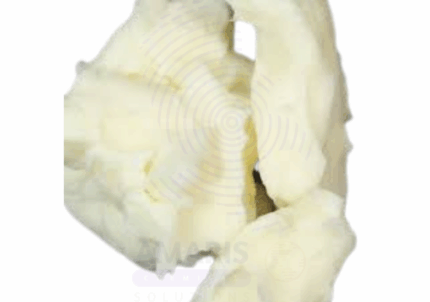
Fully Refined Paraffin Wax
$ 3.00 Original price was: $ 3.00.$ 2.86Current price is: $ 2.86.
Whatsapp Order
Fully Refined Paraffin Wax is a highly purified, odorless, white to pale yellow wax obtained from the refining of petroleum-derived crude paraffin wax. It consists primarily of saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) with chain lengths typically between C20 and C40. Due to its excellent chemical stability, non-toxicity, and versatility, Fully Refined Paraffin Wax is widely used across numerous industries including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food packaging, candle making, rubber processing, and electrical insulation. It exhibits a high melting point, low volatility, and good water resistance.
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle
Fully Refined Paraffin Wax
Primary Uses
- Candle and Fragrance Industry
- Used as a primary material for candle production due to its clean burning properties, opacity, and ability to hold fragrance oils and dyes effectively.
- Provides a smooth finish and excellent texture in molded and pillar candles.
- Acts as a carrier for fragrance oils and essential oils in scented candles.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care
- Used as a thickening agent, emollient, and moisture barrier in lip balms, creams, lotions, and ointments.
- Adds texture and stability to makeup products such as mascaras and lipsticks.
- Functions as a skin protectant by forming a water-repellent barrier.
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Employed as a base or excipient in ointments, suppositories, and topical formulations.
- Used in tablet coatings and as a release agent in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Food Industry
- Approved as a food additive (coating agent) for candies, fruits, and vegetables to prevent moisture loss and enhance appearance.
- Utilized as a release agent in baking and confectionery molds.
- Rubber and Tire Industry
- Used as an anti-tack agent and processing aid in rubber manufacturing to improve surface finish and prevent sticking during extrusion and molding.
- Packaging and Paper Industry
- Applied as a coating or impregnation material to improve moisture resistance, gloss, and flexibility of paper and cardboard.
- Used in waxed paper products and cartons for food packaging.
- Electrical and Industrial Applications
- Acts as an insulating material in electrical cables and components.
- Used as a lubricant and anti-corrosion agent for metal parts.
Secondary Uses
- Textile Industry
- Used as a finishing agent to improve fabric water repellency and handle.
- Agriculture
- Applied as a coating for seeds and fertilizers to control release and improve handling.
- Art and Sculpture
- Used in encaustic painting and modeling wax due to its workable texture and stability.
Additional information
| PACK SIZE |
50kg |
|---|
KEY PRODUCT FEATURES
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name: Fully Refined Paraffin Wax
- Common/Trade Name: Fully Refined Paraffin Wax
- CAS Number: 8002-74-2 (paraffin wax mixture)
- HS Code: 2712.90
- Molecular Formula: Mixture of hydrocarbons (primarily C20–C40 alkanes)
- Synonyms: Refined Paraffin Wax, White Paraffin Wax, Paraffin
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Solid wax, crystalline structure
- Color & Odor: White to pale yellow; odorless or faint hydrocarbon odor
- Melting Point: 54–58 °C (varies by grade)
- Density: Approximately 0.9 g/cm³
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; soluble in hydrocarbons, chloroform, benzene
- Stability: Chemically inert, stable under normal storage conditions
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Hazard Class (GHS): Not classified as hazardous; combustible solid
- Toxicity: Low toxicity; non-irritating and non-sensitizing to skin
- Exposure Limits: No established occupational exposure limits
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat and ignition sources
- Container Type: Sealed polyethylene bags, drums, or blocks in pallets
- Shelf Life: Indefinite if stored properly; protected from contamination and moisture
- Handling Precautions: Avoid dust formation and ignition sources; use standard PPE as needed
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Approved for food contact use under FDA regulations (21 CFR 172.884)
- Compliant with EU food additive regulations (E905)
- Registered under REACH and other international chemical inventories
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Biodegradability: Slowly biodegradable due to hydrocarbon nature
- Ecotoxicity: Low toxicity; non-toxic to aquatic life in typical use concentrations
- Bioaccumulation: Low potential for bioaccumulation
- Carcinogenicity/Mutagenicity: Not classified as carcinogenic or mutagenic
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Handling Precautions
- PPE Required: Protective gloves and safety goggles when handling in powdered or molten form
- Handling Guidelines: Use in well-ventilated areas; avoid inhalation of dust or fumes
- Storage Measures: Keep away from heat and sources of ignition; store in sealed containers
- Hygiene Practices: Wash hands thoroughly after handling; avoid ingestion and prolonged skin contact
First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if breathing difficulty occurs
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water; seek medical advice if irritation persists
- Eye Contact: Rinse immediately with plenty of water; seek medical attention if irritation develops
- Ingestion: Not expected to be harmful; rinse mouth and seek medical advice if large quantities ingested
Firefighting Measures
- Fire Hazards: Combustible solid; burns with a smoky flame
- Extinguishing Media: Water spray, foam, dry chemical, or carbon dioxide (CO₂)
- Special Precautions: Avoid inhalation of smoke and fumes; firefighters should wear self-contained breathing apparatus
- Decomposition Products: Carbon oxides and hydrocarbons
Related products
Almond Butter
Almond Butter is a smooth, creamy paste made by grinding roasted or raw almonds into a nutrient-rich spread. It retains the natural oils and flavor of almonds, offering a mild, nutty aroma and rich, buttery texture. Almond Butter is packed with monounsaturated fats, protein, vitamin E, magnesium, and antioxidants, making it a highly valued ingredient in the food, nutraceutical, and personal care industries.
In cosmetics and skincare, Almond Butter is prized for its emollient properties, making it a popular base for creams, balms, and body butters. It provides skin-softening, moisturizing, and barrier-protecting benefits. In the food and beverage industry, it is used as a spread, in smoothies, baked goods, energy bars, and dairy alternatives. It is also included in specialty pet food and wellness formulations.
Almond Wax
Almond Wax is a natural, plant-based wax derived from the hydrogenation of almond oil (Prunus amygdalus dulcis). It is a creamy to white, semi-solid wax with a mild, nutty scent and excellent emollient properties. Almond Wax is rich in fatty acids and has a smooth, soft texture, making it ideal for use in cosmetic, personal care, and candle formulations.
Due to its gentle consistency, skin-friendly profile, and moisturizing capabilities, Almond Wax is widely used in body butters, balms, lip care products, massage bars, and artisan soaps. It functions as a natural alternative to petroleum-based waxes and provides structure, viscosity, and glide to formulations. It also finds application in soft wax blends for natural candle products.
Ceto Stearyl Alcohol
Ceto Stearyl Alcohol 1618TA is a high-quality fatty alcohol blend primarily composed of cetyl (C16) and stearyl (C18) alcohols. It appears as a white, waxy solid or flakes with a mild fatty odor. This blend is widely used as an emollient, thickener, and co-emulsifier in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and industrial formulations. Ceto Stearyl Alcohol 1618TA offers excellent lubricity, thickening, and stabilizing properties, enhancing the texture, consistency, and moisturizing characteristics of creams, lotions, and hair care products. It serves as a skin conditioning agent and contributes to the structural integrity of emulsions.
Cetyl Alcohol Flakes
Cetyl Alcohol Flakes is a high-purity fatty alcohol derived mainly from natural sources such as palm oil and coconut oil. Presented as white to off-white waxy flakes, this product contains at least 98% pure cetyl alcohol, ensuring consistent performance and quality. It is valued for its excellent emollient, thickening, and emulsifying properties and is widely used in personal care, pharmaceutical, and industrial formulations. The flake form facilitates easy handling, melting, and dosing in manufacturing processes. Cetyl Alcohol 98% Flakes contributes to the texture, stability, and moisturizing properties of various formulations, providing a non-greasy, smooth finish.
Dimethicone Silicon Oil
Dimethicone Silicon Oil, also known as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or silicone oil, is a clear, odorless, and non-volatile silicone-based polymer widely used for its lubricating, anti-foaming, water-repellent, and skin-conditioning properties. It is a linear silicone polymer composed of repeating dimethylsiloxane units. Dimethicone exhibits excellent thermal stability, chemical inertness, and low surface tension, making it highly versatile in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, personal care, industrial, and food applications. It is available in various viscosities, from very low to high viscosity oils, enabling tailored formulations.
Illipe Butter
Illipe Butter is a natural, hard vegetable fat derived from the nuts of the Shorea stenoptera tree, native to the rainforests of Borneo. Known for its high melting point and rich moisturizing profile, Illipe Butter is prized in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food applications for its emollient qualities and stability. It closely resembles cocoa butter in composition and function, making it a sustainable alternative in formulations requiring consistency and long shelf life. The butter appears as a pale yellow to off-white solid with a mild, neutral aroma.
Olive Butter
Olive Butter is a natural, creamy, and rich emollient derived from cold-pressed olive oil combined with other natural butters (such as shea or cocoa butter) to create a luxurious skin-conditioning product. It is prized for its deep moisturizing, antioxidant-rich, and soothing properties, making it a popular ingredient in skincare, haircare, and cosmetic formulations. Olive Butter enhances skin elasticity, provides nourishment, and forms a protective barrier against environmental stressors.
Petroleum Jelly
Petroleum Jelly is a semi-solid mixture of hydrocarbons, originally derived from petroleum refining. It is odorless, colorless (or slightly yellow), and known for its moisturizing, protective, and lubricating properties. Widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications, Petroleum Jelly forms a barrier on the skin that locks in moisture and protects against irritants. The 175kg packaging is typical for bulk industrial or large-scale cosmetic use.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders