Test tube holder wire type
$ 4.50 Original price was: $ 4.50.$ 4.32Current price is: $ 4.32.

G Clamp
$ 13.60 Original price was: $ 13.60.$ 13.45Current price is: $ 13.45.
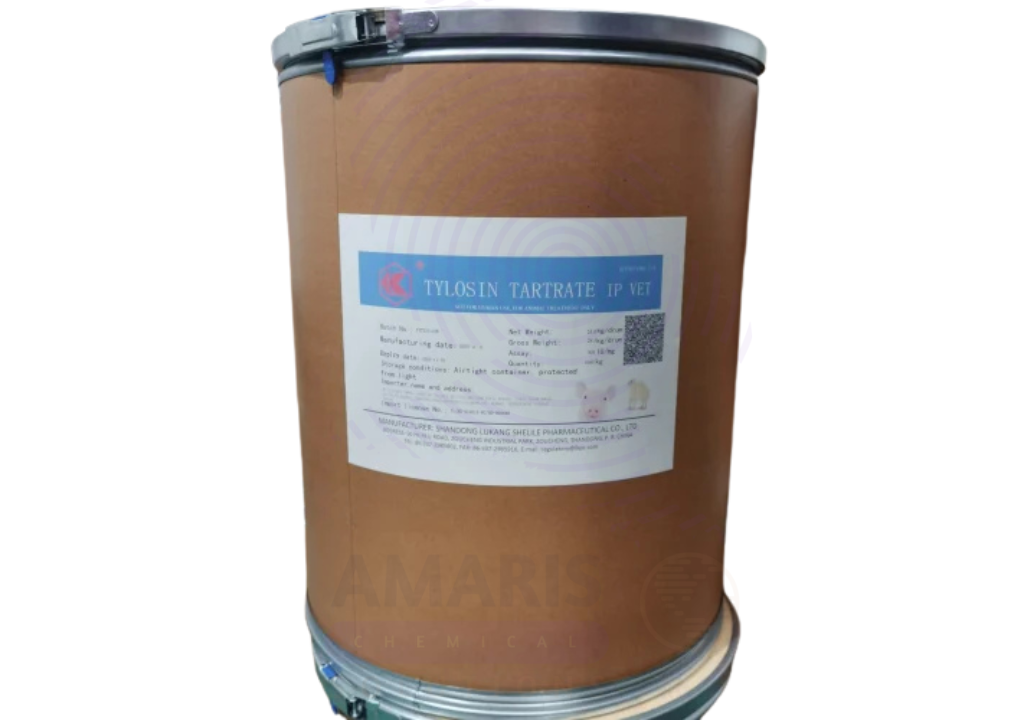
Tylosin Tartrate
Whatsapp Order
Tylosin Tartrate is a water-soluble macrolide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces fradiae, primarily used in veterinary medicine. It is the tartrate salt form of tylosin, enhancing its solubility and making it ideal for administration via drinking water or injectable solutions. Tylosin Tartrate is active against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria and some Gram-negative organisms, as well as Mycoplasma spp. It is particularly effective for treating respiratory, gastrointestinal, and reproductive infections in livestock and poultry.
Description
Table of Contents
Toggle
Tylosin Tartrate
Primary Uses
- Veterinary Medicine
- Poultry:
- Treatment and prevention of chronic respiratory disease (CRD) caused by Mycoplasma gallisepticum.
- Controls infectious sinusitis in turkeys and synovitis caused by Mycoplasma synoviae.
- Administered via drinking water or feed.
- Swine:
- Used for ileitis, swine dysentery, and enzootic pneumonia (caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Brachyspira hyodysenteriae).
- Often included in medicated feed or water.
- Cattle:
-
- Controls bovine respiratory disease complex (shipping fever) caused by Pasteurella, Mycoplasma, and Haemophilus species.
-
- Also used for foot rot and metritis.
- Sheep and Goats:
-
- Treats respiratory infections and mycoplasma-related arthritis.
- Companion Animals (off-label in some countries):
-
- Sometimes used to treat chronic colitis or diarrhea in dogs and cats under veterinary supervision.
- Aquaculture (where permitted)
- Used against Mycoplasma-like organisms and secondary bacterial infections.
Secondary Uses
- Prophylactic Use in Herds/Fluctuations
- Administered during high-stress periods (transport, weaning, vaccination) to prevent outbreaks.
- Growth Promotion (where legal)
- Historically used in low doses as a feed additive to promote growth and improve feed efficiency, though now restricted in many countries.
- Research & Microbiology
- Used as a selective antibiotic in culture media for isolating Mycoplasma
- Applied in antimicrobial resistance studies.
KEY PRODUCT FEATURES
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name (IUPAC): Tylosin hydrogen tartrate
- Common/Trade Name: Tylosin Tartrate
- CAS Number: 1405-69-0
- HS Code: 2941.90.00
- Synonyms: Tylosin hydrogen tartrate, Macrolide antibiotic tartrate salt
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Powder
- Color & Odor: Pale yellow to yellow; mild characteristic odor
- Solubility: Freely soluble in water
- Molecular Formula: C46H77NO17 · C4H6O6
- Molecular Weight: ~1009.2 g/mol
- pH (1% solution): 5.0–7.5
- Loss on Drying: ≤ 5.0%
- Assay (Potency): ≥ 800 µg/mg (potency based on tylosin activity)
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- GHS Classification:
- May cause respiratory or skin sensitization
- Harmful if swallowed or inhaled in large quantities
- Environmental hazard (to aquatic life with long-term effects)
- Toxicity: Low toxicity to treated animals when used as directed
- Irritation: May cause skin and eye irritation in handlers
- Occupational Hazards: Allergic reactions (especially in individuals sensitive to macrolides)
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions: Store below 25 °C in a dry place; protect from light and moisture
- Container Type: Fiber drums or HDPE containers with inner liner
- Shelf Life: 24–36 months under proper storage
- Handling Precautions: Avoid inhalation of dust; wear protective gloves, eyewear, and mask
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Approved for veterinary use by FDA, EMA, WHO, and OIE (in various countries)
- Not intended for human use
- Must comply with maximum residue limits (MRLs) in food-producing animals
- Complies with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for veterinary pharmaceuticals
- Use in accordance with Veterinary Prescription Regulations (region-specific)
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Biodegradability: Biodegradable under normal environmental conditions
- Ecotoxicity: Potential impact on soil and aquatic microbiota if improperly disposed
- Bioaccumulation: Low potential
- Resistance Risk: May contribute to antimicrobial resistance if overused or misused
SAFETY HANDLING PRECAUTIONS
Safety Handling Precautions
- PPE Required: Gloves, dust mask, safety goggles
- Handling Guidelines: Avoid generation of dust; use in well-ventilated areas
- Storage Measures: Keep container tightly closed and dry
First Aid Measures
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air; seek medical attention if symptoms persist
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water
- Eye Contact: Rinse with plenty of water; get medical help if irritation continues
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth; consult a veterinarian or poison control if large quantities are consumed
Firefighting Measures
- Fire Hazards: Not highly flammable but combustible in powder form
- Extinguishing Media: Use water spray, foam, dry chemical, or CO₂
- Hazardous Combustion Products: Carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides
Related products
Acid Oil Soya
Acid Oil Soya is a byproduct derived from the refining of soybean oil. It is a dark-colored, free fatty acid-rich liquid containing mainly oleic and linoleic acids. Acid Oil Soya is commonly used in industrial applications such as soap making, animal feed, and as a raw material in the production of biodiesel, lubricants, and other chemicals.
Gentamycin Sulphate
Gentamycin Sulphate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Micromonospora purpurea and Micromonospora griseorubida. It appears as a white or off-white crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, with a characteristic aminoglycoside odor. Gentamycin Sulphate is widely used in human and veterinary medicine for its broad-spectrum bactericidal activity against aerobic Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis through binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, leading to bacterial cell death. Due to its effectiveness against severe infections and multi-drug resistant strains, it is an essential antibiotic in clinical settings.
L-Lysine HCL Feed Grade
L-Lysine HCL Feed Grade is a highly pure form of the essential amino acid lysine combined with hydrochloric acid to improve its stability and solubility. It appears as a white crystalline powder and is widely used as a dietary supplement in animal feed to enhance growth, improve feed efficiency, and balance amino acid profiles. L-Lysine HCL is critical in poultry, swine, and aquaculture nutrition, helping to meet animals’ lysine requirements for protein synthesis and overall health.
Magnesium Sulphate (Epsom Salt)
Magnesium Sulphate Epsom Salt, commonly known as Epsom Salt, is an inorganic salt composed of magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen with the formula MgSO₄. It typically appears as colorless or white crystalline granules and is highly soluble in water. In its heptahydrate form (MgSO₄·7H₂O), it is widely used in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Epsom Salt is valued for its muscle relaxant, laxative, and magnesium supplementation properties, as well as for its role in improving soil fertility and plant growth.
Mineral lick ( Rock Salt)
Mineral Lick, commonly known as Rock Salt, is a naturally occurring mineral primarily composed of sodium chloride. It is harvested from salt deposits and widely used as a mineral supplement for livestock and wildlife, providing essential nutrients. Mineral Lick enhances animal health by promoting hydration, digestion, and mineral balance. It also has applications in industry, agriculture, and food processing.
Sulphamethoxazole BP
Sulphamethoxazole BP is a synthetic sulfonamide antibiotic widely used in human and veterinary medicine for treating bacterial infections. It acts by inhibiting bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, thereby preventing bacterial growth. It is commonly combined with trimethoprim for synergistic effects against a broad spectrum of bacteria. The British Pharmacopoeia (BP) grade guarantees pharmaceutical purity and quality, making it suitable for formulation into tablets, suspensions, and other dosage forms.
Toxin Binder Premix
Toxin Binder Premix is a specialized feed additive formulated to adsorb and neutralize a broad range of mycotoxins and other harmful toxins present in animal feed. It enhances animal health by preventing the absorption of toxins in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby improving feed efficiency and productivity. The premix typically contains activated clays, yeast cell wall components, and other natural or synthetic adsorbents designed for use in livestock, poultry, and aquaculture feeds. This product supports animal growth, immune function, and overall well-being by mitigating the adverse effects of feed contamination.
Zinc Bacitracin Premix Feed Grade
Zinc Bacitracin Premix Feed Grade is a veterinary-grade antibiotic premix formulated with 15% active zinc bacitracin, an antimicrobial peptide produced by Bacillus subtilis. It is commonly incorporated into animal feed to promote growth, prevent and control bacterial infections, and improve feed efficiency in livestock and poultry. This product is heat stable, easy to blend, and designed for uniform distribution in feed.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders