Carbon Disulfide 99%
Carbon disulfide (CS₂) is a colorless, volatile liquid with a sweet, ether-like odor. It is highly flammable and used primarily as a solvent in industrial processes, such as extracting fats and oils from seeds, and in the production of viscose rayon and cellophane. Carbon disulfide is also used in the manufacture of pesticides and rubber. However, it is toxic and can pose significant health risks, including neurological damage, if proper safety precautions are not followed.
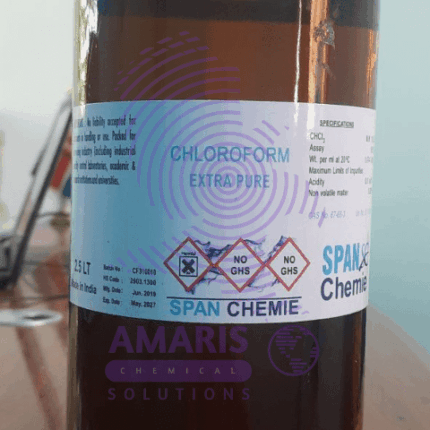
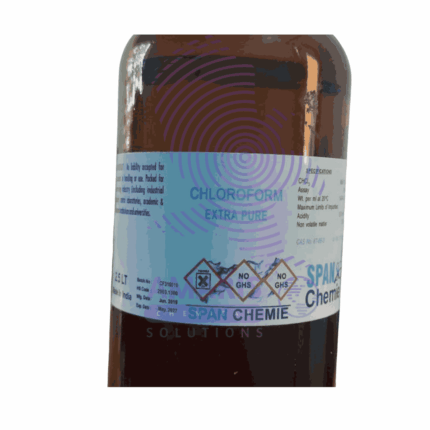
Chloroform 2.5litre extra pure
Chloroform is a colorless, volatile liquid with a slightly sweet odor. It gained notoriety as an anesthetic in the 19th century, but its use declined due to safety concerns. It's also used as a solvent in laboratories and industry. However, it's important to note that chloroform is highly toxic and can cause serious health issues, including damage to the liver and kidneys, as well as potential carcinogenic effects. Because of these risks, its use is highly regulated and alternatives are often preferred when possible.
Citric Acid Monohydrate 500gm
Citric acid is a weak organic acid that occurs naturally in citrus fruits such as lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruits. It is a tricarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C6H8O7 and is commonly used as a food additive, preservative, and flavoring agent. Citric acid is also used in the pharmaceutical industry, as a chelating agent in cleaning and personal care products, and in the production of cosmetics and detergents. It is a white crystalline powder with a sour taste and is soluble in water.
Copper Hydroxide 500gm
Copper hydroxide is a chemical compound with the formula Cu(OH)₂. It is a blue solid that is insoluble in water. Copper hydroxide is commonly used as a fungicide in agriculture to control various fungal diseases in crops. It works by disrupting the cell walls of fungi, thereby preventing their growth and reproduction.
Copper Turnings 25gm
Copper turnings refer to small pieces or shavings of copper produced during machining or shaping processes. They are typically created when copper is being worked with tools like lathes, drills, or milling machines. These turnings can vary in size, shape, and thickness depending on the specific machining operation.
Cresol Red Indicator 25gm
Cresol Red is a pH indicator dye commonly used in titrations and other laboratory experiments to determine the pH of a solution. It changes color based on the acidity or basicity of the solution it is in. Here are its key characteristics:
- Chemical Structure: Cresol Red is a sulfonephthalein dye with the molecular formula C21H18O5S.
- Color Change: It transitions from yellow in acidic solutions (pH < 1.8) to red in neutral solutions (pH around 7.0), and then to purple in basic solutions (pH > 8.8).
Crystal Violet 1% alcohol solution 25gm
Crystal Violet, also known as gentian violet, is a synthetic dye with antibacterial and antifungal properties. It's commonly used in microbiology as a staining agent to visualize bacteria and other microorganisms under the microscope.
A 1% alcohol solution of Crystal Violet would mean that 1 gram of Crystal Violet dye is dissolved in 100 milliliters of alcohol. This solution is typically used in Gram staining, a differential staining technique used to classify bacteria into two groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
In Gram staining, Crystal Violet is the primary stain that imparts a purple color to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The alcohol serves as a solvent and fixative, helping the dye penetrate the bacterial cell wall and retain its color during the staining process.
Cupric Carbonate 500gm
Cupric carbonate, also known as copper(II) carbonate, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCO3. It exists in nature as several different minerals, including malachite and azurite, which are valued for their vibrant green and blue colors, respectively. Cupric carbonate can also be synthesized in the laboratory.
In its natural form, cupric carbonate is often used as a pigment in paints and dyes due to its striking color. It has also been used historically as a source of copper in various applications, including as a fungicide in agriculture.
Cupric carbonate is insoluble in water, but it can react with acids to form soluble copper salts. Additionally, it can decompose upon heating to release carbon dioxide and form copper(II) oxide.
It's important to handle cupric carbonate with care, as copper compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large quantities.
Cupric Chloride 250gm
Cupric chloride, also known as copper(II) chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCl₂. It appears as a yellowish-brown powder in its anhydrous form and turns into a blue-green crystalline solid when hydrated. This compound is highly soluble in water, forming a blue solution.
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuCl₂
- Molecular Weight: 134.45 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellowish-brown powder (anhydrous), blue-green crystals (hydrated)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
Cupric Oxide 100gm
Cupric oxide, also known as copper(II) oxide, is a black solid with the chemical formula CuO. It is a significant compound of copper and has various applications in different fields. Here are some key points about cupric oxide:
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuO
- Appearance: Black or dark brown powder.
- Molecular Weight: 79.545 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1,326 °C (2,419 °F)
- Density: 6.315 g/cm³
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in acids.
Production:
Cupric oxide can be produced by several methods, including:- Thermal Decomposition: Heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) carbonate, or copper(II) hydroxide in the absence of oxygen.
- Direct Oxidation: Heating metallic copper in the presence of oxygen.