Corn Starch (food grade)
Corn Starch (food grade) is a fine, powdery substance derived from the endosperm of corn kernels. It is commonly used as a thickening agent in cooking and baking, as well as in other industries such as papermaking, textiles, and adhesives. Corn starch has a neutral flavor and a translucent appearance when mixed with liquid, making it a versatile ingredient in many recipes.
Corn Starch (Industrial grade)
Corn Starch (Industrial grade) is a fine, powdery substance derived from the endosperm of corn kernels. It is commonly used as a thickening agent in cooking and baking, as well as in other industries such as papermaking, textiles, and adhesives. Corn starch has a neutral flavor and a translucent appearance when mixed with liquid, making it a versatile ingredient in many recipes.
Corn Syrup
Corn syrup is a sweetener made from cornstarch that undergoes a process called hydrolysis, which breaks down the starch into smaller sugar molecules. It is a thick, sticky liquid with a high concentration of glucose and other sugars, primarily derived from corn. Corn syrup is commonly used in the food industry as a sweetening agent, and it serves as an ingredient in a variety of products such as candies, baked goods, soft drinks, and processed foods. Its purpose is to enhance sweetness, provide moisture, and contribute to the texture and stability of food products.
Cotton twine
Cotton twine is a strong and durable cord or string made from cotton fibers. It is typically twisted or braided, providing a versatile and natural material for various applications, such as packaging, gardening, crafting, and cooking. Cotton twine is known for its softness, pliability, and ability to hold knots securely, making it useful in a wide range of tasks where a reliable and biodegradable cord is needed.
Cotton twine
Cotton twine is a strong, durable, and versatile natural fiber string made from 100% cotton. Known for its soft texture and flexibility, it is easy to handle and knots securely, making it ideal for a variety of applications. Available in different thicknesses and colors, cotton twine is commonly used in crafting, gardening, and baking, as well as for packaging and decorative purposes. Its biodegradable nature makes it an eco-friendly choice, suitable for both functional and artistic projects. Whether you're tying plants, wrapping gifts, or creating handmade crafts, cotton twine is a reliable and attractive option.
Craymide 115 epoxy hardener
Cresol Red Indicator 25gm
Cresol Red is a pH indicator dye commonly used in titrations and other laboratory experiments to determine the pH of a solution. It changes color based on the acidity or basicity of the solution it is in. Here are its key characteristics:
- Chemical Structure: Cresol Red is a sulfonephthalein dye with the molecular formula C21H18O5S.
- Color Change: It transitions from yellow in acidic solutions (pH < 1.8) to red in neutral solutions (pH around 7.0), and then to purple in basic solutions (pH > 8.8).
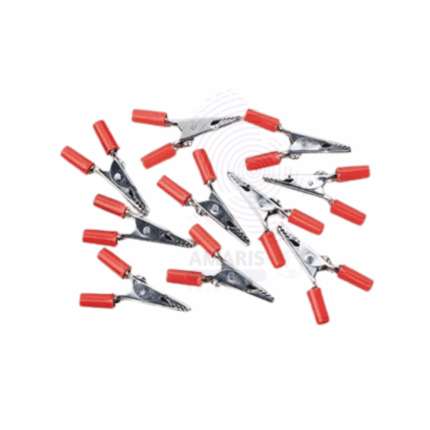
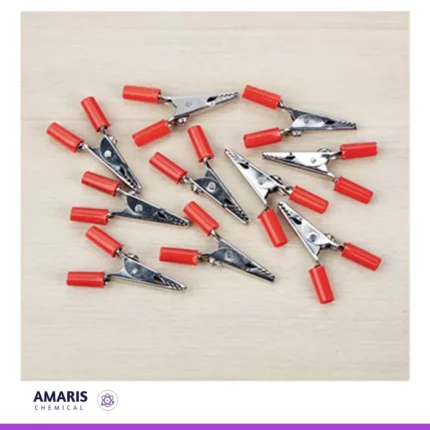
Crocodile clips
Crocodile clips, also known as alligator clips, are versatile electrical connectors featuring a spring-loaded, hinged jaw that resembles a crocodile’s mouth. Typically made of metal and often coated with an insulating material, these clips provide a secure grip on wires, terminals, or other conductive materials. They are designed to create temporary electrical connections in circuits, making them ideal for experiments, testing, and prototyping. Their ease of use and reliability make crocodile clips essential tools in laboratories, workshops, and educational settings, allowing for quick assembly and disassembly of electrical components.
