Millie ammeter
Product Description
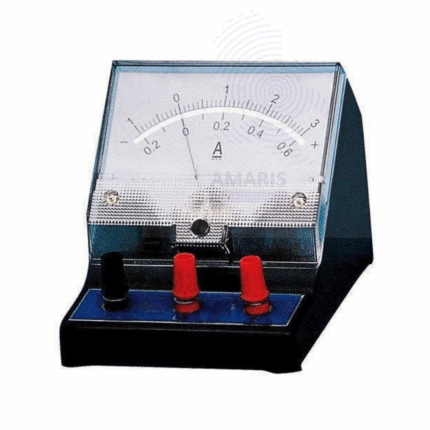
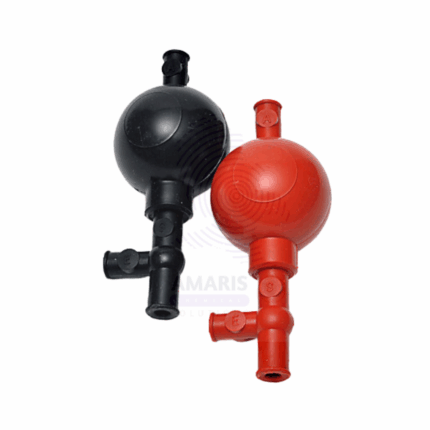
A Millie Ammeter is a precision laboratory instrument used to measure very small electrical currents in the milliampere (mA) range. It is essential for experiments and procedures requiring accurate current measurements, particularly in physics and electronics labs. The device typically features a sensitive needle gauge or digital display, calibrated for fine resolution of low current levels. Compact and robust, millie ammeters are designed for easy integration into circuits and offer reliable performance for research, educational, and industrial applications.
Model Diesel Engine
Product Description
A Millie Ammeter is a precision laboratory instrument used to measure very small electrical currents in the milliampere (mA) range. It is essential for experiments and procedures requiring accurate current measurements, particularly in physics and electronics labs. The device typically features a sensitive needle gauge or digital display, calibrated for fine resolution of low current levels. Compact and robust, millie ammeters are designed for easy integration into circuits and offer reliable performance for research, educational, and industrial applications.
Model steam engine
Product Description
A Model Steam Engine is a scaled-down, functional representation of a steam-powered engine used primarily for educational, demonstration, and hobbyist purposes. This apparatus demonstrates the basic principles of thermodynamics, mechanical energy conversion, and steam power operation in a compact, visible form. Typically constructed from metal components such as brass and steel, the model includes key parts like a boiler, piston, cylinder, crankshaft, and flywheel. Steam generated in the boiler expands and pushes the piston, converting thermal energy into mechanical motion that turns the flywheel. Model steam engines are invaluable tools for physics and engineering education, illustrating steam mechanics, energy transfer, and engine operation clearly and tangibly. They are also popular among collectors and model enthusiasts.
Mortar and pestle
Product Description
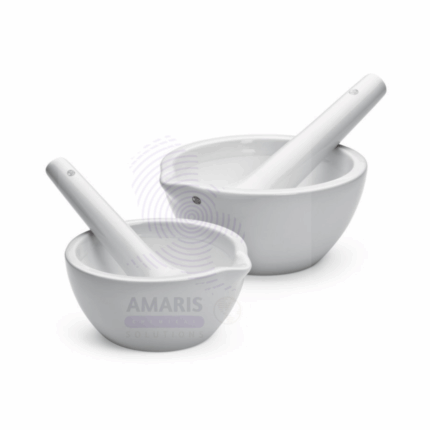
Mortar and Pestle is a traditional laboratory apparatus consisting of a bowl (mortar) and a heavy club-shaped tool (pestle) used to manually grind, crush, and mix solid substances into fine powders or pastes. Made from durable materials such as ceramic, glass, porcelain, or stone, this tool facilitates the preparation of samples for chemical analysis, pharmaceutical compounding, and food laboratory testing. The mortar’s thick walls and the pestle’s sturdy design allow effective pulverization without contamination. Mortar and pestle sets are essential in laboratories for homogenizing powders, breaking down crystals, and preparing reagents and mixtures. Their simplicity and reliability make them a staple in chemistry, biology, pharmacology, and food science labs worldwide.
