

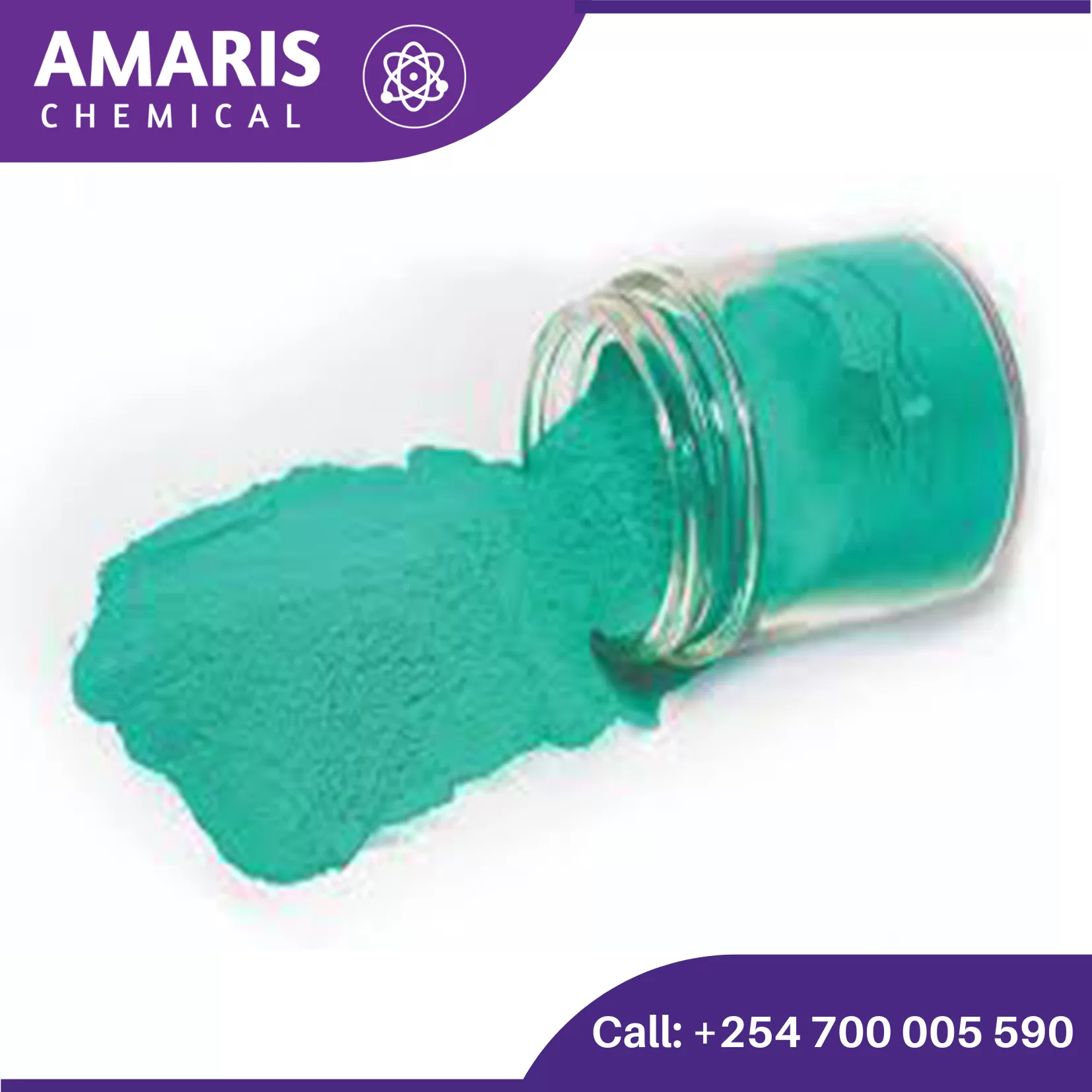
Cupric Carbonate 500gm
$2,500.00 Original price was: $2,500.00.$2,300.00Current price is: $2,300.00.
Cupric carbonate, also known as copper(II) carbonate, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCO3. It exists in nature as several different minerals, including malachite and azurite, which are valued for their vibrant green and blue colors, respectively. Cupric carbonate can also be synthesized in the laboratory.
In its natural form, cupric carbonate is often used as a pigment in paints and dyes due to its striking color. It has also been used historically as a source of copper in various applications, including as a fungicide in agriculture.
Cupric carbonate is insoluble in water, but it can react with acids to form soluble copper salts. Additionally, it can decompose upon heating to release carbon dioxide and form copper(II) oxide.
It’s important to handle cupric carbonate with care, as copper compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large quantities.
Uses of Cupric Carbonate.
Chemical Synthesis:
Cupric carbonate can serve as a precursor in the synthesis of other copper compounds or complex molecules. It may be used as a reactant in organic synthesis reactions to introduce copper into organic molecules.
Catalysis:
Copper compounds, including cupric carbonate, can act as catalysts in chemical reactions. They may catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, coupling reactions, or other transformations in organic and inorganic chemistry.
Analytical Chemistry:
Cupric carbonate can be used in analytical chemistry for qualitative and quantitative analysis. It may serve as a standard in calibration procedures or as a reagent in specific tests for the presence of certain functional groups or elements.
Education and Demonstrations:
Cupric carbonate can be used in educational laboratory experiments to demonstrate principles of chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and synthesis. It provides students with hands-on experience in working with transition metal compounds.
Electrochemistry:
Copper compounds are often used in electrochemical experiments and studies. Cupric carbonate may be used as a component in electrochemical cells or as a source of copper ions in electrolysis experiments.
Materials Science:
Cupric carbonate can be utilized in materials science research, particularly in the synthesis of materials with specific properties or applications. It may be incorporated into nanomaterials or composites for various purposes.
Biological Studies:
Copper compounds are essential for various biological processes, and cupric carbonate may be used in studies related to bioinorganic chemistry, enzymatic reactions, or the role of copper in biological systems.
Art Conservation:
In some cases, cupric carbonate or related compounds may be used in the conservation and restoration of artworks. It can be applied in the stabilization of copper-containing pigments or in the treatment of corrosion on metal artifacts.
You may also like…
Ammonium Cupric Chloride
Cupric Chloride 250gm
- Chemical Formula: CuCl₂
- Molecular Weight: 134.45 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellowish-brown powder (anhydrous), blue-green crystals (hydrated)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
Cupric Oxide 100gm
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuO
- Appearance: Black or dark brown powder.
- Molecular Weight: 79.545 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1,326 °C (2,419 °F)
- Density: 6.315 g/cm³
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in acids.
Production:
Cupric oxide can be produced by several methods, including:- Thermal Decomposition: Heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) carbonate, or copper(II) hydroxide in the absence of oxygen.
- Direct Oxidation: Heating metallic copper in the presence of oxygen.
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate
Related products
2 Propanol 2.5 litres (IPA)
Aceto Carmine 100 ml
Properties
- Color: Red to purplish-red.
- Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol.
- Staining Characteristics: Stains chromatin and cytoplasmic components, providing contrast for better visualization under a microscope.
Preparation
- Ingredients:
- Carmine dye: A natural red dye extracted from the cochineal insect.
- Acetic acid: A colorless liquid organic compound with a pungent smell.
- Procedure:
- Dissolve a specific amount of carmine powder in hot distilled water.
- Add glacial acetic acid to the solution.
- Filter the mixture to remove any undissolved particles.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.