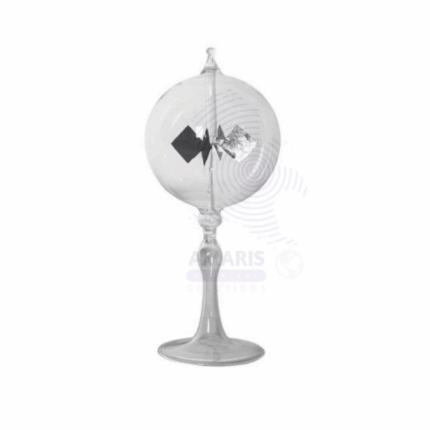
crooks radiometer
The Crookes radiometer, also known as a light mill, is a fascinating scientific instrument that consists of a glass bulb containing a vacuum and a lightweight rotor mounted on a spindle. The rotor features a series of vanes, typically painted black on one side and white or reflective on the other. When exposed to light, particularly sunlight or a strong light source, the vanes spin, with the black side moving away from the light source and the white side moving toward it.
This seemingly paradoxical motion occurs due to the differential heating of the vanes: the black surface absorbs more light energy and heats up more than the white surface, creating a temperature difference that results in a pressure difference of the residual gas molecules within the vacuum. This causes the rotor to spin, demonstrating the conversion of light energy into mechanical energy. The Crookes radiometer serves as an engaging educational tool, illustrating fundamental concepts in physics, such as light absorption, thermal dynamics, and energy transfer.
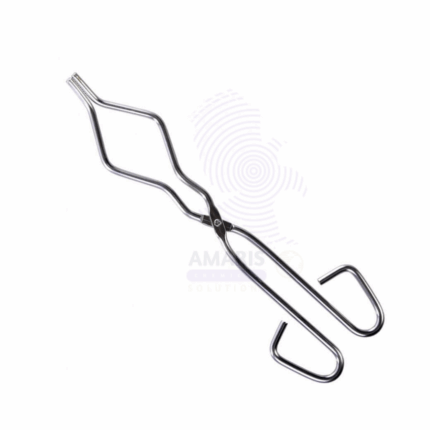
Crucible tongs
Lab crucible tongs are a laboratory tool designed for safely handling small containers called crucibles, typically made of ceramic or metal, when they are hot. These tongs consist of two arms with curved, pointed tips that can be used to grip the crucible securely and maneuver it without direct contact, protecting the user from burns or other hazards associated with high-temperature materials.
Crucible Tongs
Crucible tongs are specialized laboratory tools designed for the safe handling of hot crucibles and other heated materials. Typically made from heat-resistant metal or alloys, they feature long handles that allow users to maintain a safe distance from high temperatures. The gripping end is often shaped with a curved or pointed design, ensuring a secure hold on crucibles or glassware while minimizing the risk of spills or burns.
These tongs are essential for tasks such as transferring crucibles to and from furnaces, removing hot glassware, and handling various types of heated containers in chemical and materials research. Their ergonomic design enhances precision and control, making them indispensable for laboratory safety and efficiency.
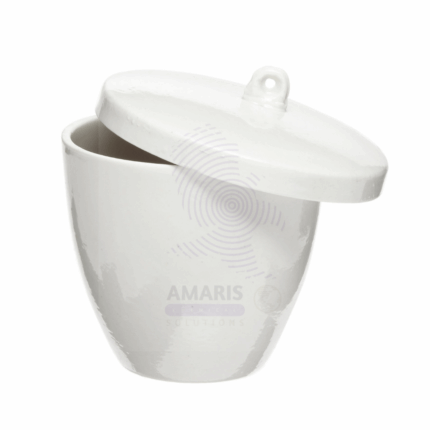
crucible with lid
A crucible with a lid is a small, heat-resistant container typically made of ceramic or metal, designed for high-temperature applications in laboratories. The lid serves to cover the crucible, minimizing heat loss, reducing the risk of contamination, and containing volatile substances during heating processes. Crucibles come in various sizes and shapes, often with a spout for easy pouring. They are essential for melting metals, conducting chemical reactions, ashing samples, and performing thermal analysis, providing a controlled environment for a range of experimental procedures. Their robust construction ensures durability and reliability in demanding laboratory settings.
Crystal Violet 1% alcohol solution 25gm
Crystal Violet, also known as gentian violet, is a synthetic dye with antibacterial and antifungal properties. It's commonly used in microbiology as a staining agent to visualize bacteria and other microorganisms under the microscope.
A 1% alcohol solution of Crystal Violet would mean that 1 gram of Crystal Violet dye is dissolved in 100 milliliters of alcohol. This solution is typically used in Gram staining, a differential staining technique used to classify bacteria into two groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
In Gram staining, Crystal Violet is the primary stain that imparts a purple color to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The alcohol serves as a solvent and fixative, helping the dye penetrate the bacterial cell wall and retain its color during the staining process.
Cupric Carbonate 500gm
Cupric carbonate, also known as copper(II) carbonate, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCO3. It exists in nature as several different minerals, including malachite and azurite, which are valued for their vibrant green and blue colors, respectively. Cupric carbonate can also be synthesized in the laboratory.
In its natural form, cupric carbonate is often used as a pigment in paints and dyes due to its striking color. It has also been used historically as a source of copper in various applications, including as a fungicide in agriculture.
Cupric carbonate is insoluble in water, but it can react with acids to form soluble copper salts. Additionally, it can decompose upon heating to release carbon dioxide and form copper(II) oxide.
It's important to handle cupric carbonate with care, as copper compounds can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in large quantities.
Cupric Chloride 250gm
Cupric chloride, also known as copper(II) chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula CuCl₂. It appears as a yellowish-brown powder in its anhydrous form and turns into a blue-green crystalline solid when hydrated. This compound is highly soluble in water, forming a blue solution.
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuCl₂
- Molecular Weight: 134.45 g/mol
- Appearance: Yellowish-brown powder (anhydrous), blue-green crystals (hydrated)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water and ethanol
Cupric Oxide 100gm
Cupric oxide, also known as copper(II) oxide, is a black solid with the chemical formula CuO. It is a significant compound of copper and has various applications in different fields. Here are some key points about cupric oxide:
Properties:
- Chemical Formula: CuO
- Appearance: Black or dark brown powder.
- Molecular Weight: 79.545 g/mol
- Melting Point: 1,326 °C (2,419 °F)
- Density: 6.315 g/cm³
- Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in acids.
Production:
Cupric oxide can be produced by several methods, including:- Thermal Decomposition: Heating copper(II) nitrate, copper(II) carbonate, or copper(II) hydroxide in the absence of oxygen.
- Direct Oxidation: Heating metallic copper in the presence of oxygen.
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
Cupric sulfate anhydrous refers to the form of copper(II) sulfate that does not contain water molecules in its crystal structure. It is used similarly to the hydrated form (cupric sulfate pentahydrate) in laboratory settings, often in analytical chemistry and as a source of copper ions in various reactions and processes.
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate
Daniel cell
Deflagrating Spoon
A deflagrating spoon is a laboratory utensil designed for heating small quantities of solids. Typically made of heat-resistant materials like metal, it features a shallow, bowl-like structure with a long handle. This design allows for safe handling and manipulation of reactive or flammable substances. The spoon is used primarily to conduct combustion reactions, melt solids, or carry out small-scale heating experiments while minimizing direct exposure to flames. Its ability to provide controlled heating makes it an essential tool in chemistry and materials science labs.
Defoamer
Defoamer, also known as an anti-foaming agent, is a chemical additive that reduces and eliminates foam formation in liquids. Foam is formed when gas is trapped in a liquid, and it can cause problems in various industrial processes, such as in the production of food and beverages, pulp and paper, and wastewater treatment. Defoamers work by destabilizing foam bubbles and breaking them apart, allowing the gas to escape from the liquid. They typically contain surfactants or oils that spread over the surface of the liquid to disrupt foam formation. Defoamers are available in various forms, including liquid, powder, and emulsion, and are used in a wide range of industries to improve process efficiency and product quality
Deionized water
Deionized water, also known as demineralized water, is water that has had its mineral ions (such as sodium, calcium, iron, and copper) and dissolved solids removed through a process called ion exchange.
Distilled water, on the other hand, is water that has been purified by boiling it into steam and then condensing the steam back into water. This process removes impurities such as minerals, bacteria, and other contaminants.
Both deionized and distilled water are highly purified forms of water, but the processes used to purify them are different. Deionized water is typically used in laboratory settings or in industrial processes, while distilled water is commonly used in medical applications, humidifiers, and in some consumer products
Desiccated coconut 25kg
Desiccated coconut is a dried, grated, and shredded coconut meat that has had most of its moisture removed. It is typically produced by taking fresh coconut meat, removing the outer husk, and then shredding or grating the white meat. The resulting coconut meat is then dried through various methods, such as hot air drying or sun drying, until it has a low moisture content, typically around 3%. Desiccated coconut is commonly used as an ingredient in baking and confectionery, and can also be used as a topping or coating for desserts or savory dishes.
Dessicated Coconut (DCMF)
Dessicated Coconut (DCMF) is a dried and finely grated form of coconut meat, processed to remove nearly all moisture (typically below 3%). Made by shredding fresh coconut kernel and then dehydrating it through baking or hot-air drying, it retains the natural flavor and nutritional benefits of coconut while extending shelf life. Available in fine, medium, or coarse textures, it is widely used in baking (cookies, cakes, macaroons), confectionery (chocolates, energy bars), and traditional dishes (curries, chutneys). Rich in healthy fats, fiber, and minerals like iron, it serves as a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory recipes. Beyond food, it finds applications in cosmetics (scrubs, hair masks) and even animal feed. Whether toasted, raw, sweetened, or unsweetened, desiccated coconut adds a distinct tropical taste and texture to culinary creations while offering a long-lasting, convenient alternative to fresh coconut.
Dextrose Monohydrate
Dextrose monohydrate is a simple sugar derived from corn starch and commonly used as a food additive or sweetener. It is a white, crystalline powder that consists of glucose molecules with one molecule of water attached. Dextrose monohydrate is chemically identical to glucose and is often referred to as a glucose monohydrate.
In the food industry, dextrose monohydrate is valued for its sweet taste, high solubility, and ability to enhance flavors. It is frequently used in the production of confectionery, baked goods, beverages, and dairy products. Dextrose monohydrate is also utilized in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly as a source of energy for intravenous solutions or in oral rehydration products.
Overall, dextrose monohydrate is a versatile and widely used ingredient known for its ability to provide sweetness, solubility, and energy, making it a valuable component in various industries.
Dextrose monohydrate 500gms
Dextrose monohydrate, also known as glucose monohydrate, is commonly used in laboratories for various purposes, especially in biological and biochemical experiments. Here are a few ways it might be used:
- Culture Media: Dextrose monohydrate is often included in culture media for microbial growth. It serves as a carbon source for microorganisms.
- Cell Culture: In cell culture, dextrose monohydrate can be used as an energy source for cells. It provides glucose, which is a vital nutrient for cell growth.
- Buffer Solutions: It can be used in buffer solutions to maintain pH levels during experiments, especially those involving enzymatic reactions or other biochemical processes.
- Analytical Chemistry: In analytical chemistry, dextrose monohydrate can be used as a standard for calibrating instruments or as a reagent in various assays.
- Freezing Medium: It can be included in freezing media for the preservation of biological samples.
- Chemical Synthesis: Dextrose monohydrate may also be used as a reactant or a reducing agent in various chemical synthesis reactions.
Dextrose Monohydrate glucose 500gm
Dextrose monohydrate is a simple sugar derived from corn starch and commonly used as a food additive or sweetener. It is a white, crystalline powder that consists of glucose molecules with one molecule of water attached. Dextrose monohydrate is chemically identical to glucose and is often referred to as a glucose monohydrate.
In the food industry, dextrose monohydrate is valued for its sweet taste, high solubility, and ability to enhance flavors. It is frequently used in the production of confectionery, baked goods, beverages, and dairy products. Dextrose monohydrate is also utilized in pharmaceutical formulations, particularly as a source of energy for intravenous solutions or in oral rehydration products.
Di-sodium Tetraborate (Borax) 500grams
Di-sodium Tetraborate, also known as sodium borate, is a naturally occurring mineral composed of sodium, boron, oxygen, and water. It is a white, odorless powder that dissolves easily in water, and has a wide range of uses, including as a laundry detergent booster, a multipurpose cleaner, and as a component in the production of glass, ceramics, and enamel. Borax has antifungal and insecticidal properties and is also used in certain industrial applications such as in the production of fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, and as a fire retardant. It is considered safe when used as directed, but can be toxic if ingested in large quantities.


 Emollients
Emollients Humectants
Humectants UV Filters
UV Filters Surfactants (cosmetic)
Surfactants (cosmetic) Preservatives (cosmetic)
Preservatives (cosmetic) Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Antioxidants (cosmetics)
Antioxidants (cosmetics)
 Solvents (lab)
Solvents (lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents
Microbiology and Cell Culture Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents
 Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers
Stabilizers Monomers
Monomers Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Antioxidants (plastics)
Antioxidants (plastics) Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
Colorants (plastic pigments,Dyes)
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants
 Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Preservatives (baking)
Preservatives (baking)
 Surfactants (cleaning)
Surfactants (cleaning) Builders
Builders Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (cleaning)
Solvents (cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances Disinfectant
Disinfectant Metal cleaning
Metal cleaning
 Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Pigments
Pigments Solvents (paint)
Solvents (paint) Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Preservatives (food)
Preservatives (food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers Antioxidants (food)
Antioxidants (food) Colorants (food)
Colorants (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Whole Spices
Whole Spices Ground Spices
Ground Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends
 Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil)
 Antibiotics
Antibiotics Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients Excipients
Excipients Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients
Nutraceutical Ingredients Solvents (pharmaceutical)
Solvents (pharmaceutical)
 Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals


 Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders Antidegradants
Antidegradants Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters