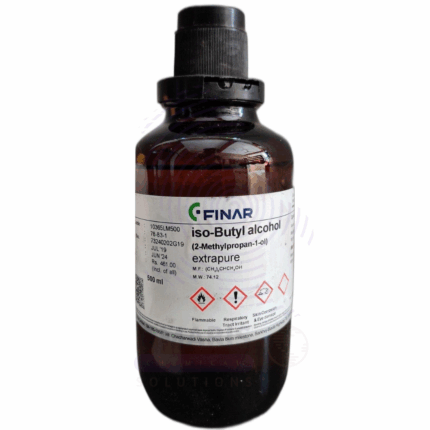
Isobutyl Alcohol Extra Pure
Isobutyl Alcohol Extra Pure is a high-purity, branched-chain aliphatic alcohol with the chemical formula C₄H₁₀O. It appears as a clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic odor and is highly soluble in organic solvents while only moderately soluble in water. This compound is commonly used in laboratories as a solvent for resins, oils, and other organic compounds, as well as in the synthesis of esters and plasticizers. Due to its volatility and purity, Isobutyl Alcohol is valuable in analytical procedures, chemical research, and as a standard in gas chromatography. Proper storage in tightly sealed containers away from heat and ignition sources is essential due to its flammability.
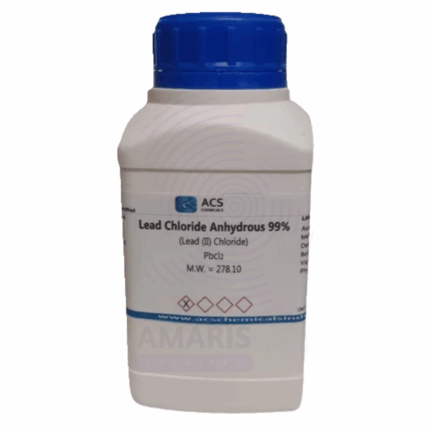
Lead Chloride Anhydrous Extra Pure
Lead Chloride Anhydrous Extra Pure is a white crystalline compound with the chemical formula PbCl₂, offered in its high-purity, moisture-free form for specialized applications. It is only sparingly soluble in cold water but dissolves more readily in hot water, forming a clear solution upon heating. This compound is used in laboratory synthesis, particularly in the preparation of other lead-based reagents, and plays a role in ceramic glazing, pigment production, and electrochemical processes. In research, it is also employed in photographic materials, optical devices, and inorganic analysis. Due to the toxic nature of lead compounds, strict safety protocols are necessary during storage and handling.
Lead Dioxide Extra Pure
Lead Dioxide Extra Pure is a dark brown or black crystalline powder with the chemical formula PbO₂, recognized for its strong oxidizing properties and high purity suitable for laboratory-grade applications. This compound is primarily used in electrochemical experiments, oxidation reactions, and battery research, especially in the development and maintenance of lead-acid batteries where it functions as the active material on the positive plate. In analytical chemistry, it is employed as an oxidizing agent and for synthesizing other lead compounds. Its stability and performance under controlled conditions make it valuable for advanced scientific research and industrial formulation trials. Due to its toxic and environmentally hazardous nature, strict safety protocols are necessary during handling and disposal.
Lead Iodide Extra Pure
Lead Iodide Extra Pure is a bright yellow crystalline compound with the formula PbI₂, known for its striking color and high chemical purity, making it ideal for laboratory and research use. It is commonly used in materials science, especially in the fabrication of perovskite solar cells and semiconductors, due to its optical properties and ability to form thin films. In academic research, it plays a role in crystal growth experiments, and its distinct color change upon heating serves as a classic demonstration in chemistry education. Owing to its lead content, appropriate handling precautions and environmental safeguards are essential when working with this compound.
Lead Monoxide Extra Pure
Lead Monoxide Extra Pure, also known as litharge (PbO), is a fine yellow or reddish powder widely used in analytical chemistry and industrial processes. Its high purity makes it suitable for laboratory-grade reactions, especially in the manufacture of lead-based compounds, ceramics, glass, and batteries. In the ceramics and glass industries, it enhances the brilliance and stability of glazes and optical glass. In metallurgy, it is used as a fluxing agent during refining. Due to its toxicity and lead content, it requires strict safety handling procedures and controlled storage conditions to prevent contamination or exposure.
Oxalic Acid Extra Pure
Oxalic Acid Extra Pure is a high-purity, crystalline organic compound known for its strong reducing and chelating properties. Appearing as a white, odorless solid, it is highly soluble in water and widely utilized in both laboratory and industrial settings.
This Extra Pure grade ensures reliable performance in analytical chemistry, metal cleaning, rust removal, and rare earth element processing. In the laboratory, it is commonly used to precipitate calcium ions and to prepare standard solutions for titration. In industries, Oxalic Acid is valued for its effectiveness in bleaching wood, cleaning marble, and removing iron stains from surfaces and textiles. Due to its toxicity and corrosiveness, it must be handled with appropriate personal protective equipment and stored securely in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
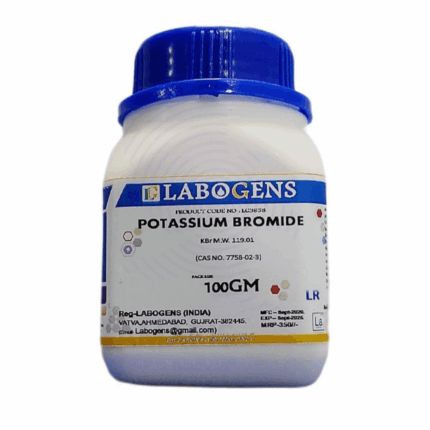
Potassium Bromide Extra Pure
Potassium Bromide Extra Pure is a highly refined, white crystalline compound with the chemical formula KBr, renowned for its exceptional purity and broad utility in scientific, medical, and industrial contexts. Its stable, non-hygroscopic nature and excellent solubility in water make it a reliable reagent in laboratory settings where consistency and accuracy are crucial.
This compound plays a central role in infrared (IR) spectroscopy, particularly for preparing transparent pellets that allow for the clear transmission of IR radiation, enabling the analysis of organic compounds. In the pharmaceutical sector, Potassium Bromide has a legacy use as an anticonvulsant and sedative, especially in veterinary practices for managing seizures. It's also employed in photographic processing in the formulation of light-sensitive silver bromide emulsions and in some chemical synthesis pathways requiring bromide ions.
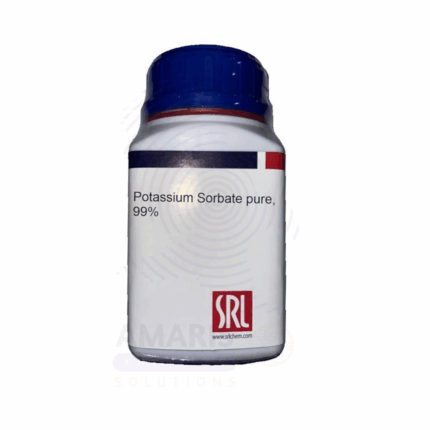
Potassium Sorbate Extra Pure
Potassium Sorbate Extra Pure is a high-grade preservative commonly used in laboratory research, food preservation, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Known for its effectiveness in inhibiting the growth of molds, yeasts, and fungi, it is a preferred choice for extending shelf life in various formulations. Its excellent solubility in water and low toxicity make it suitable for sensitive applications where purity is critical. In food and beverage testing or development, it plays a key role in microbial control without altering taste or color. The extra pure designation ensures minimal impurities, supporting accurate and consistent experimental or formulation outcomes.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders