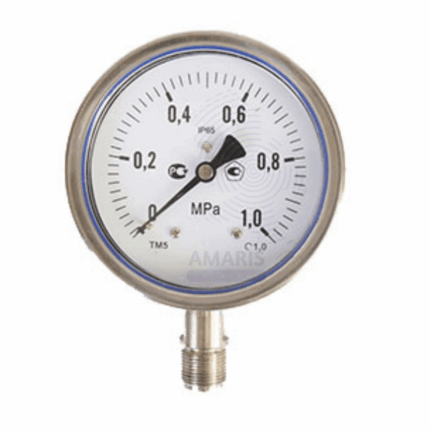
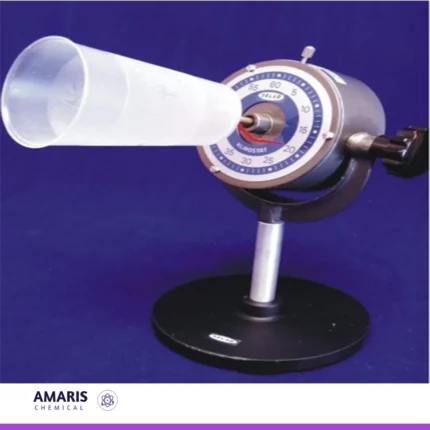
Bourdan gauge
A Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device used to measure pressure, typically of gases or liquids, with high accuracy and reliability. It consists of a curved, flexible tube (the Bourdon tube) that straightens as pressure increases. This movement is translated into a dial reading via a pointer, allowing users to easily gauge the pressure level.
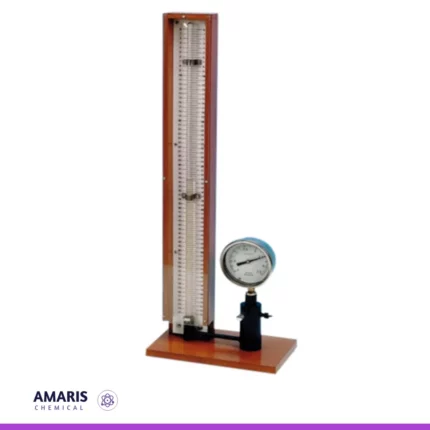
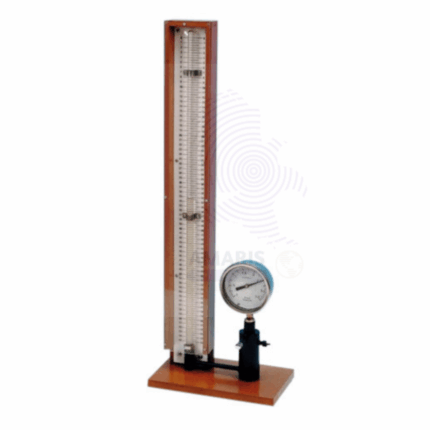
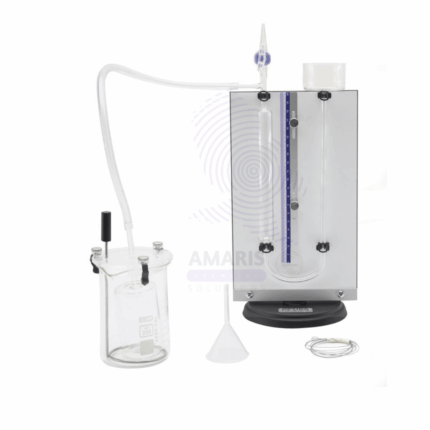
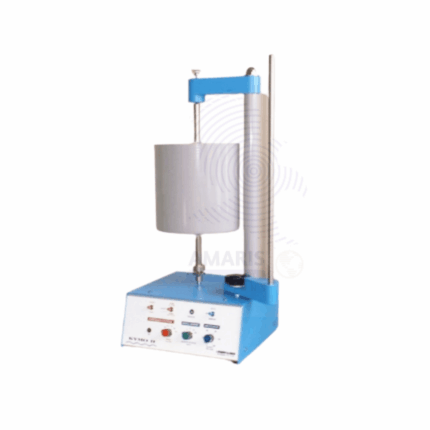
Boyles law apparatus
The Boyle's Law apparatus is a laboratory device designed to illustrate the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. It typically features a sealed transparent container or cylinder that holds the gas, allowing for visual observation of any changes in volume. Attached to the container is a pressure measurement device, such as a manometer or pressure gauge, which accurately records the gas's pressure. The apparatus includes a volume adjustment mechanism, often in the form of a movable piston, enabling the user to compress or expand the gas and observe the corresponding pressure changes. Some setups may also incorporate temperature control to maintain constant conditions during experiments. Graduated scales on the apparatus facilitate precise measurements of gas volume. Overall, this apparatus serves as an essential educational tool, providing a hands-on experience for students to explore and understand Boyle's Law, which states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume
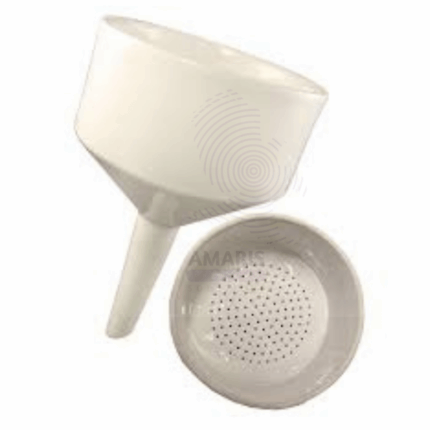
Buchner funnel
A Buchner funnel is a cylindrical filtration device typically made of porcelain, glass, or plastic, designed for vacuum filtration. It features a flat, perforated base that supports filter paper, allowing liquid to pass through while retaining solid particles. The funnel connects to a vacuum source via a side arm, creating negative pressure that accelerates the filtration process. Often used in laboratories for separating solids from liquids, purifying compounds, and clarifying solutions, the Buchner funnel enhances efficiency and effectiveness in various chemical and biological applications. Its versatility and ease of use make it an essential tool in many scientific settings.
Bunsen burner lighter
A Bunsen burner lighter is a laboratory tool designed for safely igniting a Bunsen burner. It typically consists of a long, slender metal body with a flint or electronic igniter at one end and a nozzle to direct the flame. The device is lightweight and portable, making it easy to use in various laboratory settings.
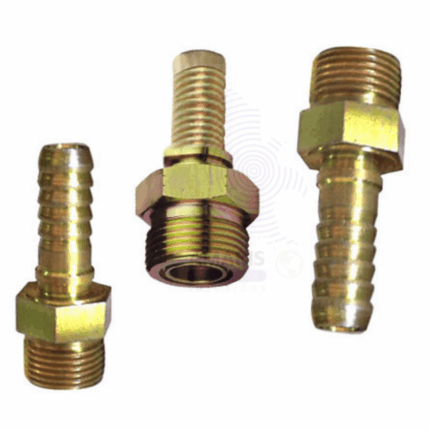
bunsen burner nipple
A Bunsen burner nipple is an integral component of a Bunsen burner, a common piece of laboratory equipment used for heating substances. The nipple is a small, protruding tube or nozzle on the burner to which the rubber tubing from the gas source is attached. Here's a breakdown of the key points related to a Bunsen burner nipple:
Function
- Gas Inlet: The primary function of the Bunsen burner nipple is to serve as the gas inlet. It connects the burner to the gas supply, allowing gas to flow into the burner.
- Attachment Point: The nipple securely holds the rubber tubing that delivers gas from the gas supply. This ensures a steady and controlled flow of gas.
Importance
- Safety: Proper attachment of the rubber tubing to the nipple is crucial for preventing gas leaks, which could lead to dangerous situations such as fires or explosions.
- Efficiency: A well-fitted nipple ensures an efficient and consistent flow of gas, which is necessary for achieving the desired flame characteristics (such as a non-luminous blue flame).
Maintenance
- Inspection: Regular inspection of the Bunsen burner nipple is important to ensure it is not clogged, cracked, or damaged.
- Cleaning: Keeping the nipple clean and free of obstructions ensures optimal performance of the burner.
Usage Tips
- Securing the Tubing: Always ensure the rubber tubing is tightly fitted onto the nipple to avoid gas leaks.
- Correct Size: Use tubing of the correct diameter for the nipple to ensure a snug fit.
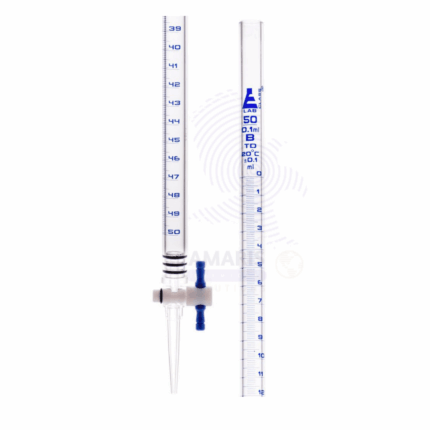
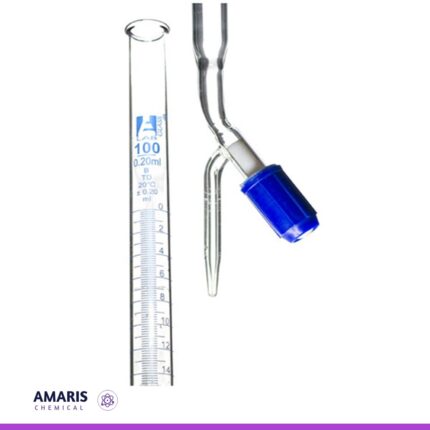
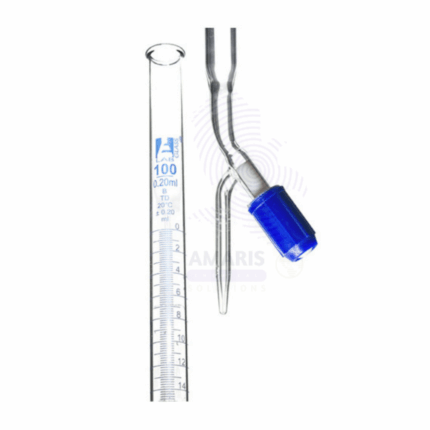
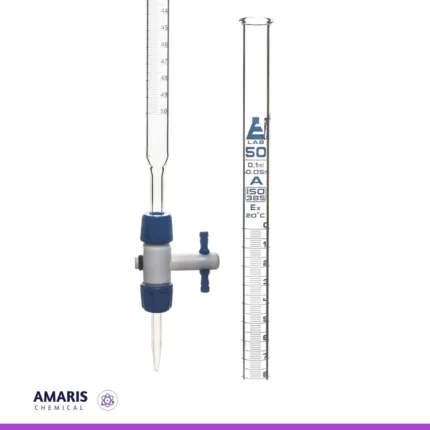
Burette acrylic
An acrylic burette is a precision laboratory instrument designed for accurate measurement and dispensing of liquid volumes. Constructed from durable, transparent acrylic, it allows for clear visibility of the liquid inside while being lightweight and resistant to breakage. The burette typically features a graduated scale for easy reading of volumes and a precision stopcock that enables controlled dispensing of liquids. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for use with a wide range of reagents, including acids and bases. Ideal for titration experiments and various analytical procedures, the acrylic burette combines functionality with safety, making it a valuable tool in both educational and professional laboratory settings.
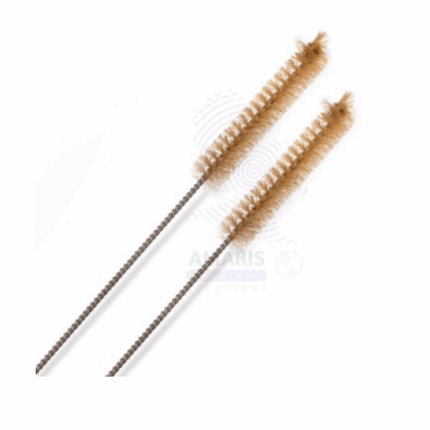
Burette brush
A burette brush is a specialized cleaning tool designed for maintaining the cleanliness of laboratory burettes. Typically featuring a long, slender handle, it has soft bristles at one end that effectively reach into the narrow, tubular structure of a burette. The bristles are gentle yet durable, allowing for thorough cleaning without scratching the glass surface. Burette brushes come in various sizes to fit different burette diameters and are essential for removing residues, stains, and contaminants, ensuring accurate measurements in titration and other analytical procedures. Their ergonomic design facilitates ease of use, making them a staple in any chemistry or laboratory setting
Burette clamp
A burette clamp is a laboratory device designed to securely hold and stabilize a burette during experiments. Typically made from durable materials like metal or plastic, it features a strong gripping mechanism that can accommodate various sizes of burettes. The clamp is often attached to a ring stand or a support rod, allowing for height adjustments to ensure the burette is positioned at eye level for accurate readings. Its design includes a hinge or screw mechanism that permits easy placement and removal of the burette. The primary purpose of a burette clamp is to prevent spills and ensure precise control of liquid dispensing, making it essential for titrations and other quantitative analysis procedures. With its reliable support, a burette clamp enhances safety and efficiency in the laboratory.
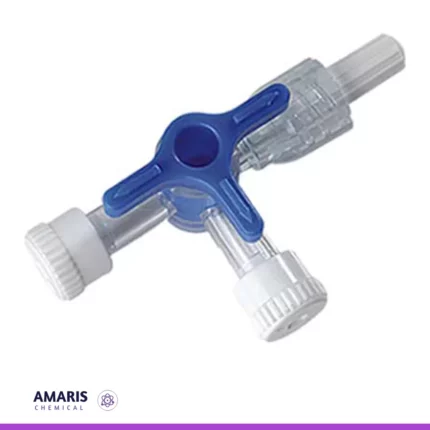
Burette rotaflow
The burette rotaflow is a precision laboratory instrument designed for accurate liquid dispensing and titration. It features a graduated glass or plastic tube with a rotating stopcock at its base, allowing for controlled flow and easy adjustment of liquid volume. The rotaflow mechanism enables a smooth, continuous release of liquid, making it ideal for applications requiring precise measurements.
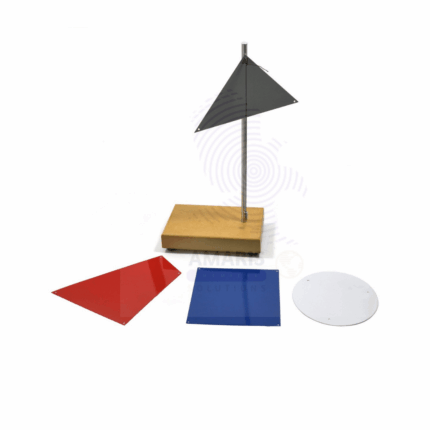
Centre of gravity apparatus
The center of gravity apparatus is a specialized tool used in physics and engineering to study the principles of balance, stability, and weight distribution. Typically consisting of a base platform with adjustable arms and a support for various objects, the apparatus allows users to precisely determine the center of gravity of different shapes and materials. By placing an object on the apparatus and adjusting weights or changing its orientation, users can visually and practically observe how the center of gravity influences stability. This hands-on experience facilitates a deeper understanding of equilibrium conditions, showcasing how an object's design affects its performance in real-world applications, such as in architecture or vehicle design. As an educational tool, the center of gravity apparatus effectively demonstrates key concepts in mechanics, making abstract theories tangible and accessible to students and researchers alike.
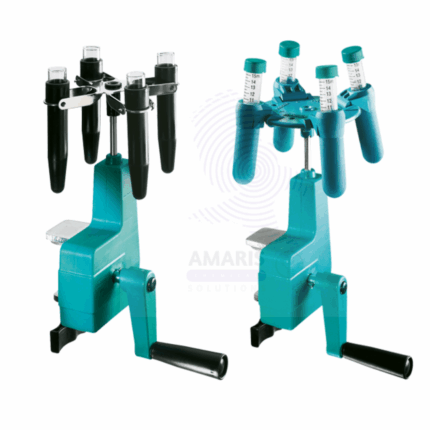
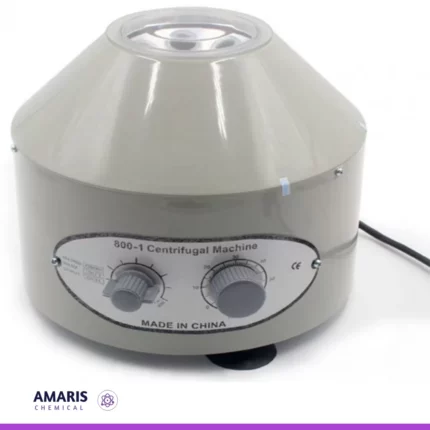
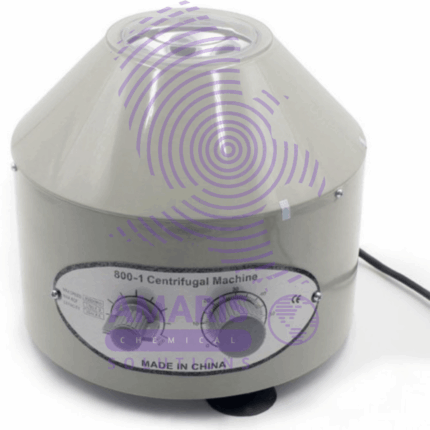
centrifudge electrical
centrifuge is a machine that spins samples at high speeds to separate components based on their density. In terms of its electrical components, a centrifuge typically consists of:
- Motor: This is the primary electrical component that drives the rotation of the centrifuge rotor. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to spin the rotor.
- Control Panel: Modern centrifuges often have electronic control panels for setting parameters such as speed, duration, and sometimes temperature. These panels may include digital displays, buttons, and knobs for user interaction.
- Safety Features: Centrifuges usually have safety mechanisms, such as lid locks and imbalance detection systems, which are often controlled by electrical circuits. These features help prevent accidents and damage to the centrifuge and its surroundings.
- Power Supply: Like any electrical device, a centrifuge requires a power supply to operate. This could be a standard electrical outlet or a specific voltage and frequency depending on the model.
- Sensors and Feedback Systems: Some centrifuges may incorporate sensors to monitor parameters such as speed, temperature, and rotor balance. These sensors provide feedback to the control system to ensure proper operation and safety.
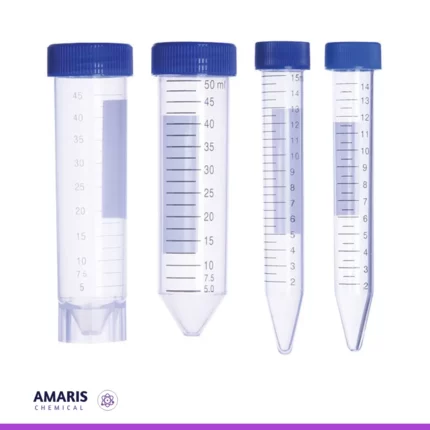
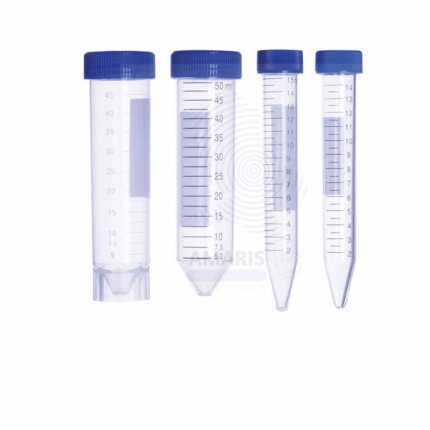
Centrifuge tubes
Centrifuge tubes are specially designed, narrow, and conical containers used in laboratory centrifuges to hold liquid samples during high-speed spinning. Their conical shape allows for the efficient separation of components by density, with heavier particles settling at the bottom and lighter ones remaining at the top. They are typically made of durable plastic or glass, with markings for volume measurement, and come in various sizes to accommodate different sample quantities. Centrifuge tubes are crucial for tasks like isolating biological materials, purifying proteins, and concentrating samples in fields such as biology, chemistry, and medical research.
Charles law apparatus
The Charles' Law apparatus is designed for laboratory demonstrations of how the volume of a gas changes in response to temperature variations while maintaining constant pressure. It provides an effective visual and quantitative way to validate Charles' Law, showing the direct relationship between volume and temperature, and is often used to estimate absolute zero in experiments.
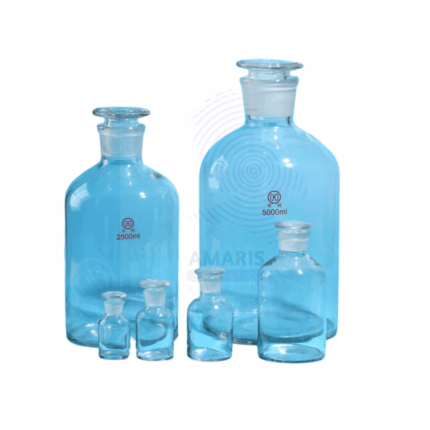
Clear laboratory reagent bottles
Clear Laboratory Reagent Bottles
These are typically made of glass or plastic and are used to store and transport various chemicals, solvents, acids, bases, and other laboratory reagents. These bottles are designed to be transparent to allow easy visibility of the contents and often come with a screw cap or stopper to seal the contents securely. They are available in various sizes to accommodate different quantities of reagents and may feature wide-mouth or narrow-mouth designs depending on the intended use. Proper labeling and handling procedures are essential to ensure the safe storage and use of reagents in these bottles.
clinostat clock type
A clinostat clock is a type of clock that incorporates a clinostat mechanism. A clinostat is a device used in scientific research to eliminate the effects of gravity on biological specimens by continuously rotating them. In the context of a clock, a clinostat mechanism is integrated to keep the clock in constant motion, typically rotating in multiple axes, which can make it difficult for a person to read the time directly. The purpose of such a clock is often artistic or conceptual, challenging traditional notions of timekeeping and perception.
clinostat clock type
A combustion tube is a laboratory glassware used primarily in organic chemistry for conducting combustion reactions. It's a straight, narrow tube made of heat-resistant glass, usually borosilicate glass, with one end sealed.
Here's how it typically works:
- Preparation: The sample to be combusted is usually placed inside the combustion tube. This sample is often an organic compound or a mixture of compounds.
- Sealing: After loading the sample, the open end of the tube is sealed, often using a stopper or a glass rod. This ensures that the combustion reaction takes place within a closed system.
- Combustion: The sealed tube is then placed in a combustion furnace, which raises the temperature to a level where combustion of the sample occurs. This typically involves heating the sample in the presence of excess oxygen.
- Collection of Products: As the sample combusts, it reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water vapor, along with other possible products depending on the composition of the sample. These products are collected and can be analyzed using various techniques such as gas chromatography.
- Analysis: The collected products can provide valuable information about the composition of the original sample. For example, the amount of carbon dioxide produced can be used to determine the carbon content of the sample, which is useful in determining its molecular formula or identifying functional groups present in organic molecules.
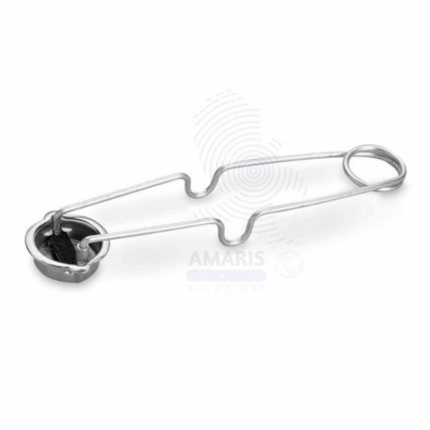
Combustion Boat
A combustion boat is a small, boat-shaped laboratory apparatus typically made of ceramic or another heat-resistant material. It is used to hold and combust solid or liquid samples in a controlled environment, allowing for precise measurement of the substances released during combustion, such as ash, gases, or residue. Combustion boats are commonly employed in analytical chemistry to determine the composition and elemental content of various samples through combustion and subsequent analysis of the combustion products.
complete kymograph equipment
A complete kymograph equipment typically includes:
- Kymograph Drum: The central component, usually made of metal or plastic, which rotates at a constant speed. It has a surface where paper or film can be attached for recording physiological data.
- Clockwork Mechanism: This regulates the rotation of the drum at a constant speed. Modern versions may use electric motors for rotation.
- Recording Mechanism: It could be a stylus or pen attached to a lever arm, which translates physiological changes into a graphical representation on the rotating drum. Alternatively, modern kymographs may use digital sensors for data acquisition.
- Mounting Stand: A stable platform to support the kymograph apparatus.
- Pulley System: This connects the drum to the clockwork mechanism, ensuring smooth and consistent rotation.
- Paper or Film: The recording surface where physiological events are transcribed. It may be attached to the drum using clips or adhesives.
- Ink or Pen: If using a stylus, ink or pen is required to make marks on the recording surface.
- Adjustment Controls: These allow fine-tuning of the drum's rotation speed and the sensitivity of the recording mechanism.
- Light Source: In some setups, a light source is positioned to enhance visibility of the recorded data, especially in dark environments.
- Supporting Software or Analysis Tools: For modern digital kymographs, software may be needed to analyze the recorded data.
- Optional Accessories: These may include additional sensors for measuring specific physiological parameters, such as temperature, pressure, or electrical signals.
- Instruction Manual: Essential for understanding the setup, operation, and maintenance of the kymograph equipment.