“Agar Agar Powder” has been added to your cart. View cart
Cupric Chloride 250gm
$2,500.00 Original price was: $2,500.00.$2,300.00Current price is: $2,300.00.

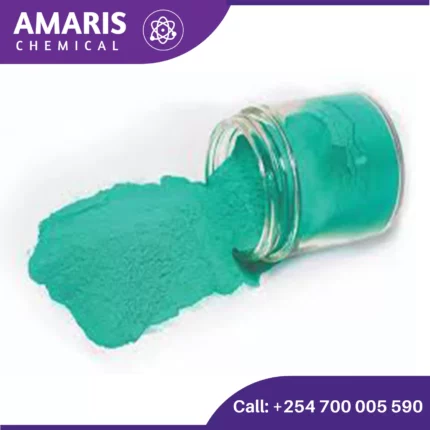
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
$2,500.00 Original price was: $2,500.00.$2,300.00Current price is: $2,300.00.
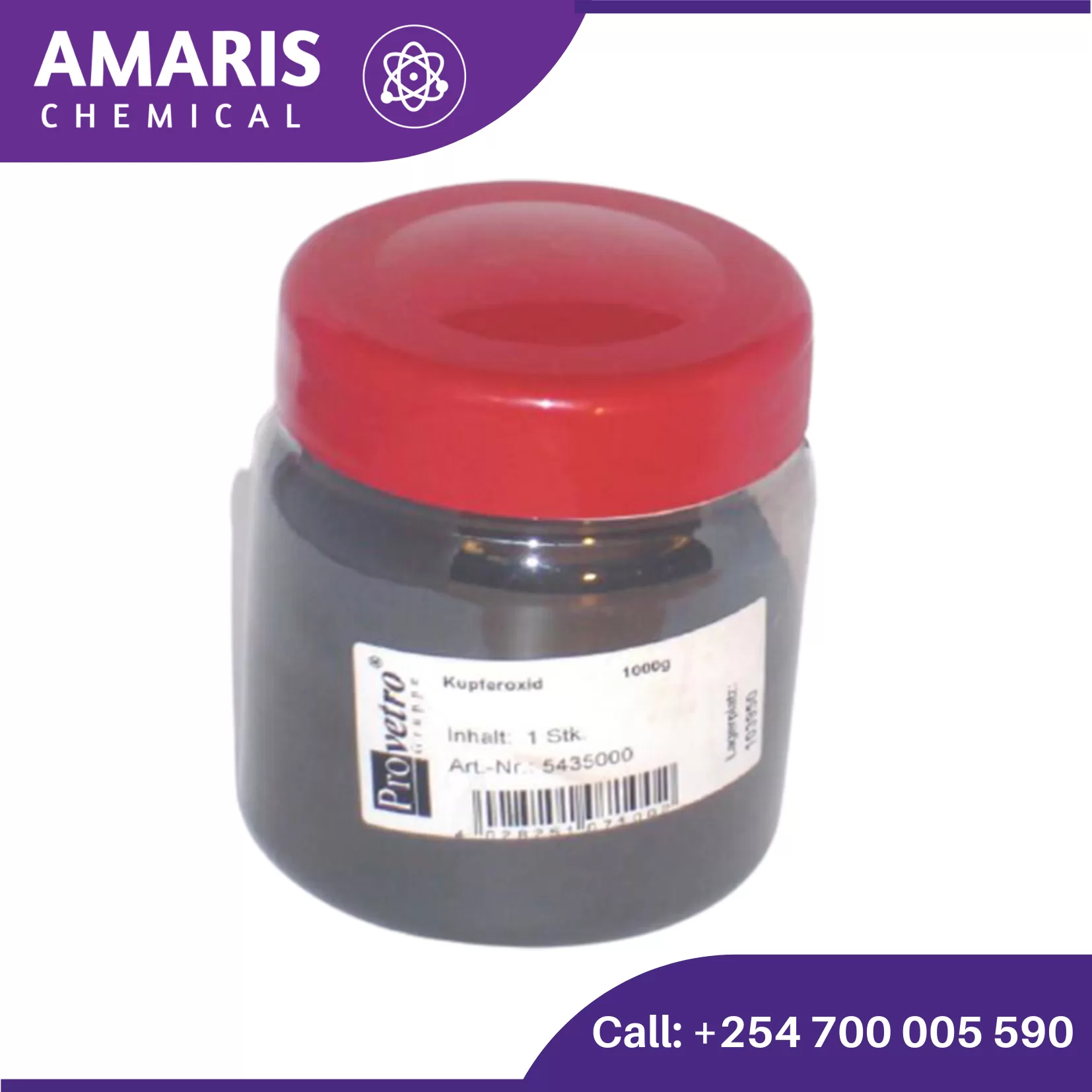
Cupric Oxide 100gm
$2,500.00 Original price was: $2,500.00.$2,300.00Current price is: $2,300.00.
Whatsapp Order
Cupric oxide, also known as copper(II) oxide, is a black solid with the chemical formula CuO. It is a significant compound of copper and has various applications in different fields. Here are some key points about cupric oxide:
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuO
- Appearance: Black or dark brown powder.
- Molecular Weight: 79.545 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1,326 °C (2,419 °F)
- Density: 6.315 g/cm³
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in acids.
Production:
Cupric oxide can be produced by several methods, including:
- Thermal Decomposition: Heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) carbonate, or copper(II) hydroxide in the absence of oxygen.
- Direct Oxidation: Heating metallic copper in the presence of oxygen.
SKU:
ACS45818CHEM0
Category: Analytical Reagents
Description
Table of Contents
ToggleUses of Cupric Oxide
1. Chemical Reactions and Experiments:
- Redox Reactions: Cupric oxide is often used in experiments to demonstrate redox reactions, where it acts as an oxidizing agent. For example, it can be reduced to copper metal by heating with hydrogen gas.
- Thermal Decomposition: Used to study thermal decomposition reactions. Cupric oxide can be obtained by heating copper carbonate or copper hydroxide.
2. Analytical Chemistry:
- Quantitative Analysis: Employed in gravimetric analysis to determine the concentration of copper in samples. Cupric oxide can be weighed before and after reactions to calculate the amount of copper present.
- Reagent in Tests: Acts as a reagent in various qualitative tests, such as detecting reducing sugars. Cupric oxide reacts with reducing sugars to form a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide (Cu2O).
3. Catalysis Studies:
- Catalyst Testing: Used as a catalyst in laboratory-scale reactions to study catalytic processes and reaction mechanisms. It can catalyze the oxidation of organic compounds and other reactions.
4. Synthesis of Compounds:
- Preparation of Other Copper Compounds: Cupric oxide is a precursor in the synthesis of other copper-containing compounds, such as copper sulfate (CuSO4) and copper acetate.
- Nanomaterials: Used in the synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles, which have applications in electronics, sensors, and antimicrobial agents.
5. Material Science:
- Ceramics and Glass: Studied for its properties in ceramics and glass production. Cupric oxide is used to impart black and other colors to glass and ceramic materials.
- Superconductors: Investigated for its role in high-temperature superconductors, such as those based on cuprate materials.
6. Electronics and Semiconductor Research:
- Thin Films: Used in the fabrication of thin films for electronic devices. Cupric oxide thin films are studied for their electrical properties and potential use in solar cells and sensors.
- Photovoltaics: Research into its application in photovoltaic cells, where it can be used as an absorber material due to its semiconducting properties.
7. Educational Demonstrations:
- Demonstration of Chemical Principles: Frequently used in educational laboratories to demonstrate basic chemical principles, such as oxidation-reduction reactions, stoichiometry, and properties of metal oxides.
- Lab Safety and Handling: Teaching proper laboratory techniques and safety protocols when handling chemicals.
8. Environmental Chemistry:
- Pollution Control Studies: Used in experiments related to pollution control and environmental remediation. For example, it can be used to study the removal of sulfur dioxide from industrial emissions through chemical reactions.
You may also like…
Ammonium Cupric Chloride
Ammonium cupric chloride is a chemical compound composed of copper(II) (Cu²⁺), ammonium (NH₄⁺), and chloride (Cl⁻) ions. It appears as a greenish or yellowish crystalline solid, depending on its hydration state and structure.
Majorly, ammonium cupric chloride is used in research and specialized industrial applications. It serves as a catalyst in organic synthesis, where copper(II) facilitates oxidation or coupling reactions. In electroplating, it can act as a copper ion source for depositing thin metallic layers.
Copper sulfate 25kg
Copper sulfate, also known as cupric sulfate or copper (II) sulfate, is a chemical compound composed of copper, sulfur, and oxygen. Its chemical formula is CuSO4, and it appears as blue crystals or a white powder. Copper sulfate is commonly used as a fungicide, herbicide, and pesticide, as well as a laboratory reagent and a catalyst in chemical reactions. It is also used in the manufacture of copper compounds, in electroplating, and in the preparation of pigments for paints and dyes.
Cupric Carbonate 500gm
Cupric carbonate, also known as copper(II) carbonate, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCO3. It exists in nature as several different minerals, including malachite and azurite, which are valued for their vibrant green and blue colors, respectively. Cupric carbonate can also be synthesized in the laboratory.
In its natural form, cupric carbonate is often used as a pigment in paints and dyes due to its striking color. It has also been used historically as a source of copper in various applications, including as a fungicide in agriculture.
Cupric carbonate is insoluble in water, but it can react with acids to form soluble copper salts. Additionally, it can decompose upon heating to release carbon dioxide and form copper(II) oxide.
It's important to handle cupric carbonate with care, as copper compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large quantities.
Cupric Chloride 250gm
Cupric chloride, also known as copper(II) chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCl₂. It appears as a yellowish-brown powder in its anhydrous form and turns into a blue-green crystalline solid when hydrated. This compound is highly soluble in water, forming a blue solution.
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuCl₂
- Molecular Weight: 134.45 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellowish-brown powder (anhydrous), blue-green crystals (hydrated)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
Cupric sulfate anhydrous refers to the form of copper(II) sulfate that does not contain water molecules in its crystal structure. It is used similarly to the hydrated form (cupric sulfate pentahydrate) in laboratory settings, often in analytical chemistry and as a source of copper ions in various reactions and processes.
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate
Related products
Acetic Acid 2.5litre
Acetic acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, sour taste and a distinctive vinegar-like odor. Acetic acid is an important industrial chemical used in the production of various products, including solvents, plastics, textiles, and food additives. It is also the main component of vinegar, which is commonly used as a condiment and preservative in cooking and food preparation.
Agar Agar Powder
Agar agar powder refers to the dehydrated and powdered form of agar agar, a natural gelling agent derived from seaweed. It is made by drying and grinding the agar agar gel, resulting in a fine powder with excellent gelling properties. Agar agar powder is commonly used in cooking, baking, and food preparation as a vegetarian and vegan substitute for gelatin. It is prized for its ability to create firm and stable gels at relatively low concentrations and temperatures. Agar agar powder is versatile and can be used in a variety of recipes, including desserts, confectioneries, jams, jellies, and savory dishes.
Aluminum Ammonium Sulphate
Aluminum ammonium sulfate, also known as ammonium alum or just alum, is a chemical compound with the formula (NH4)Al(SO4)2·12H2O. It's a white crystalline solid commonly used in water purification, leather tanning, and as a mordant in dyeing textiles.
In water purification, alum acts as a coagulant to remove impurities by causing suspended particles to clump together, making it easier for filtration to remove them. In leather tanning, it helps to stabilize the leather by tightening the collagen fibers. And in dyeing textiles, alum helps the dye adhere to the fabric.
However, it's important to note that excessive exposure to aluminum compounds like alum can be harmful, so it's typically used with caution and proper safety measures.
Aluminum Hydroxide 250gm
Aluminium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the formula Al(OH)3. It is an inorganic compound that is commonly used as an antacid to neutralize excess stomach acid, as well as a component in the manufacture of various products, such as ceramics, paper, and cosmetics. It is a white, powdery substance that is insoluble in water and has a low toxicity. When heated, it decomposes to produce aluminium oxide, or alumina, which is used in the production of aluminium metal.
Aluminum Sulphate 500gm
Aluminum sulfate, also known as alum, is a chemical compound with the formula Al2(SO4)3. It's commonly used in water treatment plants as a coagulant to clarify turbid or muddy water by causing suspended particles to clump together and settle out. In addition to water treatment, aluminum sulfate has various other industrial applications, such as in paper manufacturing, dyeing, and as a mordant in textile dyeing to help fix dyes to fabrics.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters