PIN HOLE CAMERA
$ 11.79 Original price was: $ 11.79.$ 11.61Current price is: $ 11.61.

PIPETTE BULB
$ 7.20 Original price was: $ 7.20.$ 7.08Current price is: $ 7.08.
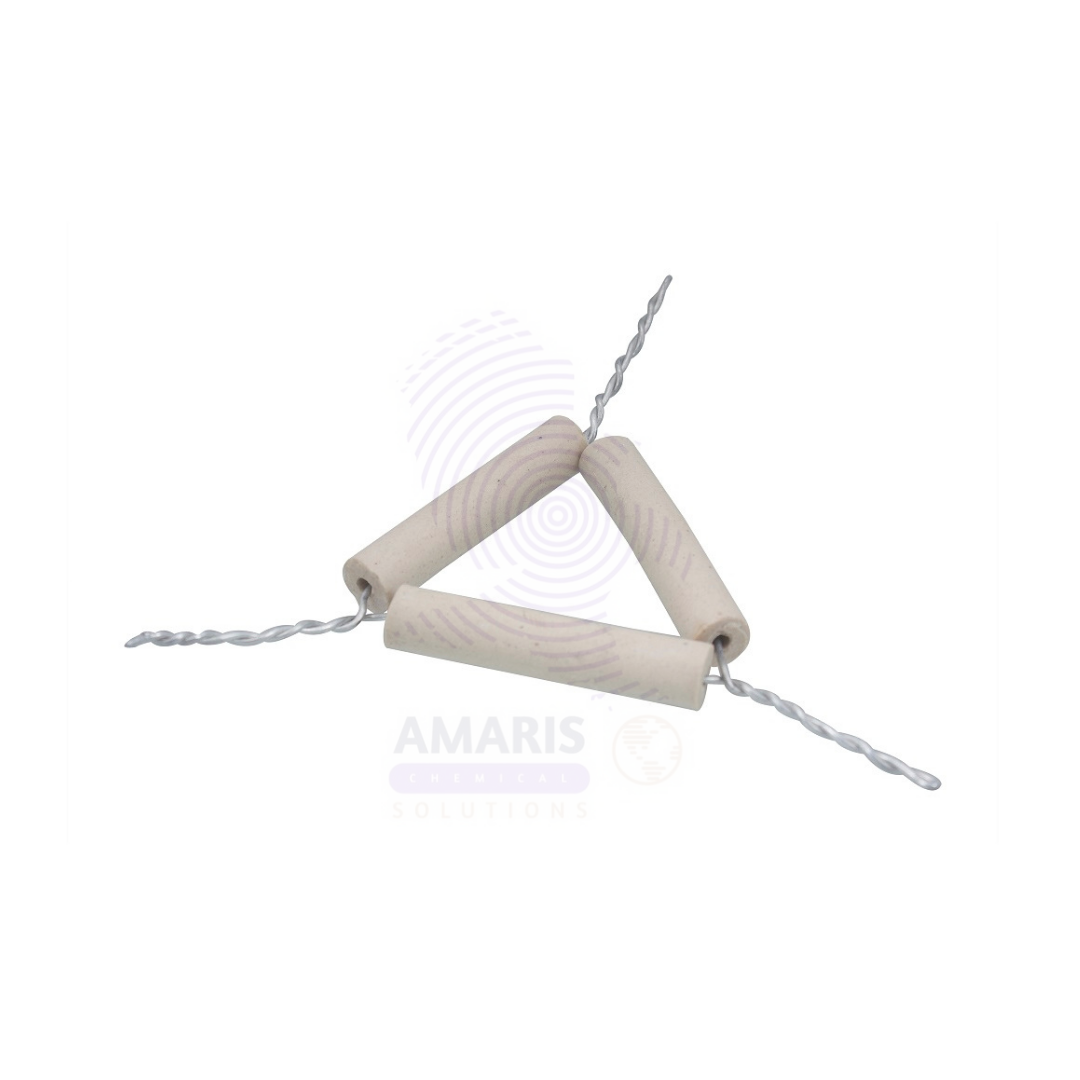
Pipe Clay Triangles
$ 6.18 Original price was: $ 6.18.$ 6.07Current price is: $ 6.07.
Whatsapp Order
Pipe Clay Triangles are heat-resistant supports used in laboratory setups to hold crucibles over a Bunsen burner or other heat sources. They consist of three lengths of ceramic (pipe clay) tubing threaded over a triangular metal wire frame, typically made of galvanized iron or nickel-chromium alloy. These ceramic-coated wires provide stable and high-temperature-resistant platforms, allowing crucibles to be heated directly during ashing, calcination, or other high-temperature experiments. Widely used in chemistry labs and educational institutions, they are essential components for supporting small containers while minimizing heat transfer loss or instability.
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle
PIPE CLAY TRIANGLES
Primary Uses
- Laboratory and Educational Applications
- Supporting crucibles during high-temperature heating over a Bunsen burner.
- Used in gravimetric analysis for ashing procedures.
- Providing heat insulation between the crucible and the support ring.
- Holding small porcelain or ceramic containers over flame.
- Common in student lab setups to teach thermal decomposition and combustion experiments.
Secondary Uses
- Research and Industrial Laboratories
- Used in metallurgical testing for supporting sample crucibles during heating.
- Supporting other ceramic or glass containers during high-temperature reactions.
- Employed in analytical chemistry for sustained heating without direct contact with metal surfaces.
KEY PRODUCT FEATURES
1.Basic Identification Attributes
- Material: Metal wire frame (galvanized iron/nickel alloy) with ceramic (pipe clay) tubes.
- Shape: Equilateral or isosceles triangle with straight sides.
- Sizes: Available in various side lengths (commonly 50 mm, 75 mm, 100 mm) to support different crucible sizes.
- Construction: Pipe clay tubes slide over the wire to provide heat insulation.
2.Physical & Chemical Properties
- Thermal Resistance: Withstands very high temperatures (over 1000°C); suitable for direct flame exposure.
- Chemical Resistance: Inert and non-reactive under standard lab conditions.
- Durability: Long-lasting with proper use; resistant to thermal shock.
3.Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Minimal risk when used correctly.
- Fragile ceramic tubes may crack or chip if dropped or mishandled.
4.Storage & Handling Attributes
- Store in a dry, padded container to prevent damage to ceramic tubing.
- Inspect ceramic tubes before use for any cracks or wear.
- Handle gently to prevent breakage of the ceramic components.
5.Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Manufactured in accordance with laboratory safety and material standards.
6.Environmental & Health Impact
- Inert materials; poses no known environmental hazards under normal use.
- Long lifespan reduces laboratory waste.
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Handling Precautions
- Use with proper tongs and heat-resistant gloves during and after heating.
- Ensure stable placement to avoid tipping over heated crucibles.
First Aid Measures
- In case of burns from heated crucible or metal, apply first aid and seek medical attention if needed.
- If ceramic shards cause cuts, clean wounds and dress appropriately.
Firefighting Measures
- Non-flammable.
- Will not contribute to combustion in a fire situation.
Related products
Complete burette stand
The Complete Burette Stand is a sturdy laboratory apparatus designed to securely hold burettes during titration and other volumetric experiments. Typically made of metal with a stable base, it features adjustable clamps and rods to accommodate different sizes of burettes and provide stability during precise liquid dispensing. Its durable construction ensures safety and accuracy in laboratory workflows.
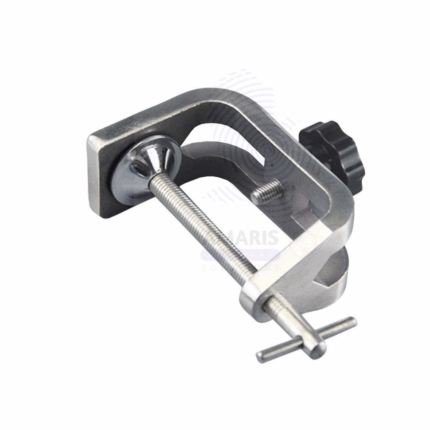
G Clamp
G Clamp is a versatile clamping tool widely used in woodworking, metalworking, and laboratory applications to hold objects securely in place. Shaped like the letter "G," it features a screw mechanism that allows adjustable pressure to firmly grip materials during assembly, welding, gluing, or testing. Made from durable cast iron or steel, G Clamps offer strong holding power and reliable stability, making them essential for precision work and safety in various industrial, construction, and laboratory settings.
Gas Stove Portable
Gas Stove Portable is a compact, lightweight stove designed for easy transport and use in various settings, including laboratories, fieldwork, and outdoor cooking. It operates on portable gas cartridges or cylinders, providing a reliable flame source for heating, boiling, or sterilization purposes. Constructed with durable materials and equipped with safety features such as flame control and automatic shut-off valves, this stove offers convenience and efficiency. Its portability and user-friendly design make it ideal for temporary setups and situations where traditional fixed stoves are impractical.
Glass Tubing Cutter File
Glass Tubing Cutter File is a specialized tool designed for scoring and preparing glass tubes before breaking them cleanly. It typically features a hardened steel or diamond-coated cutting surface combined with a file mechanism to smooth and shape the scored area, ensuring precise and controlled glass cutting. This tool is essential for laboratory technicians, glassworkers, and craftsmen who work with glass tubing, enabling safe and accurate customization of glass lengths and shapes.
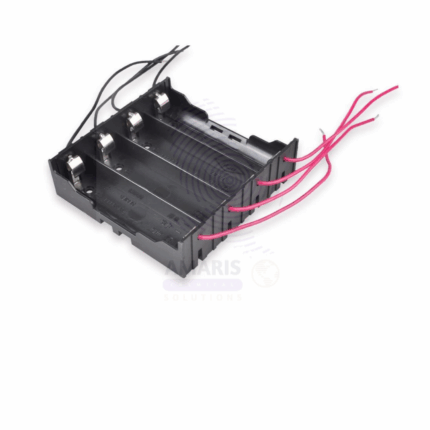
Plastic Cell Holder
A Plastic Cell Holder is a laboratory accessory used to securely hold electrochemical or dry cells (batteries) in place during physics or electrical experiments. It is typically made from non-conductive, durable plastic and may feature metal terminals or spring-loaded clips for electrical connections. These holders provide a stable and safe platform to integrate batteries into circuits for educational demonstrations, testing setups, or prototyping purposes. Designed for use with common battery sizes (such as D, C, AA, or specialized cells), the holder ensures easy insertion, removal, and reliable connection of power sources without short-circuiting. It is widely used in physics labs, electronics training, and school science kits.
PLASTIC DISSECTING TRAY WITHOUT WAX
The Plastic Dissecting Tray without Wax is a laboratory instrument used to hold specimens during dissection procedures in biology, zoology, anatomy, and educational labs. Unlike traditional dissecting trays that include a wax layer for pinning specimens, this tray offers a reusable, wax-free surface, typically designed to accommodate separate pinning pads or mats (e.g., rubber or foam inserts). It is made from high-grade, chemical-resistant plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, offering a lightweight, durable, and easy-to-clean platform. The tray typically features raised sides to contain fluids and provide a controlled
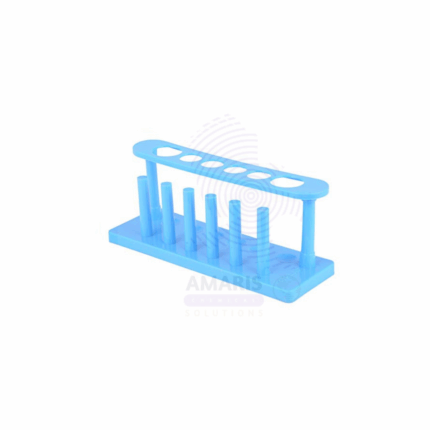
PLASTIC TEST TUBE STAND 6HOLE
The Plastic Test Tube Stand 6Hole is a laboratory support accessory designed to securely hold test tubes in an upright position during experimental procedures, storage, or drying. This version features six equally spaced holes, each capable of accommodating standard-size test tubes. Constructed from chemical-resistant, durable plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, the stand is lightweight, stable, and easy to clean. Often used in educational, analytical, and clinical laboratories, it provides a convenient and organized way to manage test tubes during chemical reactions, sample handling, or heating processes. The design may also include drying pegs or smaller side holes for inverted tube drying.
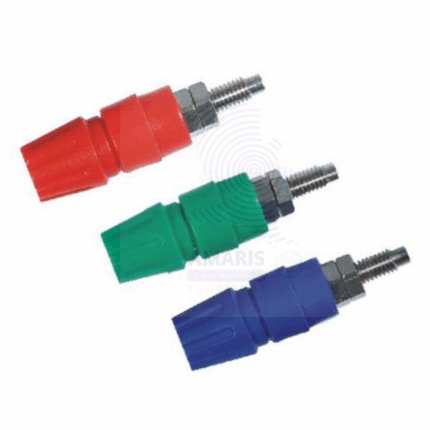
Terminals
Terminals are essential electrical connectors used in laboratory and industrial setups to create secure, reliable connections between wires, cables, and electrical equipment. Typically made from conductive metals such as copper or brass and often coated with corrosion-resistant materials, terminals facilitate the transfer of electrical signals or power with minimal resistance. They come in various types including ring, spade, fork, and blade terminals to suit diverse wiring requirements. Terminals are widely used in electrical circuits, instrumentation, and control panels within laboratories to ensure safe and efficient electrical connections.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders