
Magnesium Oxide Light Powder 250gm
KSh2,500.00 Original price was: KSh2,500.00.KSh2,300.00Current price is: KSh2,300.00.

Malachite Green 25gm
KSh1,500.00 Original price was: KSh1,500.00.KSh1,200.00Current price is: KSh1,200.00.
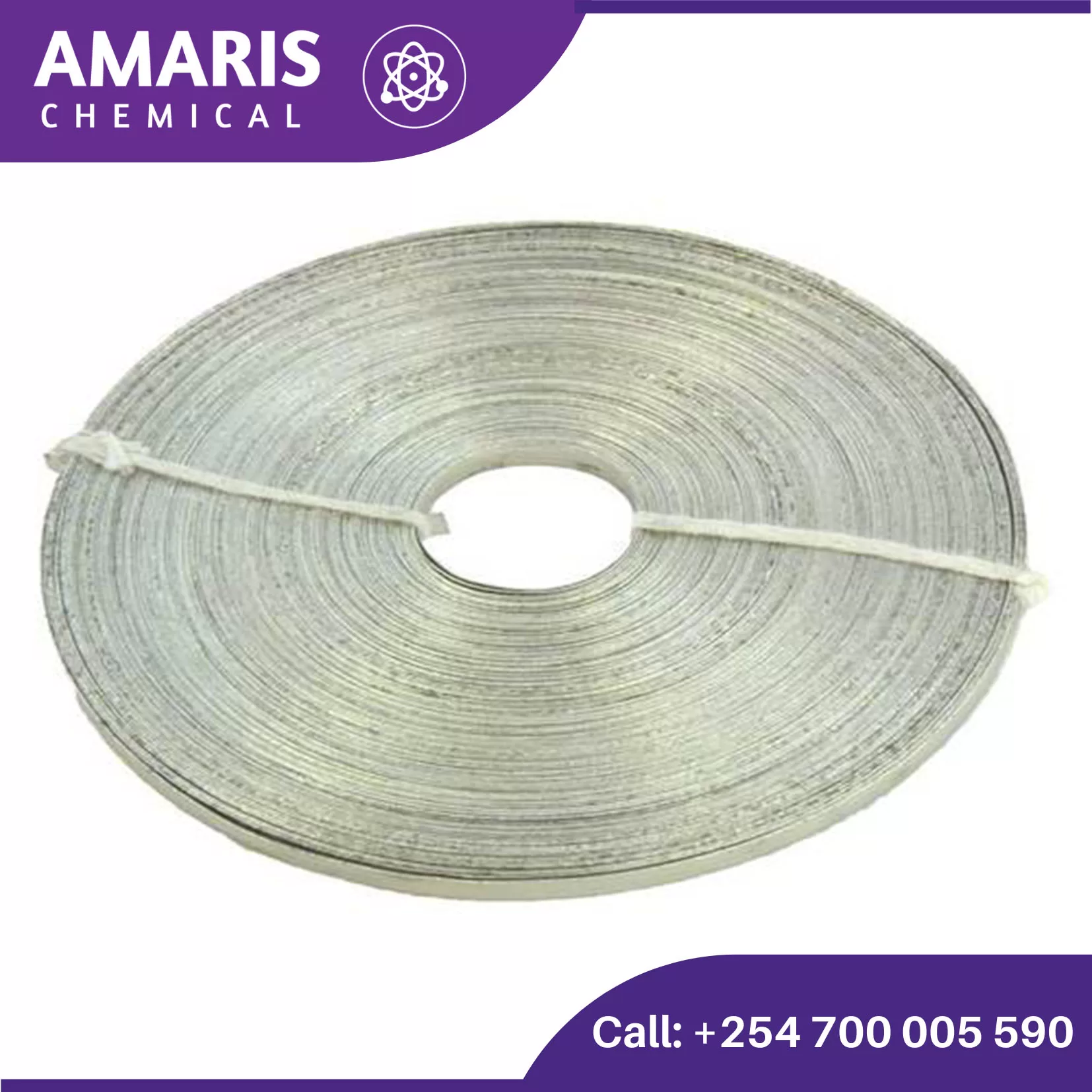
Magnesium Ribbon 25gm
KSh1,200.00 Original price was: KSh1,200.00.KSh900.00Current price is: KSh900.00.
Magnesium ribbon is a common laboratory material made from pure magnesium. It is typically supplied in thin strips or coils, making it easy to cut and handle. Magnesium ribbon has several uses and is involved in various types of experiments due to its distinct chemical and physical properties.
SKU:
ACS99293CHEM0
Category: Special Laboratory Equipment
Description
Uses of Magnesium Ribbon
1. Combustion Experiments
- Demonstration of Combustion: Magnesium ribbon is often ignited to demonstrate a combustion reaction. It burns with an intense white flame, forming magnesium oxide (MgO) and releasing a significant amount of light and heat.
2Mg+O2→2MgO2Mg+O2→2MgO
- Illustrating Exothermic Reactions: The burning of magnesium is a clear example of an exothermic reaction, showcasing the release of energy in the form of light and heat.
2. Chemical Reactions
- Reaction with Acids: Magnesium reacts vigorously with acids like hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas and magnesium chloride (MgCl₂). This reaction is used to study reactivity and gas production.
Mg+2HCl→MgCl2+H2Mg+2HCl→MgCl2+H2
- Single Displacement Reactions: Magnesium can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution, illustrating the activity series of metals.
3. Thermite Reactions
- Ignition Source: Due to its high burning temperature, magnesium ribbon can be used to ignite thermite mixtures, which involve the reaction of metal oxides with aluminum to produce molten metal and a great deal of heat.
4. Synthesis of Magnesium Compounds
- Formation of Magnesium Hydroxide: When reacted with water, magnesium forms magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas, which can demonstrate the reactivity of magnesium with water.
Mg+2H2O→Mg(OH)2+H2Mg+2H2O→Mg(OH)2+H2
- Production of Magnesium Sulfate: By reacting magnesium with sulfuric acid, magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt) can be produced, which is used in various applications.
Mg+H2SO4→MgSO4+H2Mg+H2SO4→MgSO4+H2
5. Educational Demonstrations
- Redox Reactions: Magnesium is used to demonstrate oxidation-reduction reactions, showing the transfer of electrons between substances.
- Stoichiometry: It can be used to illustrate stoichiometric principles in chemical reactions by measuring the reactants and products.
6. Energy Studies
- Heat and Light Production: The intense heat and light produced by burning magnesium can be used to study energy transformations and the characteristics of different types of energy.
7. Analytical Chemistry
- Gravimetric Analysis: Magnesium can be used in gravimetric analysis, where its reaction with other substances is used to isolate and weigh a product, helping determine the composition of a sample.
Safety Considerations
- Eye Protection: Always wear proper eye protection, such as safety goggles, when burning magnesium to protect against the bright light.
- Fire Safety: Use appropriate fire extinguishers (Class D) for metal fires. Do not use water or CO₂ extinguishers on burning magnesium.
- Handling: Handle with care to avoid skin contact and inhalation of dust or fumes.
Storage and Disposal
- Storage: Store magnesium ribbon in a dry, cool place away from moisture and oxidizing agents.
- Disposal: Neutralize small amounts with dilute acids before disposal. Follow local hazardous waste disposal regulations for larger quantities.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “Magnesium Ribbon 25gm” Cancel reply
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
Absorption Tower
KSh0.01
A laboratory absorption tower is a scaled-down version of an industrial absorption tower used for experimental purposes within a laboratory setting. It is a specialized piece of lab apparatus designed to investigate the principles of gas-liquid absorption or scrubbing processes under controlled conditions.
Typically, a lab absorption tower consists of a glass or transparent column filled with a packing material or trays to facilitate the gas-liquid contact. It is equipped with inlet and outlet ports to introduce the gas stream and remove the treated gas after absorption. Additionally, there are ports or connections to introduce the liquid solvent and monitor its flow rate. The tower may also have temperature and pressure control mechanisms to simulate specific conditions relevant to the experiment.
Laboratory absorption towers are essential tools for researchers, chemists, and engineers to study the behavior of gases and liquids during absorption processes, optimize process parameters, and assess the efficiency of different solvents or packing materials. These experiments contribute to the development and improvement of industrial-scale absorption systems and help in solving environmental challenges related to air and gas pollution.
Balance Bathroom Scale
KSh0.01
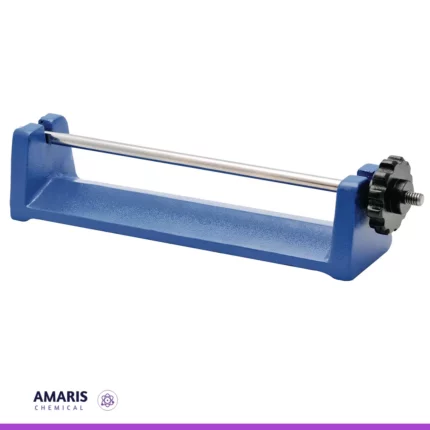
Balance lever
KSh0.01
The best definition of a balance lever is a simple machine that consists of a rigid bar or beam that pivots around a fixed point called the fulcrum. It is used to compare the weights or forces of two objects and determine if they are in equilibrium (balanced) or if one side is heavier than the other (unbalanced).
The balance lever operates on the principle of torque, where the torque (rotational force) exerted on one side of the fulcrum is equal to the torque on the other side when the system is in equilibrium. This principle is expressed by the formula: Torque = Force × Distance from fulcrum.
By placing known masses or weights on one side of the lever and an unknown weight on the other side, the balance lever can be used as a weighing scale. When the lever is in balance, the two sides are equal in weight or force. This concept has been widely used in various applications, from traditional weighing scales to more complex systems like seesaws or construction equipment.
bare enamelled copper wire
KSh0.01
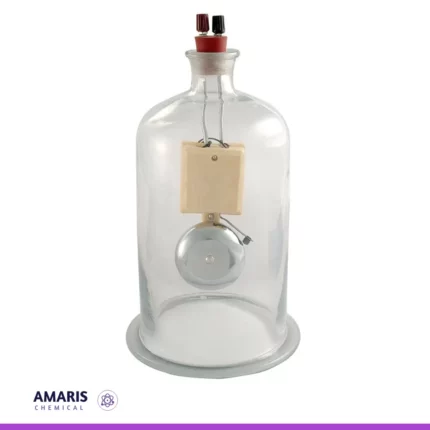
bell in vacuum
KSh0.01
A "bell in vacuum" apparatus is a scientific setup used to demonstrate the effects of reduced air pressure (vacuum) on sound transmission. It typically consists of a bell or sound-producing object enclosed within a sealed chamber from which air has been removed, creating a low-pressure environment. This apparatus is designed to illustrate how sound travels differently in a vacuum compared to in normal atmospheric conditions, highlighting the role of air molecules in sound propagation.
Blotting paper
KSh0.01
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent and thin sheet of paper, typically made from materials like cotton, linen, or other plant fibers. It is designed to quickly absorb excess liquids, such as ink, oil, or moisture, from various surfaces without smudging or smearing the substances. Blotting paper is commonly used to remove excess ink from a freshly written page, absorb oil from the skin without disturbing makeup, or dry wet items. It is often found in office settings, art studios, and cosmetic applications due to its efficient absorption properties.
blow pipes
KSh0.01
A blowpipe apparatus is a scientific instrument used in analytical chemistry and mineralogy for conducting various tests, particularly flame tests and microchemical reactions. It typically consists of a small tube or pipette through which a controlled stream of air or oxygen is blown onto a sample being heated. This stream of air or oxygen enhances the combustion of the sample, allowing the observation of characteristic colors emitted by different elements when they are vaporized and excited by the heat. The blowpipe apparatus is often used to identify and differentiate between different elements and compounds based on their unique emission spectra and reactions.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.