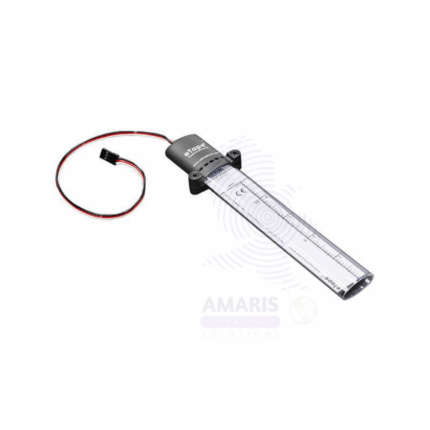
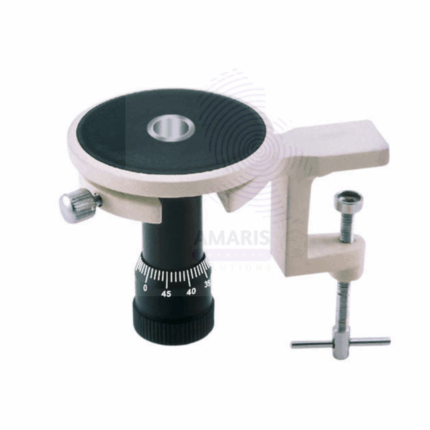
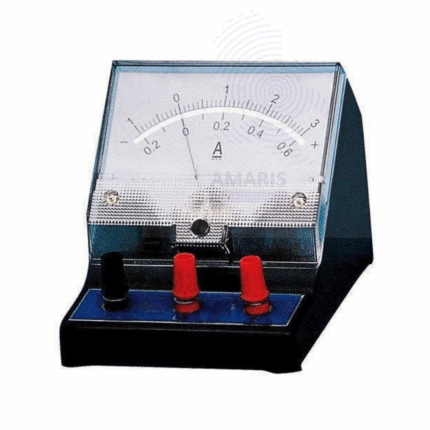
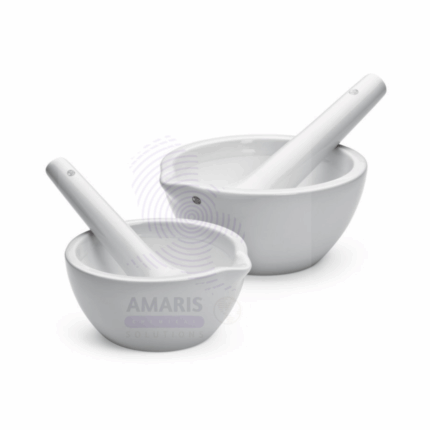
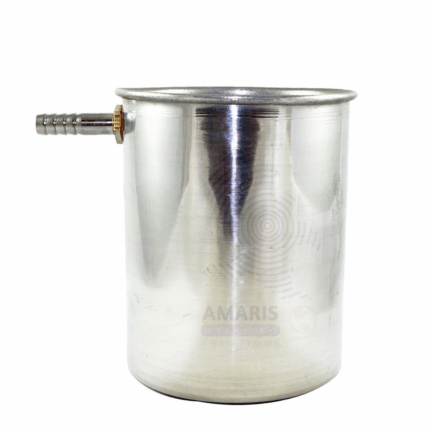
Lab liquid level
The Lab Liquid Level is a precision measuring instrument used to detect and indicate the level of liquids in laboratory containers, tanks, or systems. Designed for accuracy and ease of use, it helps scientists and technicians monitor fluid levels during experiments, processing, or storage. Typically constructed from chemically resistant materials, Lab Liquid Levels are compatible with various liquids including corrosive and volatile substances. They are essential tools for maintaining controlled conditions in chemical, pharmaceutical, and research laboratories.
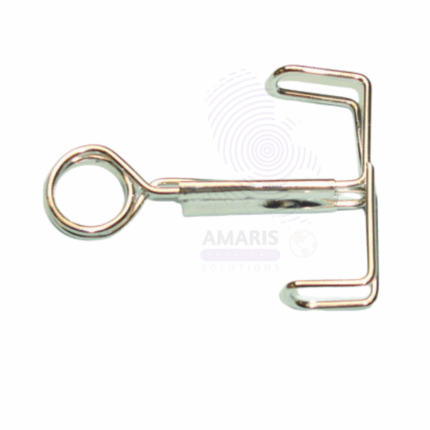
Lab pinch clip
Lab Pinch Clips are small, spring-loaded clamps designed to securely hold flexible tubing, glassware joints, or small apparatus components in laboratory setups. Made from durable materials such as plastic or metal, these clips provide quick, reliable closure to prevent leaks, fluid flow, or contamination during experiments. They are widely used in chemistry, biology, and medical labs for tubing control, sealing connections, and ensuring the integrity of fluid systems. Their compact size and ease of use make them essential accessories for efficient laboratory workflow.
Laboratory beaker
Product Description
Laboratory Beakers are versatile cylindrical glass or plastic containers used widely in scientific laboratories for mixing, stirring, heating, and measuring liquids. Made typically from borosilicate glass or durable plastic, they offer excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. Their wide mouths and spouted rims allow easy pouring and handling during experiments. Laboratory Beakers are fundamental lab apparatus for qualitative and quantitative analysis in chemistry, biology, and industrial research.
Laboratory beaker borosil
Laboratory Beaker Borosil is a high-quality, durable beaker made from borosilicate glass, renowned for its excellent chemical and thermal resistance. Designed for versatile use in laboratories, this beaker withstands rapid temperature changes and exposure to corrosive chemicals, making it ideal for heating, mixing, and chemical reactions. Its clear, transparent body allows easy observation of contents, and the spouted rim facilitates safe pouring. It is a fundamental tool in chemical, pharmaceutical, and research laboratories.
laboratory electric water bath
The Laboratory Electric Water Bath is a precision temperature-controlled apparatus used in laboratories to incubate samples in water at consistent temperatures. It features an electrically heated water reservoir with adjustable temperature settings, digital or analog controls, and safety features such as over-temperature protection. This device is essential for applications requiring uniform heating, such as incubation, warming reagents, melting solids, or enzymatic reactions. Constructed with corrosion-resistant materials and insulated housing, it provides stable temperature conditions for a wide range of laboratory procedures in chemical, biological, pharmaceutical, and industrial settings.
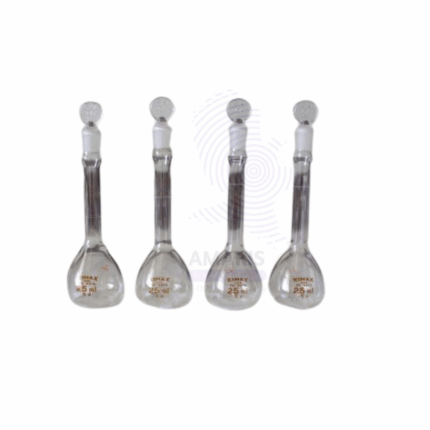
laboratory glass Volumetric flask with glass stopper
Laboratory Glass Volumetric Flask with Glass Stopper is a precision laboratory container used for preparing and measuring exact volumes of liquid solutions. Made from chemically resistant borosilicate glass, it features a flat bottom and a narrow neck with a precise calibration mark. The glass stopper ensures an airtight seal, preventing evaporation or contamination. Essential in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical labs, and research, this flask allows accurate dilution, standard solution preparation, and volumetric analysis with high reliability and chemical stability.
Laboratory stop watch
The Laboratory Stop Watch is a precision timing device used in laboratories to accurately measure time intervals during experiments and processes. Designed for reliability and ease of use, it features start, stop, and reset functions, often with digital or analog displays. This stopwatch is essential for kinetic studies, reaction timing, process control, and any experiment requiring precise time measurement. Durable and portable, it is suitable for various scientific, educational, and industrial laboratory applications.
Laboratory wheel and axel
The Laboratory Wheel and Axle is a mechanical apparatus used in physics and engineering laboratories to demonstrate principles of rotational motion, mechanical advantage, and torque. It consists of a wheel attached to a central axle, allowing students and researchers to explore fundamental mechanics concepts. Constructed from durable materials, it is designed for educational demonstrations, experimental setups, and mechanical testing.
Lens cleaning tissue
Lens Cleaning Tissue is a soft, lint-free paper designed specifically for cleaning optical lenses, microscope eyepieces, camera lenses, and other delicate glass or plastic surfaces. It effectively removes dust, fingerprints, oils, and smudges without scratching or leaving residue. Widely used in laboratories, photography, and electronics, lens cleaning tissue helps maintain clarity and prolong the lifespan of sensitive optical components.
Leslie cubes
Leslie Cubes are metal cubes used in physics laboratories to demonstrate the principles of thermal radiation and emissivity. Each face of the cube has a different surface finish—such as polished, blackened, or white—which affects its heat radiation properties. When heated, Leslie Cubes allow students and researchers to observe how surface texture and color influence heat emission, making them essential for studies in thermodynamics and heat transfer.
Linear expansion apparatus
Linear Expansion Apparatus is a laboratory device used to measure the expansion of materials when heated. It helps in studying the thermal expansion properties of solids by precisely quantifying the change in length as temperature varies. Typically made from durable metals and fitted with precise measurement scales or sensors, this apparatus is essential in physics and materials science labs for investigating thermal behavior of materials.
Litmus Paper Blue
Litmus Paper Blue is a pH indicator paper used to detect acidic substances. It is impregnated with litmus dye extracted from lichens, which changes color when exposed to acidic or basic environments. Blue litmus paper turns red under acidic conditions (pH < 4.5) and remains blue in neutral or alkaline solutions. It is widely used in laboratories, education, environmental testing, and industrial processes for quick and easy pH testing.
Litmus paper red
Litmus paper red is a specialized pH indicator paper impregnated with red litmus dye derived from natural lichens. It serves as a quick and reliable qualitative tool for detecting alkaline (basic) conditions in various liquids and substances. Upon contact with an alkaline solution, the red paper undergoes a distinct color change to blue, signaling a pH above approximately 8.3. In neutral or acidic solutions, the paper retains its red color. This simple yet essential laboratory reagent is widely used in chemistry, biology, environmental science, clinical diagnostics, food industry, and educational settings for rapid acidity and alkalinity testing without the need for sophisticated instrumentation.
Red litmus paper is highly valued for its ease of use, portability, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for field testing, classroom demonstrations, and routine lab work. It provides immediate visual feedback, which is crucial for quick decision-making during experiments, quality control processes, and environmental monitoring. Packaged typically in convenient strips or sheets within moisture-proof packets, the paper is protected from contamination and degradation, ensuring long shelf life and consistent performance.
Magnet electrode u shape
The Magnet Electrode U Shape is a specialized laboratory electrode designed in a U-shaped configuration for precise measurements involving magnetic fields or electrochemical applications. Typically fabricated from corrosion-resistant metals or alloys, these electrodes are integrated into setups requiring stable electrical contact and magnetic influence, such as in electrolysis, magnetic field studies, and sensor calibration. The U-shape design facilitates easy mounting and positioning within experimental apparatuses, allowing efficient contact with solutions or materials. They are widely used in research, industrial testing, and educational laboratories for experiments involving electromagnetism and electrochemistry.
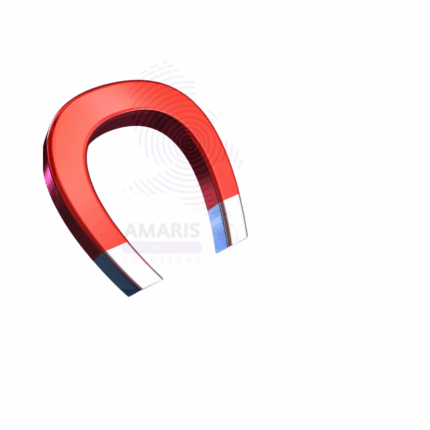
Magnet horse shoe
Product Description
The Magnet Horse Shoe is a classic U-shaped permanent magnet commonly used in laboratories for experiments involving magnetic fields and forces. Made typically from ferromagnetic materials like steel or rare-earth alloys, this magnet is designed with two poles positioned close together in a horseshoe shape to concentrate the magnetic field between them, creating a strong and uniform magnetic area. The compact design allows easy handling and application in physics demonstrations, magnetic field studies, and educational experiments. Its durable construction ensures long-lasting magnetic strength and resistance to mechanical wear.
Magnetic needle on stand
The Magnetic Needle on Stand is a precision laboratory instrument used primarily for demonstrating magnetic fields and directionality in physics and earth science education. It consists of a finely balanced magnetic needle mounted on a stable stand, allowing free rotation to align with the Earth’s magnetic field or an applied magnetic field. Constructed from magnetized metal, the needle provides a clear and accurate indication of magnetic north or the direction of a nearby magnetic field source. The sturdy stand ensures stability during demonstrations or experiments, making it an essential tool for classroom experiments, compass demonstrations, and magnetism studies.
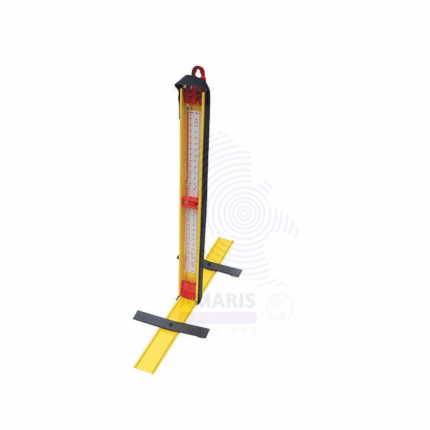
Manometer on stand
The Manometer on Stand is a precision laboratory instrument used to measure pressure differences in gases or liquids. It consists of a U-shaped or straight tube partially filled with a liquid (commonly mercury, water, or oil) mounted securely on a stable stand for ease of use and accurate readings. The manometer operates based on the principle of balancing pressure against the height of the liquid column. It is widely used in physics and engineering laboratories for experiments involving fluid mechanics, gas laws, and pressure calibration. The stand provides stability and convenient placement during measurements.
measuring cylinder glass
The Measuring Cylinder Glass is a fundamental laboratory apparatus specifically engineered for the precise measurement of liquid volumes. Constructed from high-quality, chemically resistant borosilicate glass, it ensures durability, resistance to chemical corrosion, and clarity for optimal visibility of liquid levels. The cylindrical shape provides a stable base and ergonomic design for ease of handling and pouring. Graduated volume markings, typically etched or printed with high contrast, allow accurate reading of liquid quantities down to the milliliter, supporting quantitative experiments and solution preparations. The transparent nature of the glass facilitates observation of the meniscus, which is critical for accuracy in volume measurement. Measuring cylinders vary in size, commonly ranging from small (10 mL) to large capacities (1000 mL or more), meeting diverse laboratory needs. They are widely used across chemical, biological, medical, educational, and industrial laboratories for tasks including volumetric analysis, solution preparation, and quality control. Their ability to withstand thermal fluctuations and autoclaving processes also makes them suitable for sterilized environments. Measuring Cylinder Glass is essential for maintaining precision and reproducibility in experimental and routine laboratory procedures.
Mechanical Balance
The Mechanical Balance is a precision laboratory instrument designed to measure the mass of objects through mechanical means. It operates using a system of levers, beams, and calibrated weights to determine mass with high accuracy without requiring electrical power. Mechanical balances typically feature a robust metal frame, a beam with a central pivot, and sliding weights or poises for balancing. The instrument provides reliable and repeatable mass measurements essential for quantitative analysis in chemistry, biology, physics, and industrial quality control. Known for its durability and ease of maintenance, the mechanical balance is widely used in educational settings, research laboratories, and production environments where precise weighing is necessary. Its mechanical operation ensures functionality even in environments where electronic devices may be unsuitable due to power constraints or interference.
Mercury thermometer
The Mercury Thermometer is a precise laboratory instrument designed for accurate temperature measurement using mercury as the thermometric fluid. It consists of a narrow, sealed glass tube containing mercury that expands and contracts with temperature changes, moving along a calibrated scale etched or printed on the glass. Mercury thermometers offer excellent thermal conductivity and stability, enabling precise readings over a wide temperature range typically from -39°C to 357°C (the freezing and boiling points of mercury). The clear glass casing allows easy observation of mercury levels, while the robust design resists breakage under normal laboratory conditions. Mercury thermometers are widely used in scientific research, medical labs, industrial processes, and educational settings for their reliability and accuracy. Despite their benefits, mercury thermometers require careful handling due to the toxicity of mercury, and many labs are transitioning to safer alternatives in compliance with environmental regulations.
Microscope
A Microscope is an essential laboratory instrument designed to magnify and visualize small objects or specimens that are not visible to the naked eye. It uses a system of lenses—typically an objective lens and an eyepiece lens—to enlarge images of biological samples, materials, or microscopic particles for detailed examination. Microscopes come in various types including compound, stereo, electron, and digital, each suited for specific applications in biology, materials science, medicine, and research. High-quality microscopes offer adjustable magnification, fine focus controls, and illumination systems to enhance clarity and contrast. Widely used in clinical diagnostics, microbiology, pharmaceutical research, and education, microscopes are vital for studying cell structures, microorganisms, tissue samples, and more. They provide precise, reliable visualization crucial for scientific analysis and discovery.
Microscope condenser
A Microscope Condenser is a vital optical component in a microscope designed to focus and concentrate light onto the specimen being observed. It is typically positioned beneath the microscope stage and plays a crucial role in controlling illumination intensity, contrast, and resolution during microscopic examination. The condenser gathers and directs light from the microscope’s illumination source into a cone of light focused on the specimen, enhancing image clarity and detail. Condensers often include adjustable diaphragms (such as iris diaphragms) to regulate the amount of light and improve contrast. Available in various designs including Abbe, achromatic, and aplanatic condensers, they cater to different magnification levels and imaging requirements. Microscope condensers are essential for achieving optimal image quality in biological, medical, and materials science applications.
Microscope eye piece
A Microscope Eye Piece, also known as the ocular lens, is the lens or group of lenses located at the top of a microscope through which the user views the magnified specimen. It typically provides an additional magnification—commonly 5x, 10x, or 15x—working in conjunction with the objective lenses to achieve total magnification. The eyepiece contains optical components designed to enhance image clarity, brightness, and field of view. Modern eyepieces may include features such as reticles for measurement, adjustable diopters for individual eye correction, and wide-field optics for increased viewing comfort. Made from precision optical glass and durable housing, microscope eyepieces are essential for delivering a clear, sharp, and comfortable viewing experience in scientific, medical, educational, and industrial laboratories.
Microscope mirror
A Microscope Mirror is an optical accessory used to direct and focus external light onto the specimen being examined under a microscope. Traditionally mounted beneath the microscope stage, the mirror reflects ambient or artificial light upward through the condenser and specimen to illuminate the sample. Microscope mirrors typically have one flat and one concave reflective surface, allowing users to adjust the intensity and focus of the light beam. Made from highly polished glass or metal with reflective coatings, these mirrors are essential in microscopes lacking built-in illumination systems or as backup lighting aids. They enhance visibility, contrast, and detail, making them valuable in educational, medical, and research laboratory settings.
Microscope mirror holder
A Microscope Mirror Holder is a precision laboratory accessory designed to securely mount and position the microscope mirror beneath the stage. It allows for adjustable angling and stable placement of the mirror to direct light optimally onto specimens during microscopic examination. Typically made from durable metal or plastic, the holder features clamps or brackets to hold the mirror firmly while enabling smooth rotational and tilt movements. This accessory is essential for microscopes without built-in illumination systems, facilitating better light control, improved specimen visibility, and enhanced image contrast. Widely used in educational, medical, and research laboratories, the microscope mirror holder aids in consistent and effective lighting setup.
Microtone hand type
Product Description
The Microtone Hand Type is a precision manual laboratory instrument designed for fine and controlled cutting or sectioning of specimens, particularly in biological and histological applications. It allows users to prepare thin slices or sections of tissues for microscopic examination, ensuring uniform thickness and minimal damage to samples. Typically handheld and ergonomically designed, this device is made from durable materials with sharp blades that can be replaced or adjusted as needed. The Microtone Hand Type is essential in pathology labs, research facilities, and educational settings where detailed tissue analysis is required.
Millie ammeter
A Millie Ammeter is a precision laboratory instrument used to measure very small electrical currents in the milliampere (mA) range. It is essential for experiments and procedures requiring accurate current measurements, particularly in physics and electronics labs. The device typically features a sensitive needle gauge or digital display, calibrated for fine resolution of low current levels. Compact and robust, millie ammeters are designed for easy integration into circuits and offer reliable performance for research, educational, and industrial applications.
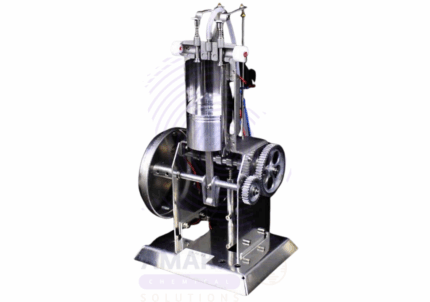
Model Diesel Engine
A Model Diesel Engine is a precision laboratory instrument used to measure very small electrical currents in the milliampere (mA) range. It is essential for experiments and procedures requiring accurate current measurements, particularly in physics and electronics labs. The device typically features a sensitive needle gauge or digital display, calibrated for fine resolution of low current levels. Compact and robust, millie ammeters are designed for easy integration into circuits and offer reliable performance for research, educational, and industrial applications.
Model steam engine
A Model Steam Engine is a scaled-down, functional representation of a steam-powered engine used primarily for educational, demonstration, and hobbyist purposes. This apparatus demonstrates the basic principles of thermodynamics, mechanical energy conversion, and steam power operation in a compact, visible form. Typically constructed from metal components such as brass and steel, the model includes key parts like a boiler, piston, cylinder, crankshaft, and flywheel. Steam generated in the boiler expands and pushes the piston, converting thermal energy into mechanical motion that turns the flywheel. Model steam engines are invaluable tools for physics and engineering education, illustrating steam mechanics, energy transfer, and engine operation clearly and tangibly. They are also popular among collectors and model enthusiasts.
Mortar and pestle
Mortar and Pestle is a traditional laboratory apparatus consisting of a bowl (mortar) and a heavy club-shaped tool (pestle) used to manually grind, crush, and mix solid substances into fine powders or pastes. Made from durable materials such as ceramic, glass, porcelain, or stone, this tool facilitates the preparation of samples for chemical analysis, pharmaceutical compounding, and food laboratory testing. The mortar’s thick walls and the pestle’s sturdy design allow effective pulverization without contamination. Mortar and pestle sets are essential in laboratories for homogenizing powders, breaking down crystals, and preparing reagents and mixtures. Their simplicity and reliability make them a staple in chemistry, biology, pharmacology, and food science labs worldwide.
OVERFLOW CAN
An Overflow Can is a laboratory apparatus designed to measure the volume of irregularly shaped solid objects using the water displacement method. It typically consists of a container with a spout or outlet near the top to allow excess water to overflow when a solid object is submerged inside. Overflow cans are usually made from durable, chemically resistant materials such as plastic or stainless steel. This device is essential in physics and material science laboratories for determining volume and density accurately by capturing displaced fluid and measuring its
PENCIL JOCKEY
A Pencil Jockey is a small laboratory tool designed to securely hold and manipulate pencils or fine writing instruments during detailed drawing, drafting, or note-taking tasks. Commonly used in scientific laboratories, drafting rooms, and educational settings, it ensures precision and comfort during use. Typically made from lightweight, durable
pendilum Bob
pendilum bob is a weighted mass attached to the end of a pendulum string or rod, used in physics laboratories to study oscillatory motion, harmonic motion, and related principles. Typically made from dense metals such as brass or steel, the bob provides the necessary mass for consistent and measurable swinging motion. Pendulum bobs come in various sizes and shapes, often spherical or cylindrical, and are designed for
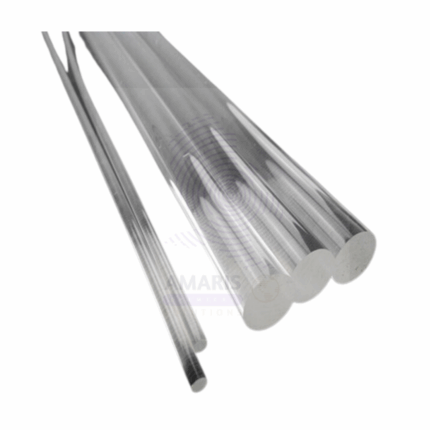
PERSPEX ROD
A Perspex Rod is a solid cylindrical rod made from Perspex (also known as acrylic or polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA), a transparent thermoplastic material widely used in laboratories, industrial applications, and educational demonstrations. Perspex rods are prized for their clarity, strength, and ease of machining, making them ideal for experiments requiring optical transparency or lightweight, durable components.
PIN HOLE CAMERA
A Pin Hole Camera is a simple optical device that demonstrates the fundamental principles of image formation through a small aperture, without the use of lenses. It consists of a light-tight box or container with a tiny hole on one side and a translucent screen or photographic paper on the opposite side where the inverted image is projected. Widely used in physics and educational demonstrations, the pin hole camera helps illustrate how light travels in straight lines and how images are formed. It’s a foundational tool in optics, enabling students and learners to explore the behavior of light and basic photography principles.
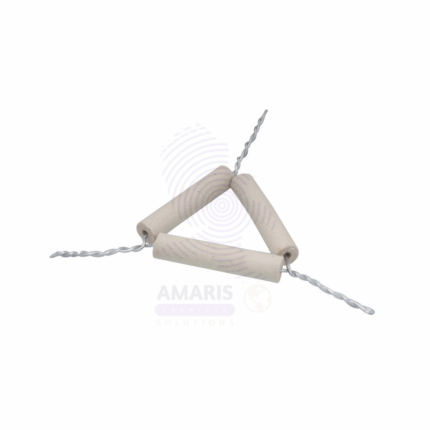
Pipe Clay Triangles
Pipe Clay Triangles are heat-resistant supports used in laboratory setups to hold crucibles over a Bunsen burner or other heat sources. They consist of three lengths of ceramic (pipe clay) tubing threaded over a triangular metal wire frame, typically made of galvanized iron or nickel-chromium alloy. These ceramic-coated wires provide stable and high-temperature-resistant platforms, allowing crucibles to be heated directly during ashing, calcination, or other high-temperature experiments. Widely used in chemistry labs and educational institutions, they are essential components for supporting small containers while minimizing heat transfer loss or instability.
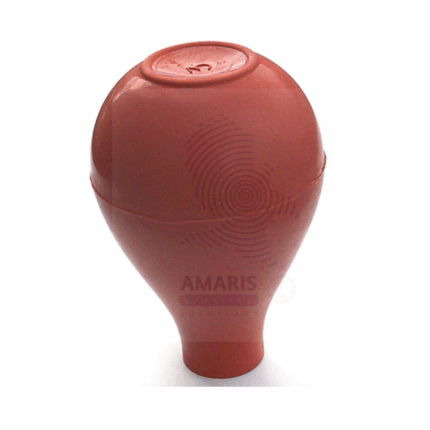
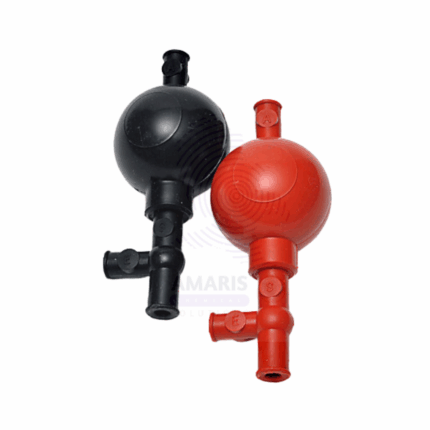
PIPETTE BULB
A Pipette Bulb is a flexible, hand-operated rubber or silicone device designed to safely draw and dispense liquids into pipettes without the need for mouth pipetting. It functions by creating a vacuum when squeezed and released, allowing for controlled aspiration and expulsion of liquids in laboratory settings. Pipette bulbs are widely used in analytical, clinical, chemical, and educational laboratories to ensure safety and precision when working with chemical or biological samples. They are compatible with various types of pipettes, including volumetric, graduated, and serological pipettes.
PIPETTE FILLER BULB TYPE
The Pipette Filler Bulb Type is a manual, rubber-based liquid handling accessory designed to provide safe and precise control over the aspiration and dispensing of liquids using pipettes. It is shaped like a bulb and typically includes one-way valves or a three-valve mechanism (Aspirate, Dispense, and Air Release) to regulate fluid movement. This tool eliminates the hazardous practice of mouth pipetting and ensures user safety when working with corrosive, toxic, or infectious substances. Compatible with both glass and plastic pipettes, the bulb-type pipette filler is widely used in educational, clinical, pharmaceutical, and analytical laboratories.
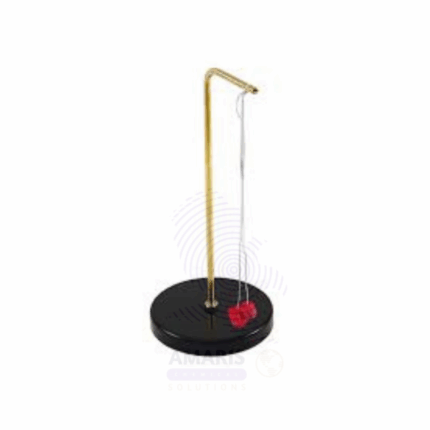
PITH BALLS ON STAND
Product Description
Pith Balls on Stand are lightweight, spherical objects typically made from dried plant pith (spongy plant tissue), suspended from insulating threads and mounted on a non-conductive support structure. These classical electrostatics demonstration tools are used in physics laboratories to visually illustrate principles of static electricity, charge induction, electric forces, and Coulomb’s Law. The balls are extremely lightweight and react readily to electrostatic forces when charged objects are brought nearby, making them ideal for teaching foundational electricity concepts. The stand is usually composed of a plastic or acrylic base and vertical support to ensure stability and electrical insulation during experiments.
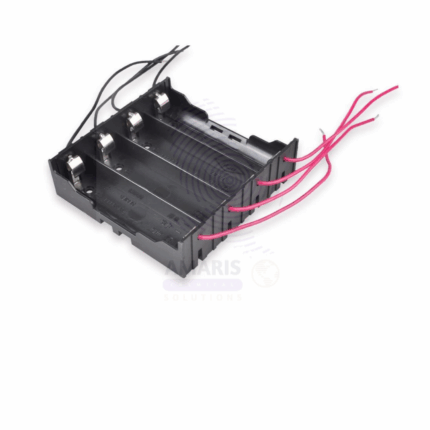
Plastic Cell Holder
A Plastic Cell Holder is a laboratory accessory used to securely hold electrochemical or dry cells (batteries) in place during physics or electrical experiments. It is typically made from non-conductive, durable plastic and may feature metal terminals or spring-loaded clips for electrical connections. These holders provide a stable and safe platform to integrate batteries into circuits for educational demonstrations, testing setups, or prototyping purposes. Designed for use with common battery sizes (such as D, C, AA, or specialized cells), the holder ensures easy insertion, removal, and reliable connection of power sources without short-circuiting. It is widely used in physics labs, electronics training, and school science kits.
PLASTIC DISSECTING TRAY WITHOUT WAX
The Plastic Dissecting Tray without Wax is a laboratory instrument used to hold specimens during dissection procedures in biology, zoology, anatomy, and educational labs. Unlike traditional dissecting trays that include a wax layer for pinning specimens, this tray offers a reusable, wax-free surface, typically designed to accommodate separate pinning pads or mats (e.g., rubber or foam inserts). It is made from high-grade, chemical-resistant plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, offering a lightweight, durable, and easy-to-clean platform. The tray typically features raised sides to contain fluids and provide a controlled
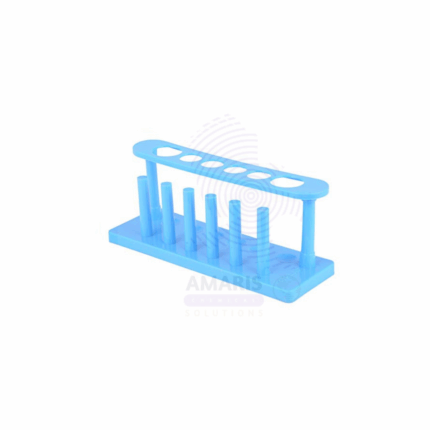
PLASTIC TEST TUBE STAND 6HOLE
The Plastic Test Tube Stand 6Hole is a laboratory support accessory designed to securely hold test tubes in an upright position during experimental procedures, storage, or drying. This version features six equally spaced holes, each capable of accommodating standard-size test tubes. Constructed from chemical-resistant, durable plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, the stand is lightweight, stable, and easy to clean. Often used in educational, analytical, and clinical laboratories, it provides a convenient and organized way to manage test tubes during chemical reactions, sample handling, or heating processes. The design may also include drying pegs or smaller side holes for inverted tube drying.
PLASTIC WASH BOTTLE
A Plastic Wash Bottle is a squeezable laboratory container designed to dispense liquids—usually water or solvents—in a controlled stream through a narrow nozzle or spout. Made from chemical-resistant, semi-flexible plastic such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), or fluoropolymer materials, the bottle allows for precision rinsing or washing of laboratory glassware, instruments, or surfaces without direct contact. The cap and nozzle are typically screw-fitted and designed to prevent leaks while enabling directional flow. It is a standard utility item in chemical, biological, educational, and analytical laboratories.
Porcelain Boat
A Porcelain Boat is a small, shallow, boat-shaped laboratory vessel made from high-quality, heat-resistant porcelain. It is designed primarily for the safe heating, drying, and combustion of solid substances. The smooth, glazed surface of the porcelain resists chemical corrosion and thermal shock, allowing for direct application of heat using burners such as Bunsen flames. Porcelain Boats are widely used in chemical analysis, qualitative testing, and sample preparation to hold small quantities of powders, crystals, or other solids during ignition or ashing procedures. Their shape facilitates easy pouring and transfer of materials and is ideal for use in muffle furnaces or over direct flames.
Porous Pot
A Porous Pot is a cylindrical or tubular laboratory apparatus made from sintered or fired ceramic material that features a permeable structure allowing the passage of gases or liquids while retaining solids or particulates. This highly porous ceramic vessel is commonly used in laboratory and industrial settings for filtration, diffusion, and separation processes. The pot’s micro-porous walls facilitate controlled fluid flow, making it ideal for applications such as gas absorption, water softening, and chemical diffusion experiments. Porous Pots are chemically inert, mechanically stable, and resistant to high temperatures, making them durable tools in analytical and preparative laboratory procedures.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders