pH adjusters are chemicals used to control the acidity or alkalinity of water in treatment processes. Common acidic adjusters like sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid lower pH, while alkaline agents such as sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) and lime (calcium hydroxide) raise pH. Maintaining optimal pH (typically 6.5–8.5) ensures effective disinfection, corrosion control, and coagulation in drinking water, wastewater, and industrial systems. Proper pH balance also enhances chemical efficiency and protects infrastructure.
Ammonia Acetate
Ammonium Acetate (NH4CH3COO) is a white crystalline solid or granular powder with a mild ammoniacal odor. It is a salt formed from ammonia and acetic acid, widely used in laboratories, industrial processes, and some niche food and pharmaceutical applications. Ammonium Acetate is highly soluble in water and often utilized as a buffer solution in biochemical and analytical chemistry due to its ability to maintain pH. It also serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various chemicals and acts as a neutralizing agent in several industrial applications.
Calcium Chloride
Calcium Chloride is an inorganic salt composed of calcium and chlorine with the chemical formula CaCl₂. It typically appears as a white crystalline solid or granular powder, highly soluble in water and exhibiting strong hygroscopic properties. Calcium Chloride is widely used for its moisture-absorbing ability, de-icing, dust control, and as a firming agent in food processing. It finds extensive applications across industrial, pharmaceutical, agricultural, and food sectors due to its efficacy in modifying physical and chemical properties of products and environments.
Deionized Water
Deionized Water (DI Water), also known as demineralized water, is highly purified water that has had almost all of its mineral ions (such as sodium, calcium, iron, copper, chloride, and sulfate) removed through ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or other purification methods. It is a clear, colorless, odorless liquid with extremely low electrical conductivity and is considered chemically pure. Deionized water is used in applications where water purity is critical, including pharmaceuticals, electronics, cosmetics, laboratory use, and various industrial processes. Its lack of minerals makes it highly reactive with contaminants, which makes it both useful and sensitive in technical applications.
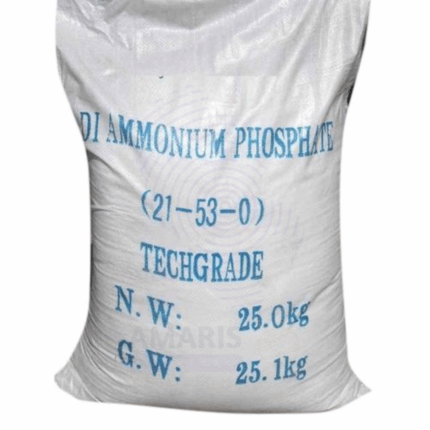
Diammonium Phosphate
Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a highly water-soluble, white crystalline fertilizer containing nitrogen and phosphorus. It is one of the most widely used phosphate fertilizers globally, providing a balanced source of nutrients essential for plant growth. DAP supplies ammonium nitrogen (NH₄⁺) and phosphate (PO₄³⁻), which promote vigorous root development, improve soil fertility, and enhance crop yield and quality. Besides agriculture, DAP serves important roles in food additives, fire retardants, and industrial applications. It’s favored for its high nutrient content, ease of application, and compatibility with other fertilizers and soil amendments.
Diethanolamine
Diethanolamine is a colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. It is a secondary amine and diol, widely used in various industrial, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. DEA is highly soluble in water and many organic solvents. It acts as an intermediate in the synthesis of surfactants, emulsifiers, corrosion inhibitors, and pharmaceuticals. It is valued for its alkalinity, emulsifying properties, and ability to form stable complexes with fatty acids.
Formic Acid
Formic Acid (methanoic acid) is the simplest carboxylic acid, typically supplied as an 85% aqueous solution. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, penetrating odor and strong acidic properties. Formic Acid naturally occurs in insect stings and plant secretions and is widely used in chemical synthesis, agriculture, textile, leather, and rubber industries. The 85% solution balances potency and safe handling for industrial applications. It serves as a preservative, antibacterial agent, and intermediate chemical in numerous manufacturing processes.
Hydrochloric Acid HCL
Hydrochloric Acid HCL is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid consisting of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in water to a concentration of approximately 33% by weight. It appears as a clear, colorless to slightly yellow liquid with a sharp, pungent odor. HCl 33% is widely used in industrial, chemical, and laboratory applications due to its strong acidic properties, high reactivity, and versatility. It plays a crucial role in pH control, metal processing, chemical synthesis, and cleaning processes across numerous sectors.
Hydrochloric Acid HCL 270 kg Drum
Hydrochloric Acid HCL 270 kg Drum is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid consisting of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in water to a concentration of approximately 33% by weight. It appears as a clear, colorless to slightly yellow liquid with a sharp, pungent odor. HCl 33% is widely used in industrial, chemical, and laboratory applications due to its strong acidic properties, high reactivity, and versatility. It plays a crucial role in pH control, metal processing, chemical synthesis, and cleaning processes across numerous sectors.
Industrial Salt
Industrial Salt, chemically known as Sodium Chloride (NaCl), is a high-purity crystalline compound widely used across industrial, chemical, agricultural, and water treatment applications. It appears as white to off-white crystalline granules or powder, depending on the grade and particle size. Industrial Salt is an essential raw material in numerous chemical processes, including chlor-alkali production, de-icing, textile dyeing, and water softening. Its versatility and cost-effectiveness make it indispensable in large-scale operations.
Lactic Acid
Lactic Acid is a colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid with a mild acidic odor. It is an organic acid naturally produced by fermentation and widely used in industrial, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food applications. The 80% concentration provides a balance of potency and ease of handling, making it suitable for pH adjustment, preservation, and chemical synthesis. Lactic acid is biodegradable, non-toxic, and valued for its multifunctionality including antimicrobial properties and chelation abilities.
Magadi Soda Ash
Magadi Soda Ash, commonly known as Soda Ash or Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃), is a white, odorless, granular or powdery alkaline compound. It is widely used in various industrial and manufacturing processes due to its strong alkaline properties and high solubility in water. Magadi Soda serves as a key raw material in glass manufacturing, detergent production, water treatment, and chemical synthesis. It is available in bulk packaging, such as 50kg bags, for easy handling and transport.
Magnesium Carbonate Light
Magnesium Carbonate Light is a fine, white, odorless powder primarily composed of magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃). It is characterized by its light texture and high purity. This mineral compound is widely used across various industries due to its excellent absorption properties, mild alkalinity, and non-toxic nature. Magnesium Carbonate Light is commonly employed as an antacid, drying agent, filler, and flow aid in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium Chloride is a white crystalline salt or granular solid composed of magnesium and chloride ions, commonly found as the hexahydrate form (MgCl₂·6H₂O). It is highly soluble in water, forming a clear, colorless solution with a slightly bitter saline taste. Magnesium Chloride is valued for its hygroscopic properties and is widely used across multiple industries including de-icing, chemical manufacturing, agriculture, food, pharmaceutical, and textile applications. It acts as a source of magnesium, a vital mineral for various biological and industrial processes.
Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate BP
Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate BP is a pharmacopeial grade white crystalline solid with the chemical formula MgCl₂·6H₂O. It is highly soluble in water and is used extensively in pharmaceutical, medical, and industrial applications. This grade meets British Pharmacopoeia (BP) standards ensuring high purity and suitability for medical and food-related uses. Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate BP provides essential magnesium ions which play a critical role in numerous physiological functions.
Magnesium Hydroxide BP
Magnesium Hydroxide BP is a white, odorless, fine powder or suspension with the chemical formula Mg(OH)₂. It is a pharmacopeial grade material meeting British Pharmacopoeia standards, widely used for its antacid, laxative, and neutralizing properties. Magnesium Hydroxide BP is sparingly soluble in water, releasing hydroxide ions that neutralize acids and increase pH. It finds broad applications in pharmaceuticals, water treatment, environmental management, and industrial processes.
Magnesium Sulphate Epsom Salt
Magnesium Sulphate Epsom Salt, commonly known as Epsom Salt, is an inorganic salt composed of magnesium, sulfur, and oxygen with the formula MgSO₄. It typically appears as colorless or white crystalline granules and is highly soluble in water. In its heptahydrate form (MgSO₄·7H₂O), it is widely used in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, food, and industrial applications. Epsom Salt is valued for its muscle relaxant, laxative, and magnesium supplementation properties, as well as for its role in improving soil fertility and plant growth.
Mono Ethanol Amine
Mono Ethanol Amine (MEA) is a clear, colorless, hygroscopic liquid with an ammonia-like odor. It is an organic chemical compound combining both amine and alcohol functional groups. MEA is widely used as a versatile chemical intermediate and is especially important in gas treatment, detergents, and chemical manufacturing due to its alkalinity and solubility in water and organic solvents.
Phosphoric acid Technical Grade
Phosphoric Acid Technical Grade is a concentrated, inorganic acid primarily used in industrial applications. It typically contains minor impurities compared to food or pharmaceutical grades but maintains excellent performance as an acidulant, rust remover, and intermediate chemical. This grade is widely used in manufacturing fertilizers, detergents, metal treatment, and other industrial processes where high purity is not critical but effective acidic properties are required.
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium Hydroxide is a highly concentrated, caustic alkaline chemical available as a solid (pellets, flakes) or concentrated aqueous solution. It is a strong base widely used in industrial processes, chemical manufacturing, and as a reagent. Potassium Hydroxide provides excellent neutralizing, saponifying, and cleaning properties and is essential in producing potassium soaps, biodiesel, fertilizers, and various chemical compounds. Its high purity and concentration (90%) make it suitable for demanding applications requiring strong alkalinity.
Soda Ash Light Bag
Soda Ash Light Bag, also known as sodium carbonate light, is a white, odorless, granular or powdered chemical with high solubility in water. It is widely used in industries as a key raw material for manufacturing glass, detergents, and chemicals. The light grade features finer particle size and lower bulk density compared to dense soda ash, making it suitable for applications requiring rapid dissolution and uniform mixing. Soda Ash Light plays a crucial role in pH regulation, water softening, and as an alkalizing agent across diverse sectors.
Sodium Bisulphate Monohydrate
Sodium Bisulphate Monohydrate, also known as sodium hydrogen sulphate, is a white crystalline powder or granular solid commonly used as an acidic cleaning agent, pH adjuster, and bleaching accelerator. It is a dry acid that releases sulfur dioxide when dissolved in water, making it effective in various industrial, food, and water treatment applications. This compound is valued for its ability to lower pH safely and is widely used where a controlled acidification is required without handling hazardous liquid acids.
Sodium Carbonate Soda Ash Light
Sodium Carbonate Soda Ash Light is an inorganic white powder with the chemical formula Na₂CO₃. It is a key industrial alkali used in glass manufacturing, water treatment, and chemical production. This light-density form is highly soluble and reacts with acids to form salts, making it essential for pH regulation and as a cleaning agent in various industrial processes.
Sodium Silicate
Sodium Silicate is a water-soluble, viscous alkaline liquid with the general formula Na₂SiO₃ (ratios vary). Commonly referred to as water glass or liquid glass, it appears as a clear to slightly cloudy solution. This 20-litre packaged product is known for its excellent adhesive, binding, and sealing properties. It is widely used in industrial, construction, detergent, and water treatment applications. Sodium silicate forms a glassy film upon drying and resists high temperatures and chemical attack, making it extremely versatile across many industries.
Sodium Sulphate
Sodium Sulphate (Na₂SO₄) is a white crystalline powder or granule, odorless and highly soluble in water. This 25kg packaged product is widely used in detergents, glass manufacturing, chemical industries, and pulp and paper processing. It acts as a filler, bulking agent, and drying agent, with excellent stability and non-reactivity under standard storage conditions. Its cost-effectiveness and availability make it an essential raw material in many industrial processes.
Sodium Sulphate Anhydrous
Sodium Sulphate Anhydrous (Na₂SO₄) is a white crystalline powder, odorless and highly soluble in water. Unlike the decahydrate form (Glauber's salt), this anhydrous grade contains minimal water content, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring low moisture levels. Supplied in 25kg packaging, it is widely used as a filler, drying agent, and raw material in detergents, glass manufacturing, pulp and paper, and chemical synthesis. Its excellent stability, non-hygroscopic nature, and cost-effectiveness make it an essential bulk chemical.
Sulphuric Acid 98%
Sulphuric Acid 98% is a dense, highly corrosive, and strong mineral acid widely used as a fundamental chemical reagent and industrial raw material. It serves as a key component in fertilizer production, chemical synthesis, petroleum refining, and many other industrial processes. The 98% concentration is the concentrated, nearly pure form commonly utilized for manufacturing and processing applications demanding high acid strength and purity.
Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine (TEA) is a viscous, colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. It is a multifunctional organic compound widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications as a pH adjuster, emulsifier, surfactant, and corrosion inhibitor. Triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids to form soaps and helps stabilize emulsions, making it essential in personal care formulations and various chemical manufacturing processes. Its versatility and compatibility with other ingredients make it a valuable additive in numerous industries.
Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine (TEA) is a viscous, colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. It is a multifunctional organic compound widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications as a pH adjuster, emulsifier, surfactant, and corrosion inhibitor. Triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids to form soaps and helps stabilize emulsions, making it essential in personal care formulations and various chemical manufacturing processes. Its versatility and compatibility with other ingredients make it a valuable additive in numerous industries.
Triethanolamine (TEA) 99%
Triethanolamine (TEA) 99% is a high-purity grade of triethanolamine, a viscous, colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. This high-concentration grade is widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications where superior purity is required. It functions primarily as a pH adjuster, emulsifier, surfactant, and corrosion inhibitor. TEA 99% is essential in neutralizing fatty acids to form soaps and stabilizing emulsions, enabling improved texture and stability in personal care products, as well as in chemical manufacturing processes demanding high-quality inputs.
Trisodium Phosphate
Trisodium Phosphate (TSP) is an inorganic, highly alkaline compound commonly available as a white, granular or crystalline solid. It is widely used for its powerful cleaning, degreasing, buffering, and water-softening properties. TSP is a versatile compound with significant utility across food processing, detergents, industrial cleaning, water treatment, and construction industries. It also acts as a flux, pH adjuster, emulsifier, and sequestrant. Both technical and food grades are available depending on the application.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders



















![Diethanolamine [C4H11NO2 or (CH2CH2OH)2NH] Amaris Chemicals](https://amarischemicalsolutions.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Diethanolamine-C4H11NO2-or-CH2CH2OH2NH-Amaris-Chemicals-430x430.png)






































