“Ammonium Carbonate LR 500gm” has been added to your cart. View cart

Ferric Sulphate 500gm
$2,500.00 Original price was: $2,500.00.$2,300.00Current price is: $2,300.00.
Formaldehyde 2.5 litres (formalin)
$4,500.00 Original price was: $4,500.00.$4,000.00Current price is: $4,000.00.
Field Stain A and B 25gm
$1,600.00 Original price was: $1,600.00.$1,500.00Current price is: $1,500.00.
Whatsapp Order
Field Stain A and B are used in a staining technique for blood films, particularly for the rapid identification of malaria parasites and other hematological purposes. The staining method is known as Field’s stain, and it is a type of Romanowsky stain.
Field Stain A
- Composition: Field Stain A is typically an aqueous solution of methylene blue, which stains the nuclei of cells blue.
- Function: It primarily stains the acidic components of the cell, including DNA and RNA. This makes the nuclei and certain cytoplasmic components appear blue.
Field Stain B
- Composition: Field Stain B is usually an aqueous solution of eosin, which stains the basic components of the cell pink.
- Function: It stains the cytoplasm and extracellular components pink to red. Eosinophilic structures, such as red blood cells and certain granules, are highlighted by this stain.
Usage
- Procedure:
- Prepare the blood smear: A drop of blood is spread thinly on a glass slide and allowed to air dry.
- Apply Field Stain A: The dried smear is immersed in Field Stain A for a short duration, typically around 5-10 seconds.
- Rinse: The slide is briefly rinsed in water to remove excess stain.
- Apply Field Stain B: The smear is then immersed in Field Stain B for another short duration, around 5-10 seconds.
- Rinse and dry: The slide is rinsed again in water and allowed to air dry.
- Outcome: The resulting stained smear allows for the differentiation of various cell components, making it easier to identify and analyze blood cells and any parasitic infections like malaria.
SKU:
ACS19336CHEM0
Category: Analytical Reagents
Description
Table of Contents
ToggleUses of Field Stain A and B
1. Malaria Diagnosis
- Identification of Malaria Parasites: Field Stains A and B are extensively used for the rapid detection of malaria parasites in blood smears. The stains highlight the parasites’ presence within red blood cells, aiding in quick diagnosis.
2. Hematological Studies
- Differentiation of Blood Cells: These stains help in differentiating various types of blood cells. For instance, they distinguish between white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets, which is crucial for diagnosing blood disorders and conducting routine blood examinations.
3. Rapid Staining in Field Conditions
- Field and Remote Laboratory Use: Due to their simplicity and quick staining process, Field Stains A and B are particularly useful in remote and field conditions where advanced laboratory equipment might not be available.
4. Microbial Identification
- Detection of Microorganisms: While not as commonly used as other stains like Gram stain, Field Stains can sometimes aid in identifying microorganisms in blood samples or other clinical specimens.
5. Veterinary Medicine
- Animal Blood Analysis: Similar to human medicine, these stains are used in veterinary laboratories to examine blood smears from animals, aiding in the diagnosis of blood-borne diseases and overall health assessment of animals.
6. Education and Training
- Teaching Tool: Field Stains A and B are used in educational settings to teach students and trainees about blood smear preparation and the identification of different cell types and parasites.
7. Clinical Research
- Research Studies: Researchers use these stains to study the morphology of blood cells and parasites, contributing to the development of new diagnostic techniques and treatments for blood-borne diseases.
Procedure for Laboratory Use
- Sample Collection: Obtain a blood sample via finger prick or venipuncture.
- Blood Smear Preparation: Place a drop of blood on a clean glass slide and spread it thinly using another slide to create a smear.
- Drying: Allow the smear to air dry completely.
- Staining:
- Immerse the smear in Field Stain A for about 5-10 seconds.
- Briefly rinse the slide in clean water.
- Immerse the smear in Field Stain B for another 5-10 seconds.
- Rinse the slide again in clean water.
- Drying and Examination: Let the slide air dry and then examine it under a microscope.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Field Stain A and B 25gm” Cancel reply
Related products
2 Propanol 2.5 litres (IPA)
Isopropyl alcohol (IPA), also known as 2-propanol, is a colorless, flammable chemical compound with the molecular formula C3H8O. It is a type of alcohol that is commonly used as a solvent, disinfectant, and cleaning agent in a variety of industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and electronics. IPA is often used as a disinfectant because it is effective at killing a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It is also commonly used as a solvent for oils, resins, and gums, and as a cleaning agent for electronic devices and other equipment.
Acetic Acid 2.5litre
Acetic acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, sour taste and a distinctive vinegar-like odor. Acetic acid is an important industrial chemical used in the production of various products, including solvents, plastics, textiles, and food additives. It is also the main component of vinegar, which is commonly used as a condiment and preservative in cooking and food preparation.
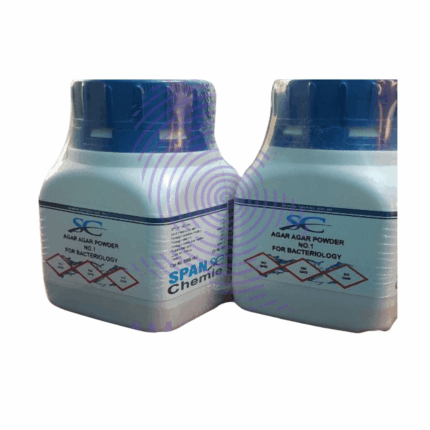
Agar Agar Powder
Agar agar powder refers to the dehydrated and powdered form of agar agar, a natural gelling agent derived from seaweed. It is made by drying and grinding the agar agar gel, resulting in a fine powder with excellent gelling properties. Agar agar powder is commonly used in cooking, baking, and food preparation as a vegetarian and vegan substitute for gelatin. It is prized for its ability to create firm and stable gels at relatively low concentrations and temperatures. Agar agar powder is versatile and can be used in a variety of recipes, including desserts, confectioneries, jams, jellies, and savory dishes.
Aluminum Ammonium Sulphate
Aluminum ammonium sulfate, also known as ammonium alum or just alum, is a chemical compound with the formula (NH4)Al(SO4)2·12H2O. It's a white crystalline solid commonly used in water purification, leather tanning, and as a mordant in dyeing textiles.
In water purification, alum acts as a coagulant to remove impurities by causing suspended particles to clump together, making it easier for filtration to remove them. In leather tanning, it helps to stabilize the leather by tightening the collagen fibers. And in dyeing textiles, alum helps the dye adhere to the fabric.
However, it's important to note that excessive exposure to aluminum compounds like alum can be harmful, so it's typically used with caution and proper safety measures.
Aluminum Hydroxide 250gm
Aluminium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the formula Al(OH)3. It is an inorganic compound that is commonly used as an antacid to neutralize excess stomach acid, as well as a component in the manufacture of various products, such as ceramics, paper, and cosmetics. It is a white, powdery substance that is insoluble in water and has a low toxicity. When heated, it decomposes to produce aluminium oxide, or alumina, which is used in the production of aluminium metal.
Aluminum Nitrate 500gm
Aluminum nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Al(NO3)3. It's a salt composed of aluminum and nitrate ions. It's commonly encountered as a hydrate with varying numbers of water molecules associated with each aluminum nitrate formula unit. It's soluble in water and is often used in various industrial processes, including as a mordant in dyeing fabrics and in the production of aluminum oxide. Additionally, it's used in some chemical reactions and as a component in some types of rocket propellants.
Aluminum Potassium Sulphate 500gm
Aluminum Potassium Sulphate, commonly known as potassium alum or potash alum, is a chemical compound with the formula KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O. It is a type of alum, a double sulfate salt, and is typically found in its dodecahydrate form. Here are some key points about this compound:
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Colorless, transparent crystals or white powder.
- Solubility: Soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol.
- Melting Point: Decomposes at high temperatures before melting.
Chemical Properties:
- Molecular Formula: KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O
- Molecular Weight: 474.39 g/mol (for the dodecahydrate form)
- Acidity: It is slightly acidic in aqueous solution.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.