“Tetrasodium EDTA” has been added to your cart. View cart





Aluminium Sulphate powder (Alum)
$6,000.00 Original price was: $6,000.00.$5,000.00Current price is: $5,000.00.

Butyl Glycol
$87,000.00 Original price was: $87,000.00.$86,000.00Current price is: $86,000.00.
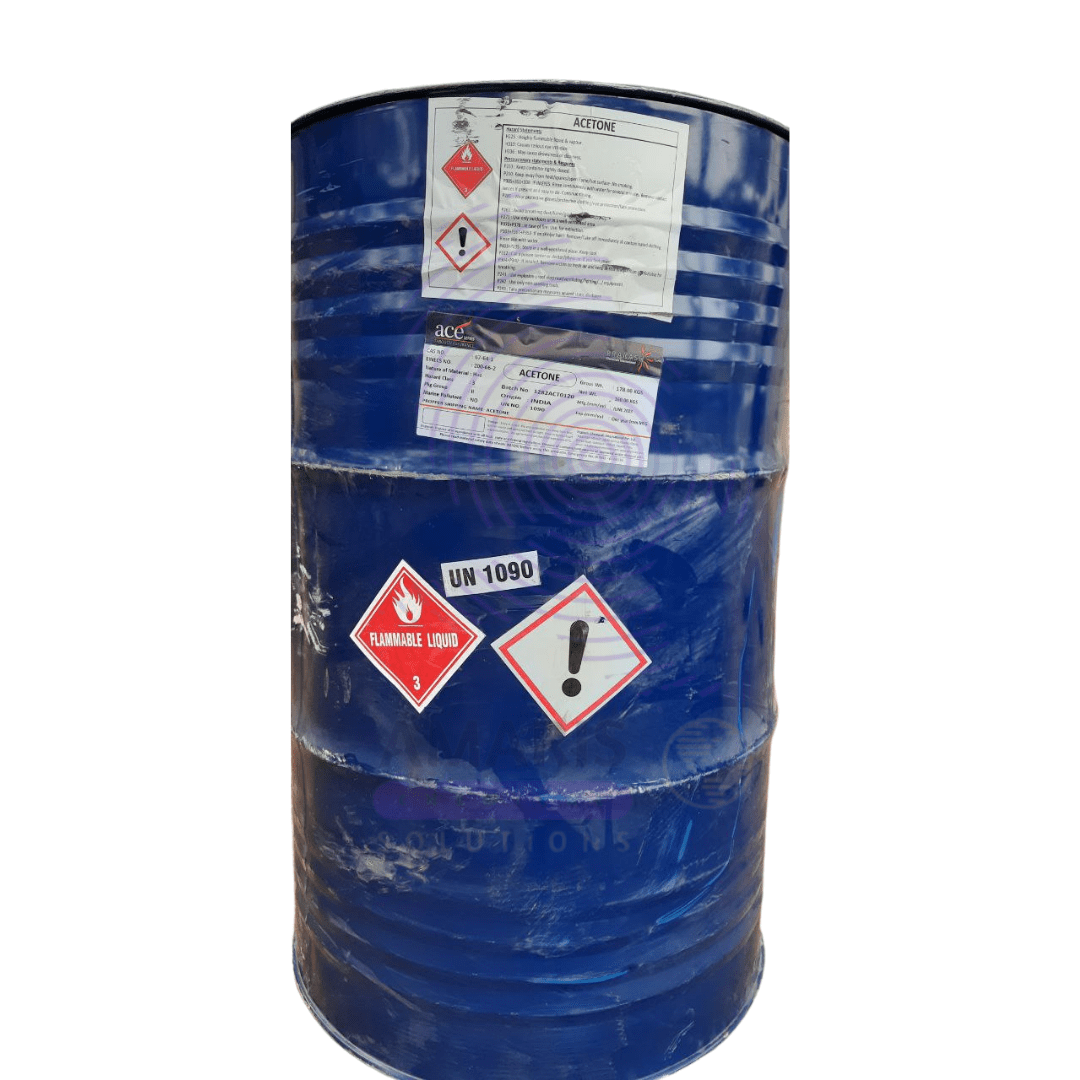
Acetone
$56,000.00 Original price was: $56,000.00.$52,668.00Current price is: $52,668.00.
Whatsapp Order
Acetone
Acetone is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. It is a common organic solvent that is widely used in the production of plastics, fibers, drugs, and other chemical compounds. Acetone is also commonly used as a cleaning agent and a nail polish remover. Chemically, it is the simplest ketone and is represented by the formula CH3COCH3.
SKU:
ACS11193CHEM0
Categories: Excipients, Analytical Reagents, Electronic Chemicals, Solvents (paint), Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Tags: acetone, nail polish remover, solvent
Description
Acetone Uses
It is a colourless, volatile, flammable organic solvent which occurs naturally in trees, vehicle exhaust, plants and as a breakdown product of animal fat for metabolism. It has a sweetish (fruity) odour. The molecular formula for the compound is CH3-CO-CH3 or CH3COCH3 or C3H6O. Other names that identify the chemical are 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone, and beta ketopropane. It dissolves in water, is toxic in high doses, is the simplest ketone. Its vapours are denser than air and it has a flash point of 0 degrees Fahrenheit. It has a boiling point of 133 degrees Fahrenheit at 760mm Hg (NTP, 1992) and a melting point of 137 degrees Fahrenheit (NTP, 1992). Its solubility is greater than or equal to 100mg/ml at 72 degrees Fahrenheit (NTP, 1992).
Some of the areas of application of Acetone include:
1. It is applied in indirect refrigeration as a brine for low-temperature heat transfer.
2. It is used in cleaning and drying precision parts.
3. It is applied as a corrosion inhibitor in hydraulic fracturing.
4. It is applied as a solvent and as a reaction intermediate for the production of other compounds that are mainly used as solvents.
5. It is applied in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics as a solvent.
6. It is used to store acetylene safely in gas cylinders.
7. It is used in spinning cellulose acetate fibres.
8. It is used in the manufacture of smokeless powder.
9. It is applied in boat manufacturing as a washing solvent in fibreglass.
10. It is applied in the electronic industry as a cleaning solvent.
11. It is applied as a solvent in the degumming of silk and the degreasing of wool.
12. It is applied in the formulations of surface coatings and related thinners and washes.
13. It is applied as a solvent for printing inks.
14. It is used as a varnish (nail polish) remover.
15. It is applied in the purification of paraffin.
16. It is used to harden and dehydrate tissues for extraction of various principles from plant and animal substances.
17. In cleaning, it is used to dissolve hazardous chemical spills.
18. It is used in rubber cement.
19. It is applied as a solvent in plastics and other synthetic fibres.
Additional information
| APPEARANCE |
Watery/Thin – Low viscosity e.g., ethanol |
|---|---|
| COUNTRIES OF ORIGIN |
CHINA ,TAWAIN |
| CONCENTRATION |
99.9% |
| AVAILABLE PACK SIZE |
160kg ( Metal or Plastic drum) |
KEY ATTRIBUTES
1. Basic Identification Attributes
- Chemical Name: Propan-2-one (IUPAC), Acetone (common)
- CAS Number: 67-64-1
- HS Code: 2914.11.00
- Molecular Formula: C₃H₆O
- Synonyms: Dimethyl ketone, 2-propanone, β-ketopropane, propanone
2. Physical & Chemical Properties
- Physical State: Colorless, volatile liquid
- Color & Odor: Colorless; sweet, pungent odor
- Boiling Point: 56.05°C
- Melting Point: -94.7°C
- Density: 0.791 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Solubility:
- Miscible with water, ethanol, ether, chloroform
- Soluble in most organic solvents
- pH Level: ~7 (neutral)
- Vapor Pressure: 233 mmHg at 25°C
- Flash Point: -20°C (closed cup)
- Autoignition Temperature: 465°C
- Viscosity: 0.32 cP at 25°C
- Refractive Index: 1.3588 at 20°C
3. Safety & Hazard Attributes
- Hazard Class:
- Flammable Liquid Category 2
- Eye Irritant Category 2B
- STOT Single Exposure Category 3
- NFPA Ratings: Health-1, Flammability-3, Reactivity-0
- Exposure Limits:
- OSHA PEL: 1000 ppm (2400 mg/m³) TWA
- ACGIH TLV: 500 ppm (1180 mg/m³) TWA
- NIOSH REL: 250 ppm (590 mg/m³) TWA
- Reactivity:
- Forms explosive peroxides with strong oxidizers
- Reacts violently with chlorosulfonic acid, nitric acid
- Incompatible with strong acids, bases, oxidizing agents
4. Storage & Handling Attributes
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in cool, well-ventilated area away from heat/sparks
- Keep containers tightly closed
- Temperature: <30°C recommended
- Incompatible Materials:
- Strong oxidizers, acids, bases, reducing agents
- Chloroform, bromine, amines
- Container Type:
- Steel, aluminum, or HDPE containers
- Glass for laboratory quantities
- Shelf Life: Indefinite if properly stored
- Special Handling:
- Ground all equipment to prevent static sparks
- Use explosion-proof electrical equipment
- PPE: Chemical goggles, gloves (nitrile), vapor respirator if needed
5. Regulatory & Compliance Attributes
- Regulatory Status:
- EPA: Listed under TSCA
- REACH: Registered
- OSHA: Regulated under 29 CFR 1910.1000
- DOT: UN 1090, Class 3, PG II
- Hazard Symbols:
- GHS Pictograms: Flame, Exclamation Mark
- Transportation Restrictions:
- Proper shipping name: Acetone
- Hazard class: 3 (Flammable liquid)
- Packing group: II
- Waste Disposal:
- RCRA hazardous waste (D001 for ignitability)
- Incineration is preferred method
6. Environmental & Health Impact
- Ecotoxicity:
- LC50 (fish): 4,400-13,100 mg/L (96h)
- EC50 (daphnia): 6,800 mg/L (48h)
- Persistence:
- Readily biodegradable (BOD5: 60-70% of ThOD)
- Atmospheric half-life: ~22 days
- Carcinogenicity:
- IARC: Not classified
- NTP: Not listed
- ACGIH: A4 (not classifiable as human carcinogen)
- Biodegradability:
- BOD5/COD ratio: 0.5-0.7 (readily biodegradable)
- Complete degradation in 5-30 days
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
General Handling:
- Use in well-ventilated areas(flammable vapors can accumulate)
- Avoid open flames, sparks, and heat sources(extremely flammable liquid)
- Ground containers during transfer to prevent static electricity sparks
- Use non-sparking tools in acetone environments
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves:Nitrile or neoprene (latex offers poor protection)
- Eye Protection:Chemical splash goggles
- Respiratory Protection:Organic vapor respirator if ventilation is inadequate
- Clothing:Flame-resistant lab coat/apron
Storage:
- Store in approved flammable liquid cabinets
- Keep containers tightly closed when not in use
- Store away from oxidizers, acids, and bases
- Maximum storage temperature: 25°C (77°F)
Spill Management:
- Small spills: Absorb with inert absorbents(vermiculite, sand)
- Large spills: Contain with spill berms, prevent entry into drains
- Evacuate area if vapors exceed exposure limits
Skin Contact:
- Symptoms:Dryness, irritation, possible dermatitis
- Action:
- Remove contaminated clothing
- Wash with soap and waterfor 15 minutes
- Apply moisturizer if irritation persists
Eye Contact:
- Symptoms:Redness, pain, temporary corneal damage
- Action:
- Immediately flush with lukewarm water for 20 minutes
- Hold eyelids open during flushing
- Seek medical attention if irritation continues
Inhalation:
- Symptoms:Dizziness, headache, nausea, CNS depression
- Action:
- Move to fresh air immediately
- Administer oxygen if breathing is difficult
- Seek medical help for prolonged exposure
Ingestion:
- Symptoms:Nausea, vomiting, drowsiness
- Action:
- Do NOT induce vomiting
- Rinse mouth with water
- Give 1-2 glasses of water to drink
- Seek immediate medical attention
Fire Hazards:
- Extremely flammable liquid and vapor
- Flash point: -20°C (-4°F)
- Vapor/air mixtures are explosive (2.5-12.8% by volume)
- Vapors are heavier than air - may travel to ignition sources
Extinguishing Methods:
- Recommended:
- Alcohol-resistant foam
- CO₂ extinguishers
- Dry chemical powder (Class B)
- Not Recommended:
- Water jets (ineffective, may spread fire)
- Water spray (only for cooling exposed containers)
Firefighting Procedures:
- Wear self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA)and full protective gear
- Stop leak if safe to do so
- Cool nearby containers with water sprayto prevent explosion
- Allow controlled burning if leak cannot be stopped
- Evacuate area if fire becomes uncontrollable
Emergency & Regulatory Information
- NFPA Rating:Health 1, Flammability 3, Instability 0
- GHS Hazard Statements:
- H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness
- OSHA PEL:1000 ppm (TWA)
- Emergency Contacts:Poison Control, local fire department
You may also like…
Acetone Extra Pure
Acetone Extra Pure
Acetone is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet, fruity odor. It is a common organic solvent that is widely used in the production of plastics, fibers, drugs, and other chemical compounds. Acetone is also commonly used as a cleaning agent and a nail polish remover. Chemically, it is the simplest ketone and is represented by the formula CH3COCH3.