OVERFLOW CAN
Product Description
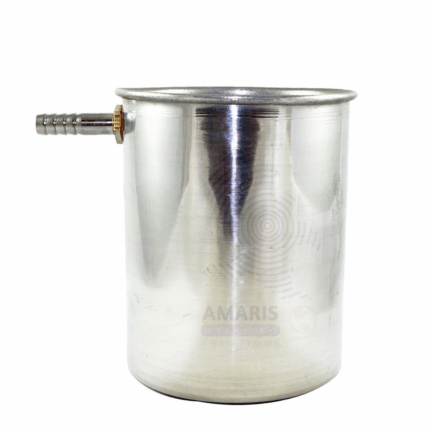
An Overflow Can is a laboratory apparatus designed to measure the volume of irregularly shaped solid objects using the water displacement method. It typically consists of a container with a spout or outlet near the top to allow excess water to overflow when a solid object is submerged inside. Overflow cans are usually made from durable, chemically resistant materials such as plastic or stainless steel. This device is essential in physics and material science laboratories for determining volume and density accurately by capturing displaced fluid and measuring its
PAINT GAUGE
Product Description
A Paint Gauge is a precise measuring instrument used in laboratories and quality control environments to measure the thickness of paint coatings and other surface finishes. It allows technicians and researchers to assess the uniformity and adequacy of paint layers on various substrates, ensuring compliance with industry standards and specifications. Paint gauges can be mechanical or digital, often employing magnetic, ultrasonic, or mechanical principles to provide accurate, non-destructive thickness measurements. They are essential tools in the manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and construction industries for maintaining coating quality and durability.
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Product Description
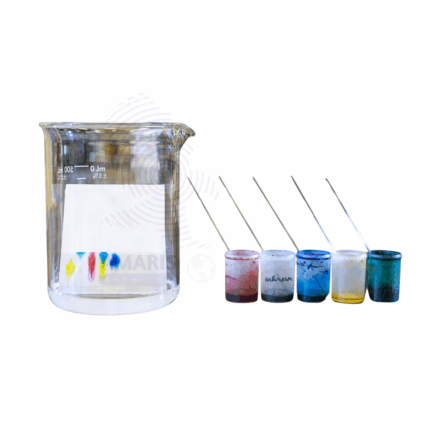
Paper Chromatography is an analytical laboratory technique used to separate and identify mixtures of substances based on their differential migration across a specially treated paper medium. It is widely used for qualitative analysis of compounds such as pigments, amino acids, and pharmaceuticals. The process involves applying a small sample spot onto chromatography paper and allowing a solvent to travel through the paper by capillary action, separating the components according to their solubility and affinity for the paper. This method is simple, cost-effective, and valuable in biochemical, pharmaceutical, and environmental laboratories for analyzing complex mixtures.
PENCIL JOCKEY
Product Description
A Pencil Jockey is a small laboratory tool designed to securely hold and manipulate pencils or fine writing instruments during detailed drawing, drafting, or note-taking tasks. Commonly used in scientific laboratories, drafting rooms, and educational settings, it ensures precision and comfort during use. Typically made from lightweight, durable
PENDILUM BOB
Product Description
A Pendulum Bob is a weighted mass attached to the end of a pendulum string or rod, used in physics laboratories to study oscillatory motion, harmonic motion, and related principles. Typically made from dense metals such as brass or steel, the bob provides the necessary mass for consistent and measurable swinging motion. Pendulum bobs come in various sizes and shapes, often spherical or cylindrical, and are designed for
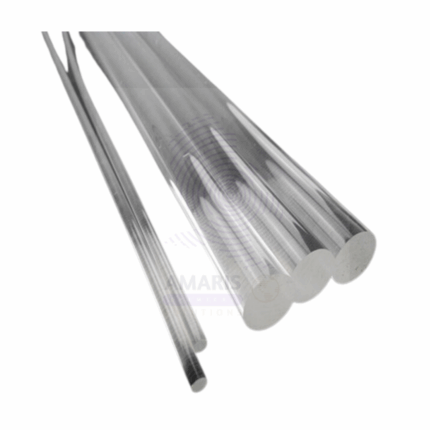
PERSPEX ROD
Product Description
A Perspex Rod is a solid cylindrical rod made from Perspex (also known as acrylic or polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA), a transparent thermoplastic material widely used in laboratories, industrial applications, and educational demonstrations. Perspex rods are prized for their clarity, strength, and ease of machining, making them ideal for experiments requiring optical transparency or lightweight, durable components. They
PH METER STRIPS
Product Description
pH Meter Strips, also known as pH indicator strips or litmus strips, are thin strips of paper or plastic impregnated with pH-sensitive dyes that change color in response to the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. These strips provide a quick, convenient, and cost-effective method to measure the pH level of liquids in laboratories, educational settings, and industrial processes. They are widely used for routine pH testing in chemistry, biology, environmental monitoring, water treatment, and quality control applications. The color change on the strips can be compared against a color chart to determine the approximate pH value of the tested solution.
PIN HOLE CAMERA
Product Description
A Pin Hole Camera is a simple optical device that demonstrates the fundamental principles of image formation through a small aperture, without the use of lenses. It consists of a light-tight box or container with a tiny hole on one side and a translucent screen or photographic paper on the opposite side where the inverted image is projected. Widely used in physics and educational demonstrations, the pin hole camera helps illustrate how light travels in straight lines and how images are formed. It’s a foundational tool in optics, enabling students and learners to explore the behavior of light and basic photography principles.
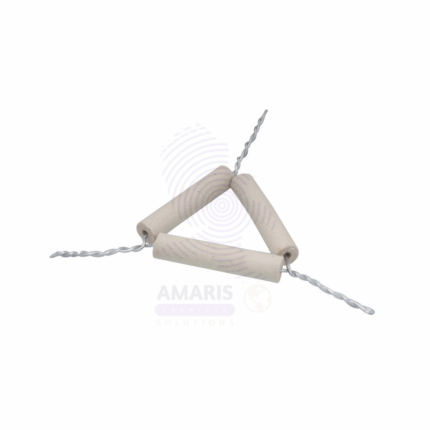
PIPE CLAY TRIANGLES
Product Description
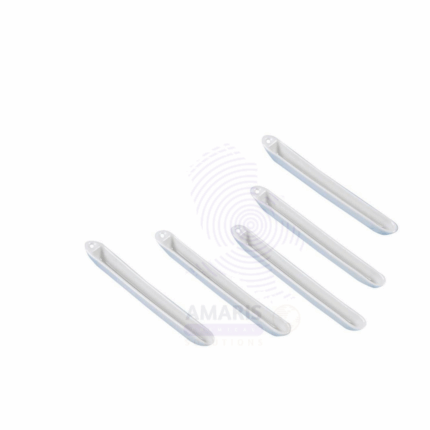
Pipe Clay Triangles are heat-resistant supports used in laboratory setups to hold crucibles over a Bunsen burner or other heat sources. They consist of three lengths of ceramic (pipe clay) tubing threaded over a triangular metal wire frame, typically made of galvanized iron or nickel-chromium alloy. These ceramic-coated wires provide stable and high-temperature-resistant platforms, allowing crucibles to be heated directly during ashing, calcination, or other high-temperature experiments. Widely used in chemistry labs and educational institutions, they are essential components for supporting small containers while minimizing heat transfer loss or instability.
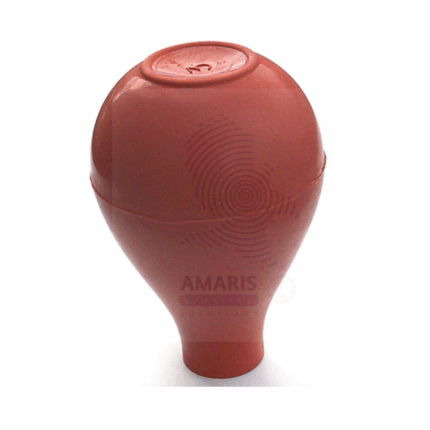
PIPETTE BULB
Product Description
A Pipette Bulb is a flexible, hand-operated rubber or silicone device designed to safely draw and dispense liquids into pipettes without the need for mouth pipetting. It functions by creating a vacuum when squeezed and released, allowing for controlled aspiration and expulsion of liquids in laboratory settings. Pipette bulbs are widely used in analytical, clinical, chemical, and educational laboratories to ensure safety and precision when working with chemical or biological samples. They are compatible with various types of pipettes, including volumetric, graduated, and serological pipettes.
PIPETTE FILLER BULB TYPE
Product Description
The Pipette Filler (Bulb Type) is a manual, rubber-based liquid handling accessory designed to provide safe and precise control over the aspiration and dispensing of liquids using pipettes. It is shaped like a bulb and typically includes one-way valves or a three-valve mechanism (Aspirate, Dispense, and Air Release) to regulate fluid movement. This tool eliminates the hazardous practice of mouth pipetting and ensures user safety when working with corrosive, toxic, or infectious substances. Compatible with both glass and plastic pipettes, the bulb-type pipette filler is widely used in educational, clinical, pharmaceutical, and analytical laboratories.
PITH BALLS ON STAND
Product Description
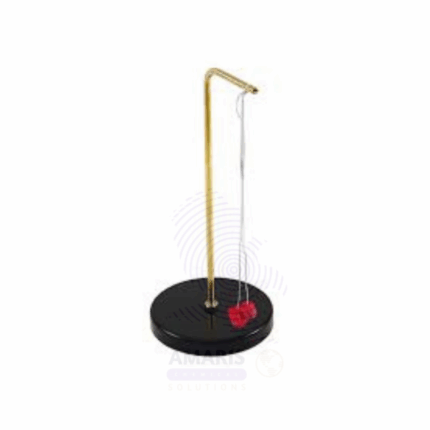
Pith Balls on Stand are lightweight, spherical objects typically made from dried plant pith (spongy plant tissue), suspended from insulating threads and mounted on a non-conductive support structure. These classical electrostatics demonstration tools are used in physics laboratories to visually illustrate principles of static electricity, charge induction, electric forces, and Coulomb’s Law. The balls are extremely lightweight and react readily to electrostatic forces when charged objects are brought nearby, making them ideal for teaching foundational electricity concepts. The stand is usually composed of a plastic or acrylic base and vertical support to ensure stability and electrical insulation during experiments.
PLASTIC CELL HOLDER
Product Description
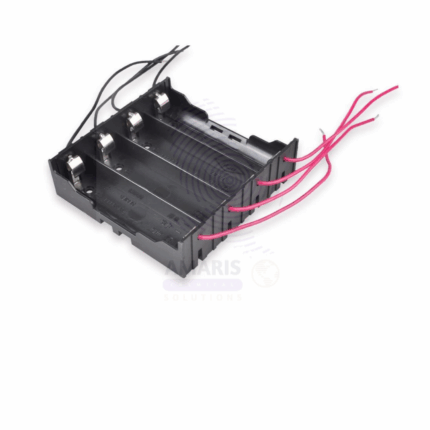
A Plastic Cell Holder is a laboratory accessory used to securely hold electrochemical or dry cells (batteries) in place during physics or electrical experiments. It is typically made from non-conductive, durable plastic and may feature metal terminals or spring-loaded clips for electrical connections. These holders provide a stable and safe platform to integrate batteries into circuits for educational demonstrations, testing setups, or prototyping purposes. Designed for use with common battery sizes (such as D, C, AA, or specialized cells), the holder ensures easy insertion, removal, and reliable connection of power sources without short-circuiting. It is widely used in physics labs, electronics training, and school science kits.
PLASTIC DISSECTING TRAY WITHOUT WAX
Product Description
The Plastic Dissecting Tray without Wax is a laboratory instrument used to hold specimens during dissection procedures in biology, zoology, anatomy, and educational labs. Unlike traditional dissecting trays that include a wax layer for pinning specimens, this tray offers a reusable, wax-free surface, typically designed to accommodate separate pinning pads or mats (e.g., rubber or foam inserts). It is made from high-grade, chemical-resistant plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, offering a lightweight, durable, and easy-to-clean platform. The tray typically features raised sides to contain fluids and provide a controlled
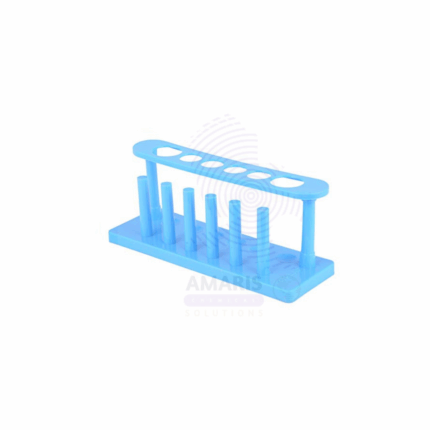
PLASTIC TEST TUBE STAND 6HOLE
Product Description
The Plastic Test Tube Stand (6-Hole) is a laboratory support accessory designed to securely hold test tubes in an upright position during experimental procedures, storage, or drying. This version features six equally spaced holes, each capable of accommodating standard-size test tubes. Constructed from chemical-resistant, durable plastic such as polypropylene or ABS, the stand is lightweight, stable, and easy to clean. Often used in educational, analytical, and clinical laboratories, it provides a convenient and organized way to manage test tubes during chemical reactions, sample handling, or heating processes. The design may also include drying pegs or smaller side holes for inverted tube drying.
PLASTIC WASH BOTTLE
Product Description
A Plastic Wash Bottle is a squeezable laboratory container designed to dispense liquids—usually water or solvents—in a controlled stream through a narrow nozzle or spout. Made from chemical-resistant, semi-flexible plastic such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), or fluoropolymer materials, the bottle allows for precision rinsing or washing of laboratory glassware, instruments, or surfaces without direct contact. The cap and nozzle are typically screw-fitted and designed to prevent leaks while enabling directional flow. It is a standard utility item in chemical, biological, educational, and analytical laboratories.
Porcelain Boat
Porcelain Boat is a specialized ceramic container made from high-quality porcelain material. It is designed for laboratory, pharmaceutical, and culinary applications requiring heat resistance, chemical inertness, and easy cleaning. The porcelain boat's smooth surface and durable construction make it ideal for use in processes like ashing, drying, and sample handling.
PORCELAIN BOAT
Product Description
A Porcelain Boat is a small, shallow, boat-shaped laboratory vessel made from high-quality, heat-resistant porcelain. It is designed primarily for the safe heating, drying, and combustion of solid substances. The smooth, glazed surface of the porcelain resists chemical corrosion and thermal shock, allowing for direct application of heat using burners such as Bunsen flames. Porcelain Boats are widely used in chemical analysis, qualitative testing, and sample preparation to hold small quantities of powders, crystals, or other solids during ignition or ashing procedures. Their shape facilitates easy pouring and transfer of materials and is ideal for use in muffle furnaces or over direct flames.
Porous Pot
Porous Pot is a specialized ceramic or composite container characterized by its permeable walls that allow the passage of liquids and gases while retaining solids. It is commonly used in filtration, diffusion, and controlled release applications. The porous structure enables efficient separation, aeration, or gradual release of substances, making it essential in chemical, environmental, and industrial processes.
POROUS POT
Product Description
A Porous Pot is a cylindrical or tubular laboratory apparatus made from sintered or fired ceramic material that features a permeable structure allowing the passage of gases or liquids while retaining solids or particulates. This highly porous ceramic vessel is commonly used in laboratory and industrial settings for filtration, diffusion, and separation processes. The pot’s micro-porous walls facilitate controlled fluid flow, making it ideal for applications such as gas absorption, water softening, and chemical diffusion experiments. Porous Pots are chemically inert, mechanically stable, and resistant to high temperatures, making them durable tools in analytical and preparative laboratory procedures.
PRESERVATION GLASS LAB BOTTLES
Product Description
Preservation Glass Lab Bottles are specialized high-quality glass containers designed to securely store and preserve liquid or solid samples in laboratory settings. Made from chemically resistant borosilicate or soda-lime glass, these bottles provide excellent clarity for easy monitoring of contents. They are engineered to protect samples from contamination, evaporation, and chemical degradation during storage. Typically equipped with airtight screw caps, stoppers, or sealable lids, Preservation Glass Lab Bottles ensure leak-proof containment and maintain sample integrity over extended periods. Widely used in medical, environmental, research, and industrial laboratories, these bottles are essential for long-term preservation and safe sample handling.
PROOF PLANE
Product Description
A Proof Plane is a flat, thin, and smooth metallic or plastic tool used in laboratory and educational settings primarily for transferring small amounts of powdered substances or samples. Its precise, rigid surface enables the easy lifting and placement of powders onto other surfaces such as balances, microscope slides, or reaction vessels without contamination. Often used in qualitative analysis, the Proof Plane facilitates accurate handling of chemicals, minimizing spillage and waste. Available in various sizes and materials, it is an essential apparatus for fine sample manipulation in analytical and teaching laboratories.
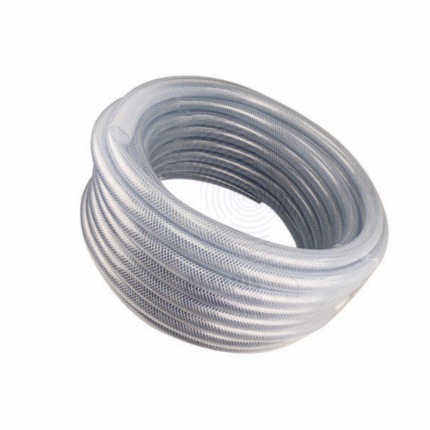
PVC TUBING
Product Description
PVC Tubing is a flexible, durable tube made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC), commonly used in laboratories for the safe and efficient transfer of gases, liquids, and chemicals. It features excellent chemical resistance, good mechanical strength, and flexibility, making it ideal for a wide range of laboratory applications including fluid transfer, vacuum lines, and connection of various lab apparatus. PVC Tubing is transparent or translucent to allow visual monitoring of fluid flow and is resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and weathering. It is available in various diameters and thicknesses to suit different laboratory requirements.
PVP Iodine
PVP Iodine is a water-soluble complex of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and iodine, widely used as a broad-spectrum antiseptic. It delivers controlled iodine release, providing effective antimicrobial action against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. This preparation is favored for its ease of application, reduced irritation compared to tinctures, and stability in aqueous solutions. PVP Iodine 10% is commonly used in medical, veterinary, and personal care settings for disinfection and wound treatment.
RAIN GAUGE
Product Description
A Rain Gauge is a precise meteorological instrument designed to measure the amount of liquid precipitation (rainfall) over a set period, typically in millimeters or inches. It consists of a collection funnel directing water into a graduated measuring container or a tipping bucket mechanism that records rainfall digitally. Constructed from durable materials such as glass, plastic, or corrosion-resistant metals, rain gauges are built to endure outdoor conditions including sun exposure, wind, and rain. Their design allows for accurate, easy-to-read measurements to support weather forecasting, agricultural planning, environmental monitoring, and hydrological research. Rain Gauges are fundamental tools in laboratories focused on environmental science, meteorology, and water resource management.
RAPESEED
Product Description
Rapeseed is a plant-derived sample commonly analyzed in laboratories for its biochemical composition, including oil content, fatty acid profile, and protein levels. Laboratory testing of rapeseed helps in quality control for food processing, nutritional analysis, and industrial applications such as biofuel research. Samples of rapeseed seeds or extracted oils undergo chromatographic, spectroscopic, and other analytical procedures to determine purity, contaminants, and nutritional value. These tests support research in agricultural science, food technology, and pharmaceutical development
RECTANGULAR GLASS BLOCK
Product Description
Rectangular Glass Block is a precisely manufactured optical glass apparatus commonly used in physics and optics laboratories. It serves as a medium for experiments involving light refraction, reflection, and dispersion. The block’s uniform rectangular shape and polished surfaces provide clear, distortion-free passage of light, making it ideal for studying phenomena such as critical angle, total internal reflection, and lens behavior. Made from high-quality, optically clear glass, this block withstands repeated handling and laboratory conditions. It is essential for educational demonstrations and research in geometric optics and photonics.
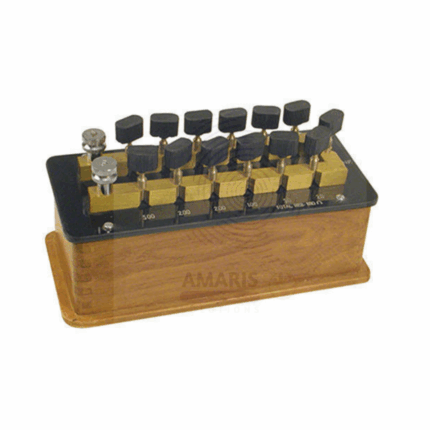
RESISTANCE BOX PLUG TYPE
Product Description
Resistance Box Plug Type is a precision electrical component used extensively in physics and electrical engineering laboratories. It comprises an insulated box containing a series of fixed-value resistors arranged in circuits accessible via plug-in terminals. By inserting plugs into designated sockets, users can combine resistors in series or parallel to achieve desired resistance values for experimental purposes. This equipment is essential for teaching Ohm’s Law, circuit analysis, and calibration of electrical devices. Constructed with durable, corrosion-resistant materials and designed for high accuracy, the resistance box supports reliable, repeatable laboratory experiments and research.
RESISTANCE COIL
Product Description
Resistance Coil is a fundamental laboratory apparatus consisting of a wire coil made from materials with a known resistance, typically nichrome or similar alloys. It is widely used in physics and electrical engineering laboratories to study electrical resistance, heating effects, and circuit behavior. The coil’s wire length and thickness determine its resistance value, enabling controlled experiments involving Ohm’s Law, Joule heating, and energy dissipation. Resistance Coils are designed to withstand electrical current and heat without significant degradation, making them ideal for demonstrations, experiments, and calibration tasks in laboratory settings.
RETORT FLASK
Product Description
Retort Flask is a specialized laboratory glassware designed for heating, distillation, and chemical reactions. It features a spherical or pear-shaped body with a long, narrow neck that allows vapors to condense and be directed away during distillation processes. Made from heat-resistant borosilicate glass, Retort Flasks withstand high temperatures and thermal shocks typical in laboratory heating applications. Commonly used in chemistry and biochemistry labs, they facilitate controlled heating of liquids and collection of distilled vapors in experiments involving organic synthesis, purification, and chemical analysis.
RING AND BALL THERMAL EXPANSION
Product Description
Ring and Ball Thermal Expansion Apparatus is a precision laboratory device used to determine the coefficient of thermal expansion of materials, particularly metals. The apparatus consists of a metal ring and a steel ball of known dimensions. When heated, the metal ring expands, allowing the ball to pass through at a specific temperature. This temperature corresponds to the expansion point of the ring material. The device is widely used in physics and materials science laboratories to study the thermal properties of materials and to teach fundamental concepts of thermal expansion and heat behavior.
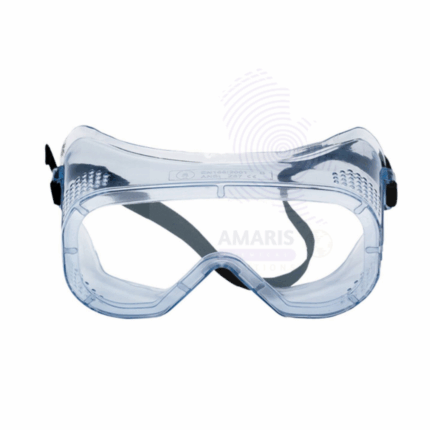
SAFETY GOGGLES
product Description
Safety Goggles are essential personal protective equipment designed to shield the eyes from chemical splashes, flying debris, dust, and other hazardous materials commonly encountered in laboratory environments. Constructed with impact-resistant lenses and a secure frame, they provide a tight seal around the eyes to prevent exposure to harmful substances. Safety Goggles typically feature adjustable straps for a comfortable and secure fit, anti-fog coatings for clear vision, and ventilation systems to reduce moisture buildup. Widely used in medical, chemical, industrial, and research laboratories, Safety Goggles ensure compliance with safety standards and help maintain a safe working environment.
Sasol Phenol
Sasol Phenol is a high-purity, industrial-grade phenol produced by Sasol, widely used as a key raw material in the manufacture of plastics, resins, and chemicals. Phenol is an aromatic organic compound characterized by a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. It serves as a precursor in producing bisphenol A, caprolactam, and phenolic resins. Sasol Phenol is known for its consistent quality, purity, and suitability for diverse industrial applications including chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and adhesives.
SEMI CICRLE GLASS BLOCK
Product Description
Semi Circle Glass Block is a precision laboratory apparatus made from high-quality optical glass, designed for experiments involving light refraction, reflection, and optics principles. The semi-circular shape allows for controlled study of how light bends when passing through different media, making it ideal for educational demonstrations and research in physics and optical sciences. The block is crafted from clear, durable glass to provide excellent transparency and minimal distortion. It is widely used in schools, colleges, and research labs for studying Snell’s Law, critical angle, and total internal reflection.
Single Gas Mask
Product Description
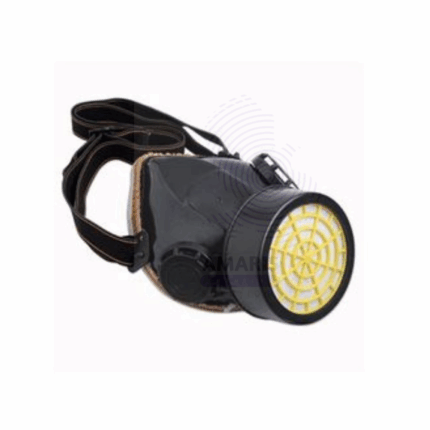
Single Gas Masks are vital personal protective equipment designed to protect the wearer’s respiratory system from harmful gases, vapors, dust, and airborne contaminants commonly encountered in laboratory, industrial, and hazardous environments. Constructed with durable, chemical-resistant materials, these masks typically feature a full-face or half-face design with a replaceable filter cartridge tailored to specific contaminants. They provide a secure seal around the face to prevent ingress of toxic substances, ensuring safe breathing in contaminated atmospheres. Single Gas Masks are essential for use during chemical handling, fumigation, and emergency response situations, safeguarding health and safety compliance.
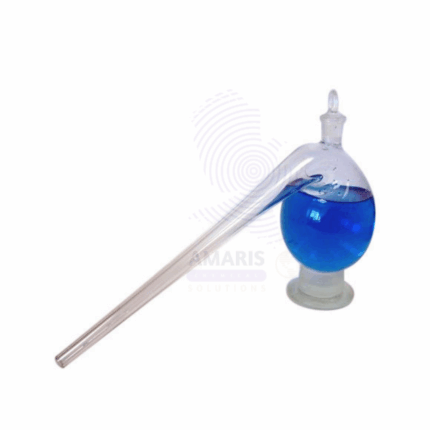
Siphon pump
Product Description
Siphon Pump is a manual laboratory apparatus designed for transferring liquids from one container to another using the principle of siphoning. Made from chemically resistant materials such as rubber tubing and plastic or glass components, siphon pumps provide an easy and safe method for liquid transfer without the need for power sources. They are commonly used in laboratories to transfer solvents, reagents, and other fluids with precision and control, minimizing spills and contamination. Available in various sizes and configurations, siphon pumps are essential for fluid handling in research, medical, and industrial laboratories.
Slinky springs
Product Description
Slinky Springs are helical coil springs made from metal or plastic materials, widely used as demonstration and educational tools in physics and engineering laboratories. These springs exhibit elastic properties, capable of stretching and compressing while returning to their original shape, making them ideal for teaching concepts such as harmonic motion, wave propagation, and energy transfer. Available in various sizes and coil thicknesses, slinky springs serve as practical models for studying mechanical behavior, oscillations, and spring constants in both academic and research settings.
Smoke cell
Product Description
Smoke Cells are specialized laboratory apparatus designed to generate and contain smoke or aerosols for experimental and educational purposes. Typically constructed from chemically resistant glass or plastic, smoke cells enable the study of particulate matter behavior, light scattering, gas flow dynamics, and air pollution analysis. The apparatus allows controlled introduction of smoke or aerosols inside a sealed chamber, facilitating observation and measurement of physical and optical properties. Smoke Cells are essential in research laboratories focusing on environmental science, physics, and chemical engineering.
Soft iron rod
Product Description
Soft Iron Rods are magnetic laboratory apparatus made from highly pure iron characterized by low carbon content, which gives them excellent magnetic permeability and low coercivity. These rods are widely used in physics and electrical laboratories for experiments involving magnetism, electromagnetism, and induction. Their softness allows them to be easily magnetized and demagnetized, making them ideal for use as cores in electromagnets, transformers, and magnetic field demonstrations. Soft iron rods are durable, corrosion-resistant when properly treated, and come in various lengths and diameters to suit different experimental needs.
Spatula plastic
Product Description
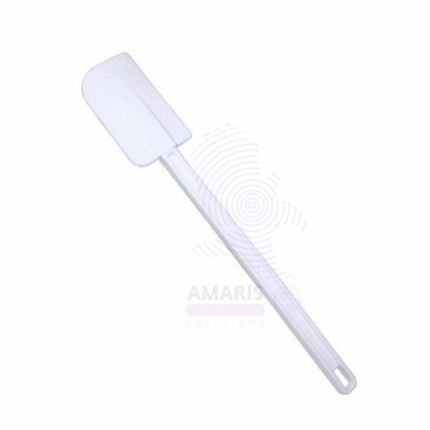
Plastic Spatulas are versatile laboratory tools designed for safely handling, transferring, and mixing small quantities of powders, granules, and liquids. Made from chemically resistant, durable plastic materials, these spatulas resist corrosion from most laboratory reagents and are lightweight for easy handling. They come in various sizes and shapes, often featuring flat or slightly curved blades to facilitate scooping and scraping. Plastic spatulas are essential in chemical, pharmaceutical, biological, and research laboratories for precise sample manipulation and contamination-free operations.
Special Kit
Product Description
A Special Kit is a versatile laboratory equipment set designed to provide essential tools and apparatus for specific scientific experiments or procedures. These kits are thoughtfully assembled with a collection of high-quality instruments, glassware, and accessories tailored to meet the needs of particular laboratory applications such as chemical analysis, biological studies, or physics demonstrations. Each component in the kit is selected for durability, accuracy, and ease of use, ensuring efficient and reliable experimental outcomes. Special Kits promote convenience by consolidating necessary items into a single, portable package, facilitating organized and systematic laboratory work.
Splints wooden
Product Description
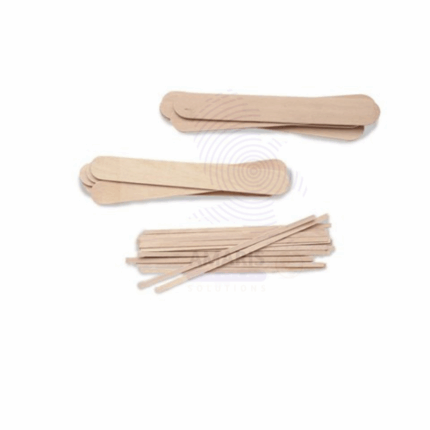
Wooden splints are narrow, thin strips of clean, untreated wood used primarily in laboratory experiments and demonstrations. Known for their ease of ignition and controlled burning, they serve as essential tools in chemistry and physics labs for conducting flame tests, ignition of chemicals, and studying combustion reactions. These splints are typically made from softwoods such as pine or basswood to ensure consistent performance. Their lightweight, disposable nature makes them convenient and safe for repeated use in controlled laboratory environments.
Syringe glass
Product Description
Glass syringes are precision laboratory instruments designed for accurate measurement and transfer of liquids. Crafted from chemically resistant borosilicate glass, these syringes provide excellent clarity for precise volume reading and ensure compatibility with a wide range of chemical substances without risk of contamination or degradation. They typically feature a smooth plunger mechanism for controlled aspiration and dispensing, and may include Luer lock or slip tips to fit various needles or tubing. Glass syringes are favored in medical, pharmaceutical, research, and analytical laboratories for their durability, reusability, and chemical inertness.
Table top pH meter
Product Description
The Table Top pH Meter is a precision electronic instrument designed to accurately measure the pH level of liquids in laboratory settings. Featuring a robust digital display and sensitive glass electrode, it provides fast, reliable, and easy-to-read pH measurements essential for chemical analysis, quality control, and research applications. The instrument typically includes calibration features, temperature compensation, and data hold functions to ensure accurate and reproducible results. Its sturdy tabletop design offers stability and convenience during extended use, making it a vital tool for analytical, environmental, pharmaceutical, and educational laboratories.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders