“Camelina” has been added to your cart. View cart
Shipping & Delivery
Related products
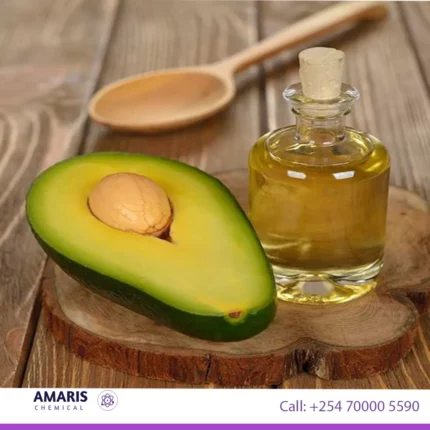
Avocado wax
Avocado wax, also known as avocado oil wax or Persea Gratissima (Avocado) Oil, is a natural wax derived from the fruit of the avocado tree (Persea americana). It is obtained by cold-pressing the flesh of the avocado fruit and then further refining the extracted oil to obtain a solid, waxy substance.
Avocado wax has a high melting point and a rich, creamy texture, which makes it an excellent ingredient for various cosmetic and personal care products. It is often used as a natural alternative to petroleum-based waxes or synthetic emollients.
The wax contains a combination of fatty acids, such as oleic acid, palmitic acid, and linoleic acid, which contribute to its emollient and moisturizing properties. Avocado wax forms a protective barrier on the skin, helping to retain moisture and prevent moisture loss. It is known for its nourishing, softening, and smoothing effects on the skin and hair.
In summary, avocado wax is a natural wax derived from avocado fruit, prized for its moisturizing, emollient, and protective properties, making it a valuable ingredient in various cosmetic and personal care products.
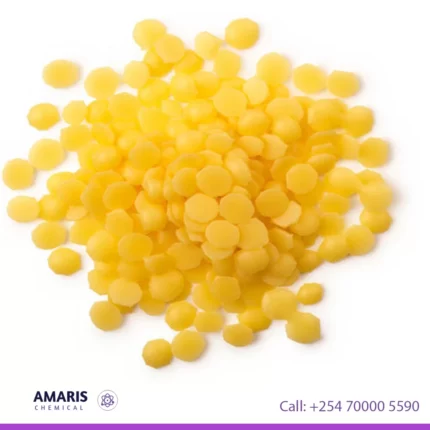
Candelilla Wax
Candelilla wax is a natural vegetable wax derived from the leaves of the candelilla shrub, scientifically known as Euphorbia cerifera. It is primarily produced in northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. Candelilla wax is obtained through a process that involves harvesting the leaves, grinding them into a powder, and then boiling the powder to extract the wax.
Candelilla wax is characterized by its yellowish-brown color and a hard, brittle texture. It is composed mainly of hydrocarbons, esters, and fatty acids. One of its key components is the hydrocarbon called cerotine, which gives the wax its unique properties. It has a melting point ranging from 68 to 73 degrees Celsius (154 to 163 degrees Fahrenheit).
This wax is widely used in various industries, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food, and household products. In cosmetics, it is employed as a natural alternative to beeswax or petroleum-based waxes in the formulation of lip balms, lotions, creams, and other skincare products. Its emollient and protective properties help to provide a smooth texture, enhance product stability, and improve moisture retention.
Furthermore, candelilla wax finds applications in the food industry as a coating or glazing agent for candies, chewing gum, and other confectionery products. It is also utilized in the production of candles, polishes, adhesives, and coatings due to its excellent film-forming and water-repellent qualities.
Overall, candelilla wax is a versatile and sustainable natural wax with various desirable properties, making it a valuable ingredient in numerous commercial products.
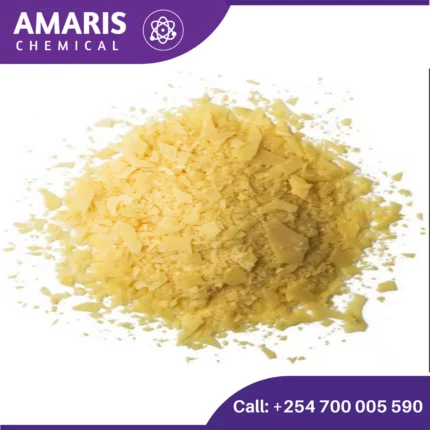
Carnauba wax
Carnauba wax is a natural wax derived from the leaves of the carnauba palm (Copernicia prunifera), which is native to northeastern Brazil. Known as the "queen of waxes," carnauba wax is highly valued for its hardness, high melting point, and glossy finish. Here are some key points about carnauba wax:
Properties
- Appearance: It comes in flakes or powder and is typically light yellow to brownish in color.
- Melting Point: It has a high melting point of about 82-86°C (180-187°F), making it one of the hardest natural waxes.
- Composition: It is composed of esters, fatty acids, and alcohols, which contribute to its hardness and water-resistant properties.
Glycerin 250 kg Drum Food Grade
Glycerin, also known as glycerol, is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. It is a type of alcohol with three hydroxyl (OH) groups, and is commonly used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and personal care products. Glycerin has numerous applications, including as a solvent, humectant, emollient, and lubricant, among others. It can be derived from both plant and animal sources, and is also produced as a byproduct of soap and biodiesel manufacturing.
Silicon emulsion
Soya Lecithin
Soya lecithin is a natural substance derived from soybeans that is commonly used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and dispersant in food products, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial applications. It is composed of a mixture of phospholipids, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylinositol, which have unique properties that make them useful in a wide range of applications. Soya lecithin is typically extracted from soybean oil and is often added to foods as an ingredient to improve texture, increase shelf life, or facilitate the mixing of ingredients that would otherwise not blend together.
Soya wax
Soy wax is a natural alternative to traditional paraffin wax, made from soybeans. It's becoming increasingly popular in candle making due to its renewable and biodegradable nature. Soy wax burns cleaner and slower than paraffin wax, emitting less soot and lasting longer. It's also non-toxic, making it a healthier option for both the environment and indoor air quality. Many people appreciate soy wax candles for their eco-friendliness and the fact that they support agricultural sustainability. Additionally, soy wax can hold fragrance oils well, providing a pleasant scent experience.
Stearic Acid (Triple Pressed) 25kg
Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2. It is a solid, waxy substance that is odorless and tasteless. Stearic acid is commonly found in natural fats and oils, such as animal fats (beef, pork, and chicken) and vegetable oils (such as coconut oil, palm oil, and shea butter).
Stearic acid is widely used in various industries and applications. In the food industry, it serves as a food additive and is commonly used as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer. It can be found in a variety of food products, including baked goods, confectionery, margarine, and chocolate.
Outside of the food industry, stearic acid has many applications. It is used in the production of candles, cosmetics, soaps, detergents, and lubricants. It is also utilized as a coating for pills and tablets in the pharmaceutical industry.
From a chemical perspective, stearic acid belongs to the class of fatty acids, which are long-chain carboxylic acids. It is called a saturated fatty acid because its carbon chain is fully saturated with hydrogen atoms, meaning it does not contain any carbon-carbon double bonds. This saturation gives stearic acid its solid form at room temperature and makes it less prone to rancidity compared to unsaturated fats.
Overall, stearic acid is a versatile compound with various industrial applications, primarily as a thickener, emulsifier, stabilizer, and lubricant.