Related products
Activated Carbon
Activated carbon, also known as activated charcoal, is a highly porous material that is produced by treating carbon-rich organic materials, such as wood, coconut shells, or peat, with heat and chemicals to create a network of pores and a large surface area. This high surface area and porosity make activated carbon an excellent adsorbent for a wide range of substances, including organic molecules, gases, and liquids. It is widely used in various applications, such as water treatment, air purification, food and beverage processing, and medical treatments.
Adipic Acid
$0.01
Adipic acid, chemically known as hexanedioic acid (C₆H₁₀O₄), is a key industrial organic compound recognized for its role in polymer production. Primarily, it serves as a crucial precursor in the manufacture of nylon 6,6, where it reacts with hexamethylenediamine to form this durable synthetic polymer, widely used in textiles, automotive components, and industrial plastics. Beyond nylon, adipic acid is integral to producing polyurethane foams, found in mattresses, insulation, and car seats, due to its ability to enhance material flexibility and strength. It also finds applications as a food additive (E355), where it acts as an acidity regulator in gelatin desserts, beverages, and baked goods. Additionally, adipic acid derivatives are used in plasticizers for PVC products, synthetic lubricants, adhesives, and even cosmetics. While traditionally derived from petroleum-based processes, growing interest in sustainable alternatives has spurred research into bio-based production methods using renewable resources. Overall, adipic acid’s versatility makes it indispensable across multiple industries, from manufacturing to food technology
Butyl Acetate
Butyl Acetate (n-Butyl Acetate, C₆H₁₂O₂) is a high-performance industrial solvent widely recognized for its excellent solvency, moderate evaporation rate, and pleasant fruity aroma. This clear, flammable liquid is a preferred choice in paints, coatings, and printing inks due to its ability to dissolve resins and polymers effectively while ensuring smooth application and quick drying. Its versatility extends to adhesives, where it enhances bonding strength and drying speed, as well as to the electronics industry, where it serves as a reliable cleaning agent for circuit boards and precision components. Butyl acetate is also valued in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations as a flavoring agent and extraction solvent. With its low toxicity and balanced properties, it offers a safer alternative to more aggressive solvents, making it ideal for industrial and commercial applications where both performance and safety are paramount. Proper handling and ventilation are recommended to ensure safe usage.
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CaCl2. It is a salt composed of calcium and chlorine ions and is highly soluble in water. Calcium chloride is commonly used as a desiccant, de-icer, and in various industrial processes. It is also used in food and beverage applications as a firming agent, and in medicine as a source of calcium for people with calcium deficiencies.
Cetyl alcohol
Cetyl alcohol is a fatty alcohol with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)15OH. It is a waxy substance that is used in a variety of industries, including cosmetics, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals. Cetyl alcohol is commonly derived from vegetable oils such as coconut or palm oil, and is often used as an emulsifier, thickener, or lubricant in formulations such as lotions, creams, and ointments. It is also sometimes used as a surfactant, meaning it helps to dissolve other substances and improve their absorption.
Citric Acid Anhydrous
Citric Acid Anhydrous is a weak organic acid that occurs naturally in citrus fruits such as lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruits. It is a tricarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C6H8O7 and is commonly used as a food additive, preservative, and flavoring agent. Citric acid is also used in the pharmaceutical industry, as a chelating agent in cleaning and personal care products, and in the production of cosmetics and detergents. It is a white crystalline powder with a sour taste and is soluble in water.
Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate is a chemical compound with the formula CaHPO4. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement for its high calcium content, as well as a food additive and a pharmaceutical excipient. Dicalcium phosphate can be produced by reacting calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide with phosphoric acid. It exists in various forms, including anhydrous and dihydrate, and is commonly used in the production of fertilizers, animal feed, and dental products.
Glycerin Food Grade
Glycerin Food Grade, also known as glycerol, is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. It is a type of alcohol with three hydroxyl (OH) groups, and is commonly used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, and personal care products. Glycerin has numerous applications, including as a solvent, humectant, emollient, and lubricant, among others. It can be derived from both plant and animal sources, and is also produced as a byproduct of soap and biodiesel manufacturing.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS
LABORATORY EQUIPMENT & APPARATUS Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters