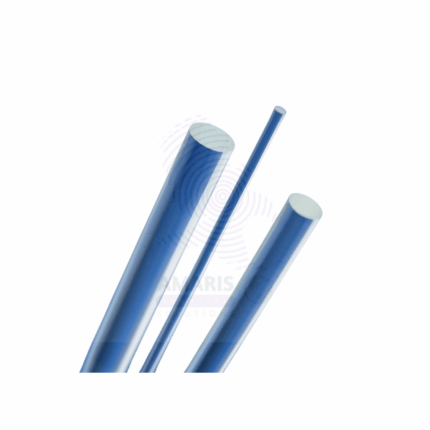
Glass Rod for Static Electricity
KSh0.01
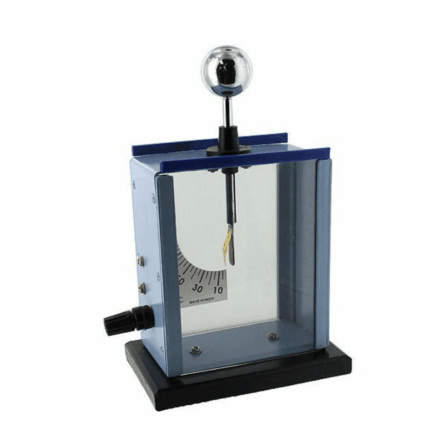

Gold Leaf Electroscope
KSh1,800.00 Original price was: KSh1,800.00.KSh1,700.00Current price is: KSh1,700.00.
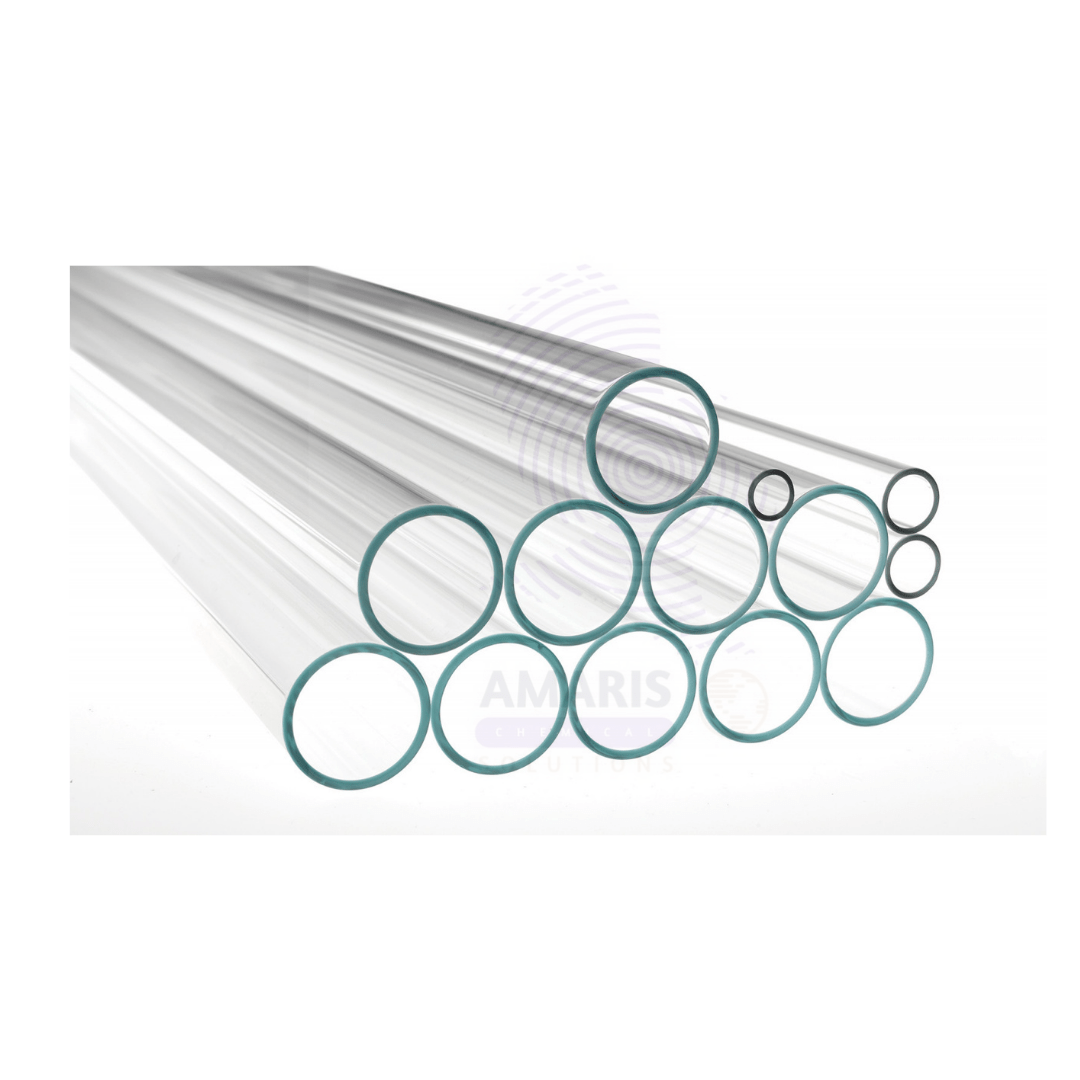
Glass Tubing
KSh500.00 Original price was: KSh500.00.KSh400.00Current price is: KSh400.00.
Glass tubing is a versatile material commonly used in various scientific, industrial, and decorative applications. It is typically made from borosilicate glass, which is known for its low thermal expansion and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for laboratory use.
SKU:
ACS29438CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Glass tubing
1. Manufacture of Laboratory Apparatus
- Test Tubes: Glass tubing is cut and shaped into test tubes, which are essential for holding, mixing, and heating chemical substances.
- Pipettes: Used for transferring precise volumes of liquids, glass pipettes are made from drawn glass tubing.
- Burettes: Graduated glass tubes with a stopcock at one end, used for titrations.
- Condensers: Glass tubing is used to make condensers for cooling vapor in distillation processes.
2. Fluid Transfer and Flow Systems
- Connecting Tubes: Used to connect various pieces of lab equipment, allowing the transfer of gases or liquids between them.
- Capillary Tubes: Very fine glass tubes used for tasks such as drawing small quantities of fluids or for chromatography.
3. Reactions and Heating
- Reaction Tubes: Glass tubing can be used to construct reaction tubes for carrying out small-scale chemical reactions.
- Heating Elements: Glass tubing can be used to hold and heat samples in controlled conditions due to its resistance to thermal shock.
4. Measurement Instruments
- Manometers: U-shaped glass tubes filled with liquid (such as mercury or water) used to measure pressure differences.
- Gas Syringes: Glass syringes connected via glass tubing are used to measure and manipulate gases.
5. Gas Handling and Sampling
- Gas Collection: Glass tubing is often used in setups for collecting and analyzing gases produced in reactions.
- Gas Sampling Tubes: Used to capture and analyze gaseous samples from various environments or reactions.
6. Distillation and Separation
- Distillation Columns: Made from glass tubing, these columns are essential for separating mixtures based on different boiling points.
- Fractionating Columns: Used in fractional distillation to improve the separation of mixtures.
7. Chromatography
- Chromatography Columns: Glass tubing is used to make columns for liquid chromatography, which are used to separate chemical mixtures.
8. Protective and Insulating Uses
- Sheaths for Thermocouples: Glass tubing can encase thermocouples, protecting them from corrosive substances.
- Insulating Tubes: Used to insulate wires or other components in high-temperature environments.
9. Specialized Uses
- Optical Systems: Sometimes glass tubing is used in optical instruments for its clarity and purity.
- Spectroscopy: Glass tubing can be part of setups for spectroscopic analysis, where it helps guide and contain light or samples.
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Absorption Tower
KSh0.01
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
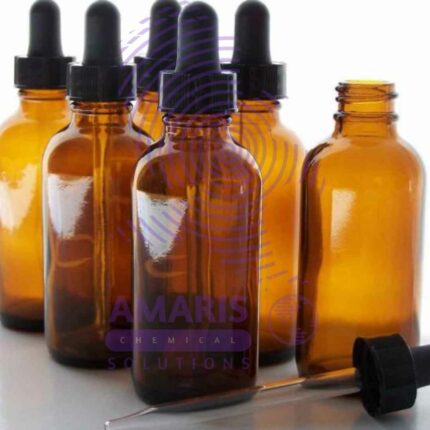
Amber Bottles Polystop
KSh0.01
A laboratory glass amber bottle is a specialized container commonly used in laboratories to store and protect light-sensitive substances, chemicals, or solutions. These bottles are made from amber-colored glass, which provides protection against ultraviolet (UV) and visible light radiation. The amber glass helps to minimize the degradation and decomposition of light-sensitive contents by blocking a significant portion of the light spectrum.
The amber color of the glass is achieved by adding iron, sulfur, and other compounds during the glass manufacturing process. This coloration is what gives the bottles their distinctive amber or brown appearance.
Laboratory glass amber bottles typically come in various sizes, ranging from small volumes of a few milliliters to large capacities of several liters. They often have a screw-on or snap-on cap, providing a secure and airtight seal to prevent spills, evaporation, and contamination.
Due to their ability to protect light-sensitive substances, laboratory glass amber bottles are widely used in chemistry, biology, pharmaceuticals, and other scientific fields where sample integrity and stability are crucial.
Balance Bathroom Scale
KSh0.01
Balance lever
KSh0.01
The best definition of a balance lever is a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or beam that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. It is used to compare the weights or forces of two objects and determine if they are in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the other (unbalanced).
The balance lever operates on the principle of torque, where the torque (rotational force) exerted on one side of the fulcrum is equal to the torque on the other side when the system is in equilibrium. This principle is expressed by the formula: Torque = Force × Distance from fulcrum.
By placing known masses or weights on one side of the lever and an unknown weight on the other side, the balance lever can be used as a weighing scale. When the lever is in balance, the two sides are equal in weight or force. This concept has been widely used in various applications, from traditional weighing scales to more complex systems like seesaws or construction equipment.
bare enamelled copper wire
KSh0.01
beaker hysil
KSh0.01
A glass beaker is a cylindrical, open-top container made of glass, typically with graduated volume markings on its side. It is commonly used in laboratories for holding, mixing, and heating liquids, as well as for performing various experiments and chemical reactions. Glass beakers come in various sizes and are designed to provide easy observation of the contents and to withstand temperature changes without significant deformation or chemical interaction with the substances being used.
Blotting paper
KSh0.01
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent and thin sheet of paper, typically made from materials like cotton, linen, or other plant fibers. It is designed to quickly absorb excess liquids, such as ink, oil, or moisture, from various surfaces without smudging or smearing the substances. Blotting paper is commonly used to remove excess ink from a freshly written page, absorb oil from the skin without disturbing makeup, or dry wet items. It is often found in office settings, art studios, and cosmetic applications due to its efficient absorption properties.
blow pipes
KSh0.01
A blowpipe apparatus is a scientific instrument used in analytical chemistry and mineralogy for conducting various tests, particularly flame tests and microchemical reactions. It typically consists of a small tube or pipette through which a controlled stream of air or oxygen is blown onto a sample being heated. This stream of air or oxygen enhances the combustion of the sample, allowing the observation of characteristic colors emitted by different elements when they are vaporized and excited by the heat. The blowpipe apparatus is often used to identify and differentiate between different elements and compounds based on their unique emission spectra and reactions.