Malachite Green Extra Pure
Malachite Green Extra Pure is a synthetic dye of exceptional purity, recognized for its intense green coloration and versatile laboratory uses. It is commonly used as a biological stain, especially in microbiology for identifying and differentiating bacterial species, and in histology for staining cell structures. Additionally, Malachite Green serves as an effective fungicide and antiparasitic agent in aquaculture and laboratory testing. Its high purity ensures reliable performance in analytical applications, including redox titrations and as a pH indicator in specific chemical reactions. Its vivid color and chemical stability make it a valuable reagent in both teaching and professional research settings.
Maleic Acid Extra Pure
Maleic Acid Extra Pure is a high-purity organic compound valued for its strong acidic properties and wide range of laboratory and industrial applications. It appears as a white crystalline solid and is primarily used in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of polymers, resins, and plasticizers. In research laboratories, Maleic Acid serves as a buffering agent, a precursor to fumaric acid, and an intermediate in various chemical reactions. Its excellent solubility in water and compatibility with other reactants make it especially useful in biochemical and analytical procedures. The extra pure grade ensures minimal contamination, providing reliable results in sensitive experiments and high-precision manufacturing processes.
Maltose Extra Pure
Maltose Extra Pure is a disaccharide composed of two glucose units, commonly known as malt sugar. This extra pure grade ensures exceptional quality and consistency, making it ideal for use in biochemical research, fermentation studies, and laboratory analysis. In the food industry, maltose is valued for its mild sweetness and is often used in brewing, baking, and confectionery to promote fermentation and enhance flavor. It also plays a role in energy metabolism studies and is frequently used as a carbon source in microbiological media. Its stability and solubility in water make it easy to incorporate into various formulations, offering a dependable ingredient for scientific and industrial use where high purity is essential.
Manganese Dioxide Extra Pure
Manganese Dioxide Extra Pure is a high-purity, dark brown or black powder widely used in laboratories and industrial processes for its strong oxidizing properties. In analytical chemistry, it serves as an effective oxidizing agent and is often involved in the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and other redox reactions. It is also used in the preparation of oxygen and chlorine gases in laboratory settings. Beyond the lab, manganese dioxide plays a crucial role in battery manufacturing, particularly in dry cell batteries, and in ceramics and glass production for coloring and decolorizing. Its consistent purity makes it ideal for sensitive experiments and formulations.
Manganese Sulphate Extra Pure
Manganese Sulphate Extra Pure is a highly refined, pale pink crystalline compound widely valued for its use in both laboratory and industrial applications. In the lab, it serves as a reliable source of manganese ions in analytical chemistry, synthesis of manganese-based catalysts, and as a micronutrient in biological research. Industrially, it plays a crucial role in fertilizers, where it addresses manganese deficiency in crops, and in animal feed formulations. Due to its high solubility and purity, this compound is also used in electroplating, ceramics, and pigment production, making it a versatile and essential chemical in many scientific and manufacturing settings.
Manganous Dihydrogen Phosphate Extra Pure
Manganous Dihydrogen Phosphate Extra Pure is a high-purity, white to pale pink crystalline compound composed of manganese and phosphate ions. It is primarily used in analytical chemistry, research laboratories, and specialized industrial processes where a precise and reliable manganese source is required. This compound is valued for its solubility in water and its role as a reagent in studies involving nutrient uptake, coordination chemistry, and phosphate-related reactions. Additionally, it finds niche applications in fertilizers and micronutrient formulations, particularly in controlled agricultural studies. Its extra pure grade ensures minimal contamination, making it suitable for sensitive experiments and formulations.
Methyl Orange Disodium Salt Extra Pure
Methyl Orange Disodium Salt Extra Pure is a high-purity pH indicator commonly used in titrations and analytical chemistry to determine acidity levels. It exhibits a sharp color change from red in acidic environments to yellow in alkaline conditions, typically within the pH range of 3.1 to 4.4. This disodium salt form ensures excellent solubility in water, making it especially reliable for use in aqueous solutions. Its stability and sensitivity make it ideal for laboratory applications involving strong acid–base reactions, particularly in titrations of mineral acids. Methyl Orange Disodium Salt Extra Pure is a trusted choice for consistent and accurate results in both educational and professional lab settings.
Methyl Orange Solutions Extra Pure
Methyl Orange Solutions Extra Pure is a ready-to-use, high-grade pH indicator solution widely utilized in acid-base titrations and general analytical chemistry. Known for its distinct and sharp color transition—from red in acidic environments to yellow in alkaline conditions—it provides rapid and clear visual cues for end-point detection. This extra pure formulation ensures maximum accuracy, reliability, and reproducibility in laboratory settings. It is especially effective in titrations involving strong acids and weak bases, commonly used in educational, research, and industrial labs. The solution is precisely prepared to standardized concentrations, eliminating the need for dilution or mixing, and is ideal for professionals seeking precision and ease of use.
Methyl Red Extra Pure
Methyl Red Extra Pure is a high-grade pH indicator commonly used in analytical chemistry, especially in titration processes to identify the endpoint between acidic and basic solutions. It exhibits a clear color change from red in acidic environments (pH below 4.4) to yellow in alkaline conditions (pH above 6.2), making it ideal for monitoring pH transitions in laboratory procedures. Beyond titrations, it is also used in microbiological media to distinguish between types of bacterial metabolism. This extra pure quality ensures excellent sensitivity, precision, and reliability in both educational and professional scientific settings.
Methyl Red Solution Extra Pure
Methyl Red Solution Extra Pure is a ready-to-use, high-purity pH indicator solution widely used in laboratories for acid-base titrations and biochemical assays. It changes color from red at pH below 4.4 to yellow above pH 6.2, making it highly effective in detecting pH shifts with clear visual transitions. This solution is particularly valuable in analytical chemistry, microbiology (such as the methyl red test in bacterial identification), and educational experiments. Its extra pure grade ensures consistent performance, high accuracy, and minimal impurities, making it suitable for precise scientific applications.
Methylene Blue Powder Extra Pure
Methylene Blue Powder Extra Pure is a high-grade dye with diverse laboratory and industrial applications. It is widely used as a biological stain in microscopy for highlighting cellular structures such as nuclei, bacteria, and parasites, particularly in blood smear and bacteriological studies. In chemistry, it serves as a redox indicator due to its distinct color change properties, and in aquaculture, it acts as a treatment for fungal and bacterial infections in fish. Its extra pure formulation ensures maximum staining clarity, minimal contamination, and reliable results in research, diagnostics, and educational settings.
Methylene Blue Solution Extra Pure
Methylene Blue Solution Extra Pure is a ready-to-use aqueous formulation of high-purity methylene blue dye, ideal for laboratory, biological, and analytical applications. It is commonly employed as a vital stain in microscopy to highlight cellular components such as nuclei and mitochondria, especially in live or fixed cells. This solution also functions as a redox indicator in various chemical experiments and is used in microbiology for bacterial identification and differentiation. With its extra pure quality, the solution delivers consistent and precise staining results, making it a reliable tool for research, diagnostics, and teaching laboratories.
Millions Reagent Extra Pure
Millions Reagent Extra Pure is a specialized analytical solution primarily used to detect phenolic amino acids, particularly tyrosine, in proteins. It functions by producing a reddish-brown coloration when heated with compounds containing phenol groups, making it highly valuable in biochemical testing and protein analysis. This reagent is a mixture of mercury(I) and mercury(II) nitrates in nitric acid, and its high purity ensures sharp, interference-free results, especially in sensitive laboratory experiments or educational demonstrations.
Due to its toxic and corrosive nature, proper handling is essential. It must be used in a fume hood with appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Millon’s Reagent remains a reliable and well-established tool for identifying proteins with tyrosine residues and is commonly found in chemical, clinical, and educational labs.
Neutral Red Solution Extra Pure
Neutral Red Solution Extra Pure is a high-purity, ready-to-use solution of the pH indicator dye Neutral Red, widely employed in biological, biochemical, and analytical laboratories. Known for its distinct color change—red in acidic environments and yellow in alkaline—it is commonly used to stain lysosomes in viable cells, making it invaluable in cell viability assays, cytotoxicity studies, and microscopic cell structure investigations.
This Extra Pure grade ensures excellent clarity and precision in results, especially in sensitive microbiological and histological procedures. It is frequently used in conjunction with culture media to observe metabolic activities and in vital staining techniques to differentiate between live and dead cells. Proper handling involves storing it in tightly sealed amber containers away from light and heat to maintain its stability and effectiveness.
Nitric Acid Extra pure
Nitric Acid Extra pure is a high-purity, concentrated mineral acid supplied in a secure 2.5-litre packaging, ideal for laboratory and industrial applications requiring precision and consistency. Known for its strong oxidizing properties, nitric acid (HNO₃) is widely used in analytical chemistry, metal etching, sample digestion, and nitrate salt preparation.
This Extra Pure grade ensures minimal contaminants, making it especially suitable for trace analysis, high-purity synthesis, and quality control laboratories. Its sharp, acrid odor and highly corrosive nature demand careful handling with proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including acid-resistant gloves, goggles, and fume hoods. It must be stored in tightly sealed, compatible containers away from organic materials, bases, and flammable substances. This reagent is essential in both academic research and industrial processes involving nitration reactions, fertilizer formulation, and explosives development.
Pepsin Extra Pure
Pepsin Extra Pure is a highly refined proteolytic enzyme derived from porcine gastric mucosa, widely recognized for its ability to break down proteins into peptides. Appearing as a white to off-white, amorphous powder, it retains strong enzymatic activity and is soluble in dilute acids, making it ideal for biological and analytical applications.
This Extra Pure grade is extensively used in biochemical research, pharmaceutical formulations, digestive studies, and food processing, particularly in the production of protein hydrolysates. It plays a crucial role in simulating gastric digestion in lab experiments and is also employed in diagnostic preparations and enzyme assays. Pepsin should be stored in a tightly sealed container under refrigerated conditions to maintain its activity, and care should be taken to avoid exposure to moisture and alkaline conditions, which can denature the enzyme.
Phenol Detached Crystals Extra Pure
Phenol Detached Crystals Extra Pure is a high-purity form of phenol, presented as colorless to white crystalline solids with a distinct, sharp odor. Known chemically as hydroxybenzene, phenol is both a weak acid and an effective antiseptic, offering versatile utility across laboratory, pharmaceutical, and industrial settings.
This Extra Pure grade is ideal for analytical chemistry, microbiological applications, and organic synthesis, especially in the production of resins, dyes, and plasticizers. It is also used in limited concentrations in medical preparations for its disinfectant properties. Phenol is highly corrosive and toxic upon contact or inhalation, requiring strict adherence to safety precautions, including the use of gloves, goggles, and fume hoods. It should be stored in tightly closed, light-resistant containers in cool, dry areas away from oxidizing agents.
Phenol Red Extra Pure
Phenol Red Extra Pure is a highly refined pH indicator dye widely used in biological and chemical laboratories. Appearing as a reddish crystalline powder, it changes color based on pH—yellow in acidic environments (pH < 6.8), red in neutral to slightly basic conditions (around pH 7.4), and fuchsia in more alkaline solutions (pH > 8.2).
This Extra Pure grade is particularly suited for cell culture media, where it helps monitor pH fluctuations during cell growth and metabolic activity. It is also employed in analytical chemistry, water quality testing, and titrations. Phenol Red is stable under normal storage conditions but should be kept in a dry, tightly sealed container away from strong acids or bases. Proper lab safety protocols—such as wearing gloves and goggles—are recommended when handling the powder or concentrated solutions.
Phenolphthalein Powder Extra Pure
Phenolphthalein Powder Extra Pure is a high-purity pH indicator extensively used in analytical chemistry and laboratory applications. This fine, white to pale pink crystalline powder is colorless in acidic solutions but turns a vivid pink to deep magenta in basic environments, typically transitioning around a pH of 8.2 to 10.0. Its sharp and distinct color change makes it ideal for acid-base titrations, particularly in educational, industrial, and research settings.
In addition to its primary role in titrations, Phenolphthalein is also used in various chemical formulations, soil pH testing, and sometimes as a dye component in forensic applications. Although previously used as a laxative, it is now restricted to laboratory use due to health concerns. It should be handled with care—using gloves, protective eyewear, and in well-ventilated areas—to avoid inhalation or prolonged contact. Store in a cool, dry place, away from strong oxidizers and light.
Phenolphthalein Solution Extra Pure
Phenolphthalein Solution Extra Pure is a laboratory-grade pH indicator solution, commonly used in titration procedures to determine the endpoint of acid-base reactions. It is prepared by dissolving phenolphthalein powder in an appropriate solvent, typically ethanol or water-alcohol mixtures, resulting in a clear, colorless solution that turns vivid pink in basic conditions—usually in the pH range of 8.2 to 10.0.
This high-purity solution offers excellent sensitivity and reliability for analytical chemistry, quality control, and educational demonstrations. It is especially favored in alkalinity testing, neutralization reactions, and various standard laboratory protocols. Proper handling is essential, including the use of gloves and eye protection, as the solution may cause skin or eye irritation upon contact. Store tightly sealed, away from direct light and incompatible substances like strong acids or oxidizers, to maintain its stability and effectiveness.
Phenoxyethano Extra Pure
Phenoxyethano Extra Pure is a high-purity aromatic glycol ether widely used as a preservative, solvent, and stabilizer in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and laboratory formulations. This colorless, slightly viscous liquid possesses a mild pleasant odor and offers effective antimicrobial properties, particularly against Gram-negative bacteria.
Due to its excellent solvency and low volatility, Phenoxyethanol is ideal for use in creams, lotions, serums, and vaccines, where it extends shelf life by preventing microbial growth. In laboratory settings, it serves as a dependable solvent for dyes, resins, and plasticizers. Its low toxicity and compatibility with other preservatives make it a preferred alternative to parabens in personal care products.
Phloretin Extra Pure
Phloretin Extra Pure is a high-grade dihydrochalcone flavonoid renowned for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and skin-penetration-enhancing properties. Derived from apples and certain other fruits, this compound appears as a pale-yellow crystalline powder and is sparingly soluble in water but dissolves well in ethanol and other organic solvents.
In cosmetic and dermatological applications, Phloretin is used to combat oxidative stress, brighten skin tone, and reduce the appearance of fine lines, pigmentation, and UV-induced damage. It also enhances the absorption of active ingredients across the skin barrier, making it a valuable addition to advanced skincare formulations.
In laboratory and pharmaceutical settings, it is utilized for research into cell signaling, anti-cancer mechanisms, and metabolic modulation, given its biological activity on various enzyme systems.
Phosphorous Red Extra Pure
Phosphorous Red Extra Pure is a high-purity allotrope of elemental phosphorus, presented as a dark red to violet amorphous powder. Unlike its white counterpart, red phosphorus is significantly more stable and less reactive at room temperature, making it safer to handle under controlled conditions. It is insoluble in water and most organic solvents and must be stored under inert conditions due to its flammability in finely divided form.
This grade of red phosphorus is commonly used in laboratories for chemical synthesis, pyrotechnics, match production, and flame retardant formulations. In education and research, it is employed in demonstrations of allotropy and in preparing organophosphorus compounds.
Pigment Orange Extra Pure
Pigment Orange Extra Pure is a high-quality organic pigment known for its bright, vibrant orange hue and excellent tinting strength. Comprising 20% active pigment content in a stable carrier base, this formulation ensures consistent dispersion and color intensity in various applications. It is finely milled for enhanced performance in both aqueous and solvent-based systems.
This pigment is widely used in paints, plastics, inks, coatings, and cosmetic formulations, where color consistency, purity, and chemical stability are critical. Its resistance to light, heat, and chemical degradation makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications, particularly in artistic, industrial, and educational settings.
Due to its powdery nature, appropriate dust control and personal protective equipment (PPE) are recommended during handling. Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain its quality and performance.
Poly Aluminium Chloride Extra Pure
Poly Aluminium Chloride Extra Pure is a high-efficiency inorganic coagulant widely used in water treatment, paper manufacturing, and various industrial processes. In its extra pure grade, PAC is characterized by a high degree of purity, minimal impurities, and consistent performance, making it suitable for critical applications requiring stringent quality control.
PAC works by neutralizing the negative charges on suspended particles, allowing them to coagulate and settle quickly. It is highly effective in clarifying drinking water, treating industrial and municipal wastewater, and removing heavy metals, organic matter, and pathogens. Additionally, in the paper industry, PAC improves paper strength and retention of fillers.
This compound should be handled with appropriate PPE, including gloves and eye protection, and stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from reactive substances. PAC is non-flammable but may cause irritation on contact with skin or eyes.
Polydextrose Extra Pure
Polydextrose Extra Pure is a premium-grade synthetic polymer of glucose, widely used as a dietary fiber, bulking agent, and low-calorie carbohydrate substitute in food, pharmaceutical, and nutraceutical applications. Its high purity ensures suitability for laboratory, formulation, and quality-sensitive uses.
This compound is valued for its excellent solubility, neutral taste, and stability across a wide pH range and temperatures. It is commonly incorporated into sugar-free, low-calorie, or high-fiber food products such as baked goods, beverages, and nutritional supplements. In pharmaceutical formulations, it may serve as an excipient or filler in tablets and capsules.
Polydextrose is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) and well-tolerated, though excessive intake may have a mild laxative effect. It should be stored in a cool, dry place, sealed tightly to avoid moisture absorption.
Potassium Bromide Extra Pure
Potassium Bromide Extra Pure is a highly refined, white crystalline compound with the chemical formula KBr, renowned for its exceptional purity and broad utility in scientific, medical, and industrial contexts. Its stable, non-hygroscopic nature and excellent solubility in water make it a reliable reagent in laboratory settings where consistency and accuracy are crucial.
This compound plays a central role in infrared (IR) spectroscopy, particularly for preparing transparent pellets that allow for the clear transmission of IR radiation, enabling the analysis of organic compounds. In the pharmaceutical sector, Potassium Bromide has a legacy use as an anticonvulsant and sedative, especially in veterinary practices for managing seizures. It's also employed in photographic processing in the formulation of light-sensitive silver bromide emulsions and in some chemical synthesis pathways requiring bromide ions.
Potassium Chlorate Extra Pure
Potassium Chlorate Extra Pure is a high-purity, crystalline compound with the chemical formula KClO₃. It appears as a white, odorless solid and is well known for its strong oxidizing properties. In its Extra Pure form, it meets analytical-grade standards, making it suitable for sensitive laboratory and controlled industrial applications.
This chemical is extensively used in analytical chemistry, especially in oxygen production experiments and thermal decomposition studies, as it decomposes to release oxygen when heated. It is also used as a reagent in pyrotechnics, match compositions, and explosive formulations, where a powerful oxidizer is needed. In botanical tissue culture, potassium chlorate is sometimes used to induce flowering in certain plant species.
Due to its reactive and potentially explosive nature, Potassium Chlorate must be handled with extreme caution. It should be stored away from combustible materials, acids, and heat sources, in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, in tightly sealed containers. Personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats must be worn during handling, and it should never be ground or mixed with sulfur, phosphorus, or organic matter unless under strictly controlled conditions.
Potassium Chloride Extra Pure
Potassium Chloride Extra Pure is a high-purity, crystalline inorganic salt with the chemical formula KCl. It appears as a white, odorless, and highly soluble solid, widely used across laboratory, medical, and industrial applications due to its chemical stability and essential role in biological systems.
In laboratory settings, it serves as a reagent in buffer solutions, electrolyte standards, and ionic strength adjustment. In biochemistry, it’s frequently used to prepare isotonic solutions and simulate intracellular fluid composition. Its high purity ensures accuracy in molecular biology, analytical chemistry, and instrument calibration.
Industrially, Potassium Chloride is vital in fertilizer production (as potash), water softening systems, and food processing (as a sodium-free salt alternative).
Potassium Chromate
Potassium Chromate is an inorganic chemical compound and a bright yellow crystalline solid commonly used as an oxidizing agent and pigment. It serves as a source of chromate ions in various chemical, industrial, and laboratory applications. Due to its toxic and carcinogenic nature, careful handling and strict regulatory compliance are essential. Potassium Chromate is widely used in corrosion inhibition, dyeing, and chemical synthesis processes.
Potassium Chromate Extra Pure
Potassium Chromate Extra Pure is a high-purity, bright yellow crystalline compound known for its reliability in precise laboratory analyses. It is commonly used as an indicator in argentometric titrations, particularly for the detection of chloride ions in solution. Its strong oxidizing nature also makes it valuable in various industrial processes, including metal passivation, pigment manufacturing, and dyeing applications. In educational and research laboratories, it serves as a dependable reagent for redox reactions and chemical demonstrations. Given its toxicity and environmental hazards, it should be stored securely and handled using proper protective equipment to ensure safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Potassium Citrate Extra Pure
Potassium Citrate Extra Pure is a fine, white crystalline powder recognized for its high solubility in water and excellent buffering capabilities. It is widely used in analytical chemistry and pharmaceutical formulations, particularly as a systemic alkalizer to manage conditions such as kidney stones or metabolic acidosis. In laboratories, it serves as a buffering agent in biochemical applications, helping to maintain stable pH conditions. Its compatibility with food and pharmaceutical standards also makes it useful in food science for flavor enhancement and preservation. This compound should be stored in a tightly sealed container in a dry environment to maintain its stability and prevent moisture absorption.
Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate Extra Pure
Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate Extra Pure, also known as monopotassium phosphate (MKP), is a white crystalline compound with excellent solubility in water and a slightly acidic pH. It serves as a valuable buffering agent and a source of both potassium and phosphorus in various chemical, agricultural, and food-grade applications. In laboratories, it is commonly used in the preparation of buffer solutions and nutrient media for microbial culture. In agriculture, it is employed as a high-efficiency fertilizer due to its dual nutrient content, promoting strong root development and flowering. This compound should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible substances and moisture to preserve its purity and effectiveness.
Potassium Hydrogen Carbonate Extra Pure
Potassium Hydrogen Carbonate Extra Pure, also known as potassium bicarbonate, is a fine white crystalline powder with excellent purity and stability. It is commonly used in laboratories as a buffering agent due to its mild alkalinity. In food processing, it functions as a leavening agent and pH regulator, and in agriculture, it is applied as a fungicide and a source of potassium. Its high solubility in water and non-toxic nature make it a versatile and safe compound for a range of analytical and technical applications. Proper storage in tightly sealed containers, away from moisture and acids, ensures optimal shelf life and performance.
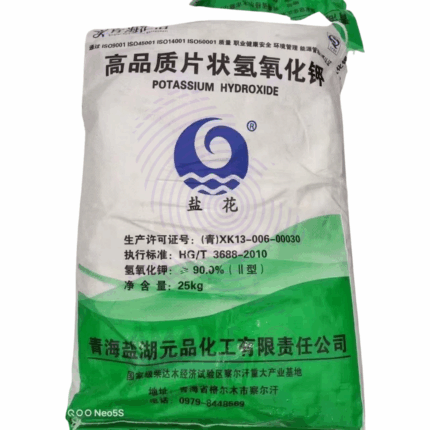
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium Hydroxide is a highly concentrated, caustic alkaline chemical available as a solid (pellets, flakes) or concentrated aqueous solution. It is a strong base widely used in industrial processes, chemical manufacturing, and as a reagent. Potassium Hydroxide provides excellent neutralizing, saponifying, and cleaning properties and is essential in producing potassium soaps, biodiesel, fertilizers, and various chemical compounds. Its high purity and concentration (90%) make it suitable for demanding applications requiring strong alkalinity.
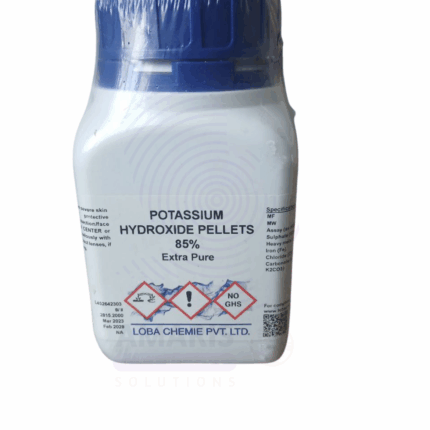
Potassium Hydroxide Pellets Extra Pure
Potassium Hydroxide Pellets Extra Pure are solid, white, hygroscopic pellets known for their strong alkalinity and high reactivity. This compound is widely used in laboratories for pH adjustment, titrations, and chemical synthesis. In industrial settings, it plays a key role in soap and detergent manufacturing, biodiesel production, and water treatment processes. Its ability to absorb moisture and carbon dioxide from the air requires careful storage in airtight containers. With exceptional purity and consistent performance, it is a critical reagent in both academic and industrial chemistry environments.
Potassium Iodide Extra Pure
Potassium Iodide Extra Pure is a high-purity, white crystalline salt widely recognized for its excellent solubility in water and its versatile applications. In laboratories, it is commonly used as a reagent in iodometric titrations and for preparing iodine solutions. In the medical field, it serves as a key source of iodine and is used for thyroid protection against radioactive iodine exposure. Its antioxidant properties also make it valuable in pharmaceutical formulations and as a stabilizer in various chemical processes. The extra pure grade ensures maximum consistency and reliability for precise experimental and industrial outcomes.
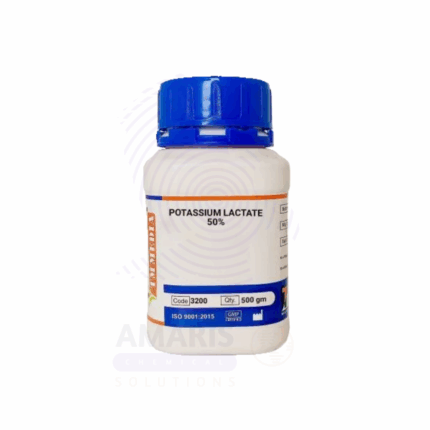
Potassium Lactate Extra Pure
Potassium Lactate Extra Pure is a colorless to pale yellow, clear, viscous liquid known for its high purity and effectiveness as a buffering and humectant agent. It is widely used in food processing as a preservative and moisture-retaining compound, especially in meat and poultry products to enhance shelf life and flavor retention. In pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications, it functions as a pH regulator and skin-conditioning agent due to its mild and non-irritating nature. Its extra pure grade ensures consistent performance and safety in sensitive formulations, making it suitable for laboratory, medical, and high-standard industrial uses.
Potassium Nitrate Extra Pure
Potassium Nitrate Extra Pure is a high-purity, crystalline chemical compound widely used in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, and food-grade applications. It serves as a strong oxidizing agent, commonly employed in analytical chemistry, fertilizer formulation, and pyrotechnics. In pharmaceutical settings, it may be used in toothpaste for sensitive teeth, while in food processing, it can function as a preservative under strict regulatory control. Its extra pure grade ensures low levels of impurities, making it ideal for precision-dependent procedures. The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances to maintain its stability and reactivity.
Potassium Permanganate Extra Pure
Potassium Permanganate Extra Pure is a powerful oxidizing agent recognized for its deep purple crystals and wide range of applications. In laboratory settings, it is frequently used in redox titrations, organic synthesis, and as a disinfectant due to its strong antiseptic properties. This compound is also valued in water treatment for removing iron, hydrogen sulfide, and organic impurities. Its extra pure grade guarantees high chemical integrity, making it ideal for analytical procedures, research work, and high-precision industrial uses where purity is critical.
Potassium Sorbate Extra Pure
Potassium Sorbate Extra Pure is a high-grade preservative commonly used in laboratory research, food preservation, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Known for its effectiveness in inhibiting the growth of molds, yeasts, and fungi, it is a preferred choice for extending shelf life in various formulations. Its excellent solubility in water and low toxicity make it suitable for sensitive applications where purity is critical. In food and beverage testing or development, it plays a key role in microbial control without altering taste or color. The extra pure designation ensures minimal impurities, supporting accurate and consistent experimental or formulation outcomes.
Potassium Sulphate Extra Pure
Potassium Sulphate Extra Pure is a premium-grade inorganic salt widely used in laboratories and industrial research. It serves as a reliable source of both potassium and sulfur, making it essential in analytical chemistry, fertilizer testing, and solution preparation. Its high solubility and chemical stability allow it to be used in qualitative and quantitative analysis, as well as in preparing culture media. The extra pure quality ensures that it contains minimal contaminants, providing consistent performance in sensitive experimental procedures, including high-purity formulations and calibration standards.
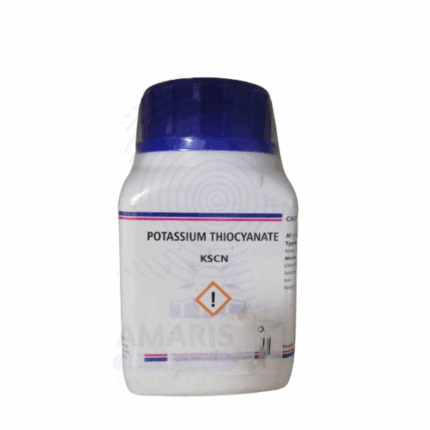
Potassium Thiocyanate Extra Pure
Potassium Thiocyanate Extra Pure is a high-purity crystalline compound commonly used in analytical chemistry, forensic science, and complexometric titrations. Known for forming deeply colored complexes with iron and other metal ions, it is frequently employed as a qualitative reagent for detecting ferric ions. In laboratory environments, it also plays a role in spectrophotometric analysis, chemical synthesis, and photographic processing. Its extra pure grade ensures exceptional clarity and consistency in results, making it suitable for precision applications where reagent-grade chemicals are not sufficient.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders






























![Nickel Sulphate [NiSO4(H2O)6] Extra Pure Amaris Chemicals](https://amarischemicalsolutions.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Nickel-Sulphate-NiSO4H2O6-Extra-Pure-Amaris-Chemicals-430x430.png)