Leaching agents are chemicals used to extract valuable metals (e.g., gold, copper, uranium) from ores by dissolving them into a solution. Common agents include cyanide (for gold/silver), sulfuric acid (for copper), and thiourea (alternative to cyanide). They enable cost-effective metal recovery from low-grade ores but require strict environmental controls to prevent contamination.
Ammonium Cupric Chloride
Ammonium Cupric Chloride is a blue-green crystalline inorganic compound composed of copper, ammonium, and chloride ions. It is widely used as a source of copper in agricultural fungicides and bactericides, as well as in electroplating, chemical synthesis, and textile dyeing. Its antimicrobial properties make it valuable for controlling fungal and bacterial infections in plants. Additionally, it serves as a precursor in various industrial and laboratory applications.
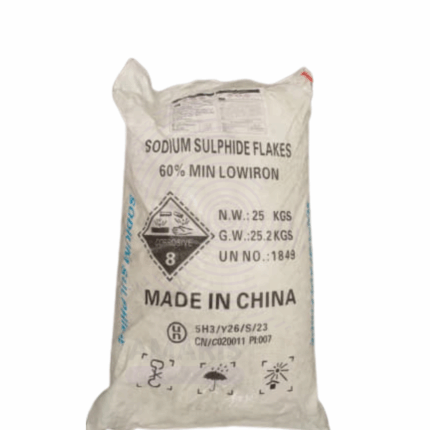
Sodium Sulphide
Sodium Sulphide (Na₂S) is a yellow to red-yellow crystalline solid or powder with a characteristic odor of hydrogen sulfide. It is highly soluble in water, forming strongly alkaline solutions. This 25kg packaged product is widely used in the chemical, leather, pulp and paper, and textile industries as a reducing agent, sulfur donor, and in flotation processes. Due to its strong reducing properties and reactivity, it must be handled with care under proper safety measures.
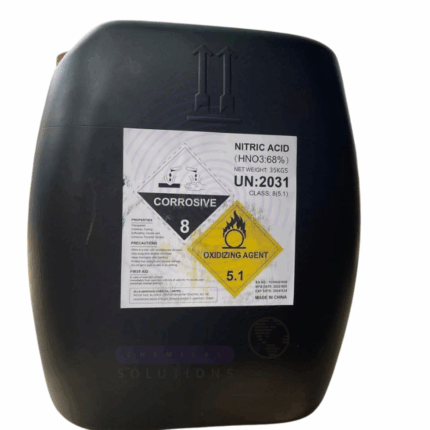
Sulphuric Acid
Sulphuric Acid is a dense, highly corrosive, and strong mineral acid widely used as a fundamental chemical reagent and industrial raw material. It serves as a key component in fertilizer production, chemical synthesis, petroleum refining, and many other industrial processes. The 98% concentration is the concentrated, nearly pure form commonly utilized for manufacturing and processing applications demanding high acid strength and purity.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders