Acetic Acid Tech grade
Acetic acid Tech grade
Acetic acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, sour taste and a distinctive vinegar-like odor. Acetic acid is an important industrial chemical used in the production of various products, including solvents, plastics, textiles, and food additives. It is also the main component of vinegar, which is commonly used as a condiment and preservative in cooking and food preparation.Activated Carbon
Activated carbon, also known as activated charcoal, is a highly porous material that is produced by treating carbon-rich organic materials, such as wood, coconut shells, or peat, with heat and chemicals to create a network of pores and a large surface area. This high surface area and porosity make activated carbon an excellent adsorbent for a wide range of substances, including organic molecules, gases, and liquids. It is widely used in various applications, such as water treatment, air purification, food and beverage processing, and medical treatments.
Aluminium sulphate Alum Rock
Aluminium sulphate, also known as alum, is a chemical compound made up of aluminium, sulphur and oxygen. It has the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3 and is commonly used in water treatment plants as a coagulant to remove impurities such as suspended particles, organic matter, and bacteria from water.
Alum is a white crystalline substance that dissolves in water to form a colourless solution. It has a variety of other applications, including in the manufacturing of paper, textiles, and in various industrial processes. In addition, alum has medicinal uses as an astringent and as a component of antiperspirants.
Aluminium Sulphate powder (Alum)
Aluminium Sulphate powder (Alum)
Aluminium sulphate, also known as alum, is a chemical compound made up of aluminium, sulphur and oxygen. It has the chemical formula Al2(SO4)3 and is commonly used in water treatment plants as a coagulant to remove impurities such as suspended particles, organic matter, and bacteria from water.
Alum is a white crystalline substance that dissolves in water to form a colourless solution. It has a variety of other applications, including in the manufacturing of paper, textiles, and in various industrial processes. In addition, alum has medicinal uses as an astringent and as a component of antiperspirants.
Overall, aluminium sulphate or alum is a versatile compound with a range of practical uses in various industries and applications.
Ammonium bicarbonate
Ammonium bicarbonate is a white, crystalline compound with the chemical formula NH4HCO3. It is a type of inorganic salt that is commonly used in the food industry as a leavening agent for baking, as well as in the production of ceramics, dyes, and other chemicals. When heated, ammonium bicarbonate decomposes into ammonia, carbon dioxide, and water vapor, which causes dough to rise and become light and fluffy. It is also known as hartshorn or baker's ammonia.
Ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid, also known as vitamin C, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays an important role in various physiological processes in the human body. It is an essential nutrient that cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through dietary sources or supplements. Ascorbic acid acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells and tissues from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a critical role in the production of collagen, which is important for the health of skin, bones, and other connective tissues. Additionally, ascorbic acid is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the metabolism of proteins and fats. Deficiency in ascorbic acid can lead to a range of health problems, including scurvy, a condition characterized by fatigue, weakness, and bleeding gums.
Bentonite Powder
Bentonite powder is a naturally occurring, highly absorbent clay-like substance derived from volcanic ash. It is composed primarily of montmorillonite, a mineral that is known for its ability to absorb water and other liquids. Bentonite powder is commonly used in a variety of industries, including construction, drilling, and cosmetics, due to its unique properties such as its ability to swell and form a gel-like substance when it comes into contact with water, making it useful as a binding, thickening, and clarifying agent.
Bleaching Earth
Bleaching earth is a vital industrial adsorbent that purifies oils, fats, and fuels by removing impurities, improving quality, and ensuring stability. Its effectiveness, versatility, and cost-efficiency make it indispensable in food processing, biofuels, petrochemicals, and environmental applications.
Borax Decahydrate
Borax decahydrate, also known as sodium borate, is a naturally occurring mineral composed of sodium, boron, oxygen, and water. It is a white, odorless powder that dissolves easily in water, and has a wide range of uses, including as a laundry detergent booster, a multipurpose cleaner, and as a component in the production of glass, ceramics, and enamel. Borax has antifungal and insecticidal properties and is also used in certain industrial applications such as in the production of fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, and as a fire retardant. It is considered safe when used as directed, but can be toxic if ingested in large quantities.
Borax Pentahydrate
Borax Pentahydrate, also known as sodium borate, is a naturally occurring mineral composed of sodium, boron, oxygen, and water. It is a white, odorless powder that dissolves easily in water, and has a wide range of uses, including as a laundry detergent booster, a multipurpose cleaner, and as a component in the production of glass, ceramics, and enamel. Borax has antifungal and insecticidal properties and is also used in certain industrial applications such as in the production of fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, and as a fire retardant. It is considered safe when used as directed, but can be toxic if ingested in large quantities.
Boric Acid
Boric acid is a weak, water-soluble acid that occurs naturally in some minerals, volcanic waters, and hot springs. It is a white, odorless, and crystalline powder that is often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, and in various industrial applications. Boric acid is also commonly used in households as an eyewash, as a preservative for food and cosmetics, and as an ingredient in some laundry and cleaning products. It is considered a safe and effective substance when used properly, but can be toxic in high doses.
Calcium Carbonate (uncoated)
Calcium Carbonate (uncoated) refers to a natural mineral substance that is composed of calcium carbonate without any additional coatings or surface treatments. It is a white, powdery material that is commonly used in various industrial applications, including the manufacture of paper, paints, plastics, and rubber products, as well as in construction, agriculture, and the food and pharmaceutical industries. Uncoated calcium carbonate is typically mined from natural deposits of limestone or chalk and is often ground into fine particles to achieve the desired particle size and purity for specific applications
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CaCl2. It is a salt composed of calcium and chlorine ions and is highly soluble in water. Calcium chloride is commonly used as a desiccant, de-icer, and in various industrial processes. It is also used in food and beverage applications as a firming agent, and in medicine as a source of calcium for people with calcium deficiencies.
Calcium chloride Dihydrate
Calcium chloride dihydrate is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CaCl2·2H2O. It is a crystalline salt that is highly soluble in water and has a variety of industrial and medical applications. It is commonly used as a desiccant to absorb moisture, as a de-icing agent for roads and sidewalks, and as a food preservative. It is also used in the production of cement, as a laboratory reagent, and in medicine as a source of calcium for intravenous therapy.
Calcium Hydroxide(Hydrated lime)
Calcium Hydroxide(Hydrated lime) , also known as hydrated lime, is a chemical compound with the formula Ca(OH)2. It is a white, odorless, and alkaline substance that is produced by adding water to calcium oxide, also known as quicklime. The resulting reaction produces calcium hydroxide and releases a large amount of heat.
Hydrated lime is commonly used in various industrial applications such as water treatment, construction, agriculture, and food processing. It is also used as a pH regulator and a flocculant in wastewater treatment plants. Additionally, it is used in the production of cement, as a soil stabilizer, and in the manufacture of chemicals such as calcium stearate and calcium hypochlorite.
In summary, calcium hydroxide, or hydrated lime, is a chemical compound with various industrial applications, produced by adding water to calcium oxide.
Calcium propionate
Calcium propionate is a food additive that is commonly used as a preservative to prevent the growth of mold and other microorganisms in various food products. It is the calcium salt of propionic acid and is often referred to by its chemical formula, Ca(C2H5COO)2. Calcium propionate is white crystalline powder or granules that are easily soluble in water. When added to food, it helps extend its shelf life by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and molds, thereby preventing spoilage. It is commonly used in baked goods, dairy products, processed meats, and other foods where mold and bacterial growth are a concern.
Calcium Saccharin
Calcium saccharin, also known as calcium cyclamate, is a synthetic sweetener derived from saccharin. It is a calcium salt of saccharin, and it is often used as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products. Calcium saccharin is several hundred times sweeter than sugar, yet it contains no calories and does not affect blood sugar levels, making it suitable for individuals with diabetes or those looking to reduce their sugar intake. It is commonly used in tabletop sweeteners, diet sodas, baked goods, and other low-calorie or sugar-free products
Dextrose Monohydrate
Dextrose monohydrate is a simple sugar derived from corn starch and commonly used as a food additive or sweetener. It is a white, crystalline powder that consists of glucose molecules with one molecule of water attached. Dextrose monohydrate is chemically identical to glucose and is often referred to as a glucose monohydrate.
In the food industry, dextrose monohydrate is valued for its sweet taste, high solubility, and ability to enhance flavors. It is frequently used in the production of confectionery, baked goods, beverages, and dairy products. Dextrose monohydrate is also utilized in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly as a source of energy for intravenous solutions or in oral rehydration products.
Overall, dextrose monohydrate is a versatile and widely used ingredient known for its ability to provide sweetness, solubility, and energy, making it a valuable component in various industries.
Diammonium phosphate (DAP)
Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a water-soluble ammonium phosphate salt with the chemical formula (NH₄)₂HPO₄. It serves as an important source of nitrogen (18%) and phosphorus (46%), making it widely useful in agriculture as a high-efficiency NP fertilizer to promote plant growth. Beyond farming, DAP is used as a yeast nutrient in winemaking/brewing, a fire retardant in industrial applications, and a corrosion inhibitor in water treatment systems. It also finds roles in animal feed supplements, pyrotechnics, and laboratory reagents. With its alkaline pH (~8.0) and solubility, DAP is versatile but requires careful handling due to ammonia release when heated.
Dicalcium phosphate
Dicalcium phosphate is a chemical compound with the formula CaHPO4. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement for its high calcium content, as well as a food additive and a pharmaceutical excipient. Dicalcium phosphate can be produced by reacting calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide with phosphoric acid. It exists in various forms, including anhydrous and dihydrate, and is commonly used in the production of fertilizers, animal feed, and dental products.
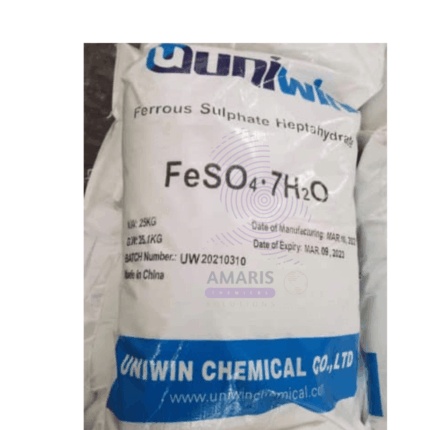
Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate
Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate is a chemical compound with the formula FeSO4, which is made up of iron, sulfur, and oxygen. It is a type of salt that is commonly used as a nutritional supplement and a medicine to treat iron deficiency anemia. Ferrous sulfate is also used in various industrial applications, such as water treatment, fertilizers, and pigments. In its solid form, ferrous sulfate appears as a white or grayish-white crystalline powder, and it is soluble in water.
Formalin Formaldehyde
Formalin Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a pungent odor, which is used as a disinfectant, preservative, and in the production of various materials and chemicals.
Formalin is a solution of formaldehyde gas in water, typically containing 37% formaldehyde by volume. It is commonly used as a tissue preservative in biological specimens for medical and research purposes. Formalin is also used in various industrial applications such as manufacturing plastics, resins, and textiles.
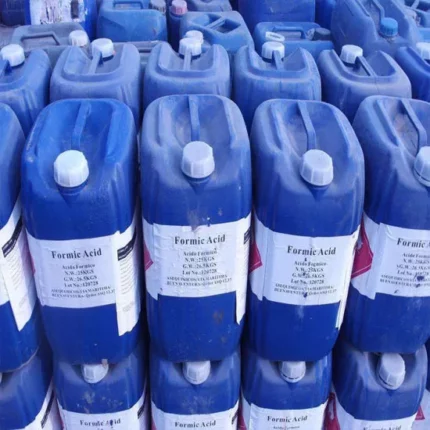
Formic Acid
Formic acid is a colorless, pungent liquid with a chemical formula of HCOOH. It is the simplest carboxylic acid, naturally occurring in certain fruits and vegetables and in the venom of some ants. It has a wide range of industrial applications as a preservative, antibacterial agent, solvent, and in the production of textiles, leather, rubber, and other materials. It also has some medical applications and is used in organic chemistry reactions as a reducing agent. However, formic acid is highly corrosive and can be dangerous if ingested or inhaled in large quantities.
Kaolin
Magadi Soda-Soda ASh
Magadi Soda (Soda ASh)
Magadi Soda-Soda ASh, also known as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), is a white, crystalline powder or solid substance that is widely used in various industrial and domestic applications. It is an essential compound in the chemical industry and has numerous uses in manufacturing, water treatment, glass production, detergents, and several other processes. Soda ash is primarily composed of sodium ions (Na+) and carbonate ions (CO3^2-). It can be derived from natural sources, such as trona ore or sodium carbonate-rich brines, or produced synthetically through the Solvay process. The chemical formula for soda ash, sodium carbonate, represents its composition: two sodium atoms (Na) bonded to a carbonate group (CO3). This compound has alkaline properties and is soluble in water, forming an alkaline solution. Its ability to act as a pH regulator and its alkalinity make soda ash a valuable ingredient in many industrial applications.Urea 50 kg
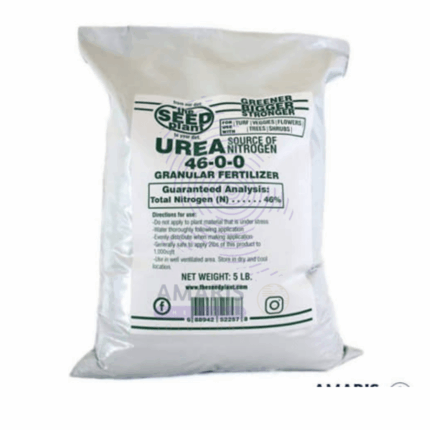
Urea is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH2)2. It is a crystalline substance that is highly soluble in water. Urea is produced naturally in the bodies of mammals as a byproduct of protein metabolism and is excreted in urine. It is also synthetically produced on a large scale for various industrial applications.
In simple terms, urea is a nitrogenous compound that contains two amine groups (-NH2) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O). It plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle, serving as a primary vehicle for the excretion of nitrogenous waste in mammals. Urea is commonly used as a fertilizer in agriculture due to its high nitrogen content, and it is also utilized in the production of plastics, resins, adhesives, and various other industrial applications.
Select options
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters