Understanding Oxalic Acid Extra Pure: Properties, Applications, And Safety
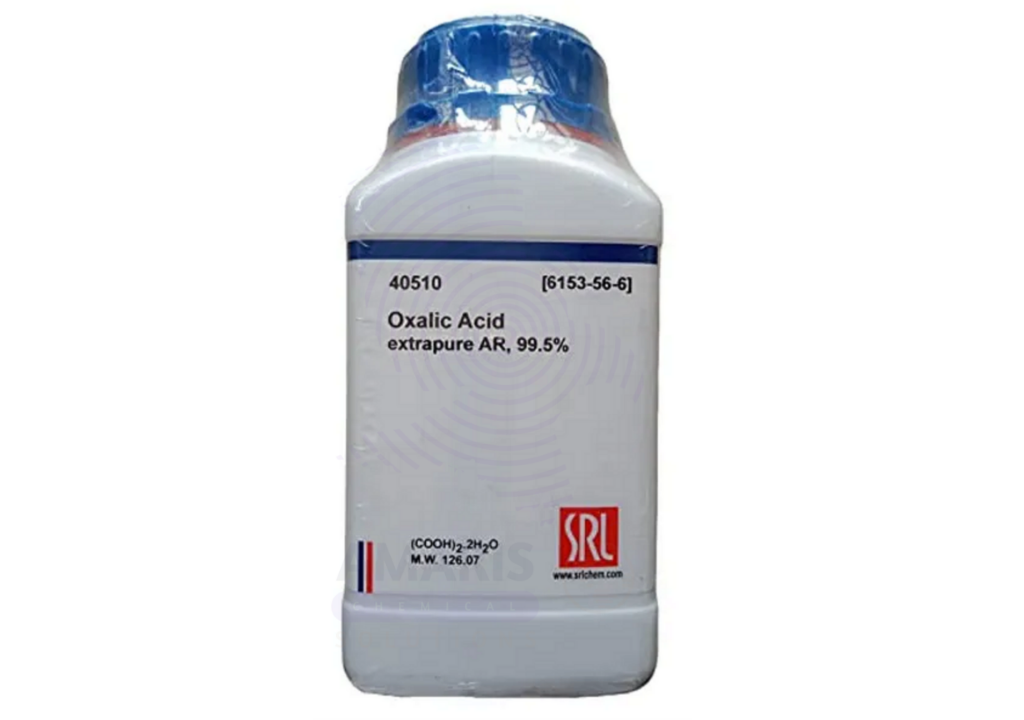

Oxalic Acid Extra Pure is a high-purity crystalline organic compound that plays a significant role in various laboratory, industrial, and even domestic applications. With the chemical formula C₂H₂O₄·2H₂O (in its most common dihydrate form), oxalic acid is known for its strong acidic nature and powerful chelating ability—particularly for metal ions like calcium and iron.
This blog aims to delve into the essential characteristics, applications, safety concerns, and handling guidelines of Oxalic Acid Extra Pure, helping students, researchers, technicians, and chemical buyers understand its full potential and proper use.
What is Oxalic Acid Extra Pure?
Oxalic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in many plants, such as spinach, rhubarb, and beetroot. In its extra pure laboratory-grade form, it is highly refined and free from significant impurities, making it suitable for analytical chemistry, synthesis, and pharmaceutical testing.
In appearance, it is a white crystalline solid that dissolves easily in water, forming a colorless, acidic solution. It has a slightly sour taste and is odorless in solid form.
Key Physical & Chemical Properties:
- Chemical Formula: C₂H₂O₄·2H₂O (dihydrate)
- Molecular Weight: 126.07 g/mol
- Melting Point: 101–102 °C (dihydrate loses water)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and alcohol
- Acidity: A strong organic acid with two replaceable hydrogen atoms
These characteristics make it a versatile compound that reacts with various bases and metal ions, making it particularly useful in titration procedures and surface cleaning applications.
Common Applications of Oxalic Acid Extra Pure
1. Analytical Reagent in Laboratories
In chemistry labs, oxalic acid is frequently used as a primary standard for titrations involving strong bases like sodium hydroxide. Its high purity and stable crystalline structure make it ideal for accurate standardization procedures.
2. Metal Cleaning and Rust Removal
Due to its strong chelating properties, oxalic acid is a preferred agent for cleaning metal surfaces and removing rust stains. It reacts with iron oxides to form soluble iron oxalates that can be rinsed away.
3. Textile and Leather Industry
Oxalic acid serves as a bleaching agent in textile processing, where it helps remove stains and iron deposits. It is also used in the tanning of leather, helping achieve specific surface finishes.
4. Pharmaceutical and Food Analysis
In its extra pure form, oxalic acid is sometimes employed in the pharmaceutical industry for pH adjustment, analytical control, and precipitation reactions. It is not added directly to foods but is important in the analysis of oxalate levels in raw materials.
5. Wood Bleaching and Restoration
Oxalic acid is used in woodworking and restoration to bleach and brighten wood, especially in cases where water damage or iron staining has occurred.
Safety and Handling
While useful, oxalic acid poses several hazards if not handled properly. It is toxic if ingested in large quantities and can cause irritation or burns to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
Safety Guidelines:
- PPE: Always wear gloves, goggles, and a lab coat when handling oxalic acid.
- Ventilation: Use in a well-ventilated area or fume hood to avoid inhaling vapors or dust.
- Storage: Store in tightly sealed containers away from heat and incompatible materials such as strong oxidizers or bases.
- First Aid:
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical help if irritation persists.
- Contact: Wash skin or eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes.
- Ingestion: Seek immediate medical attention; do not induce vomiting.
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical help if irritation persists.
Environmental Impact
Oxalic acid is biodegradable and breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. However, due to its toxicity in concentrated form, disposal must be done in compliance with local chemical waste management regulations to avoid groundwater contamination.
Final Thoughts
Oxalic Acid Extra Pure is more than just a chemical—it’s a tool that supports essential processes in chemistry, industry, and restoration work. Whether you’re standardizing a solution in the lab or restoring an antique wooden table, oxalic acid’s unique properties make it a reliable and powerful compound. But with that power comes responsibility, and safe handling practices are non-negotiable.
If you’re sourcing oxalic acid for laboratory or industrial use, ensure you obtain the Extra Pure grade to guarantee performance, reliability, and minimal impurities.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders