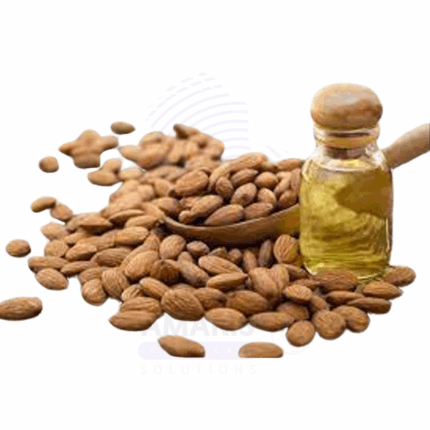
Almond Bitter Oil
Almond Bitter Oil, derived from the kernels of bitter almonds (Prunus amygdalus var. amara), is an essential oil known for its sharp, nutty, and marzipan-like aroma. This oil is produced through steam distillation of crushed bitter almond kernels and contains a naturally occurring compound called benzaldehyde, which gives it its characteristic scent. In purified form (free of hydrogen cyanide), bitter almond oil is used in fragrance, flavoring, and pharmaceutical applications.
Due to its potent aroma and biochemical properties, it is widely used in perfumery, baked goods flavoring (in controlled quantities), aromatherapy, and traditional topical remedies. It is important to distinguish between natural bitter almond oil, which must be detoxified, and synthetic benzaldehyde, which is commonly used as a substitute in commercial formulations.
Ammonia Acetate
Ammonia Acetate is a white crystalline solid or granular powder with a mild ammoniacal odor. It is a salt formed from ammonia and acetic acid, widely used in laboratories, industrial processes, and some niche food and pharmaceutical applications. Ammonium Acetate is highly soluble in water and often utilized as a buffer solution in biochemical and analytical chemistry due to its ability to maintain pH. It also serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various chemicals and acts as a neutralizing agent in several industrial applications.
Avobenzone
Avobenzone (chemical name: Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane) is an oil-soluble organic compound widely used as a UVA filter in sunscreen formulations. It is valued for its ability to absorb a broad spectrum of ultraviolet A (UVA) rays (320–400 nm), protecting the skin from premature aging and damage caused by sun exposure. Avobenzone is often combined with other UV filters to provide broad-spectrum sun protection. It is a pale yellow liquid or crystalline powder, soluble in oils and alcohols but unstable in sunlight unless stabilized with other agents.
Bitter Masking Pharmaceutical Liquid flavors
Bitter Masking Pharmaceutical Liquid Flavors are specially formulated liquid flavors designed to mask the bitter taste of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). These flavors improve the palatability of oral syrups, suspensions, and liquid medications, enhancing patient compliance. Compatible with various pharmaceutical formulations, they exhibit excellent solubility and stability in aqueous systems and provide a pleasant taste profile without affecting the efficacy of the medication.
Calcium Sulphate Dihydrate
Calcium Sulphate Dihydrate, commonly known as gypsum, is a naturally occurring mineral widely used in agriculture, construction, and various industrial processes. It appears as a white or slightly translucent crystalline powder with moderate solubility in water. The compound is primarily used as a soil conditioner to improve soil structure and supply calcium and sulfur nutrients essential for plant growth. It also finds applications in the manufacture of plaster, cement, and as a filler in various products.
Cellulose Acetate Phthalate (CAP)
Cellulose Acetate Phthalate (CAP) is a cellulose derivative obtained by esterification of cellulose with acetic acid and phthalic anhydride. It appears as a white to off-white, free-flowing powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in alkaline solutions and certain organic solvents. CAP is primarily used as an enteric coating agent in pharmaceutical formulations, providing resistance to acidic gastric fluids and enabling targeted release of drugs in the intestines. Due to its film-forming, pH-sensitive solubility, and protective properties, CAP is also applied in food, cosmetics, and specialty industrial uses.
Cetyl Alcohol Flakes
Cetyl Alcohol Flakes is a high-purity fatty alcohol derived mainly from natural sources such as palm oil and coconut oil. Presented as white to off-white waxy flakes, this product contains at least 98% pure cetyl alcohol, ensuring consistent performance and quality. It is valued for its excellent emollient, thickening, and emulsifying properties and is widely used in personal care, pharmaceutical, and industrial formulations. The flake form facilitates easy handling, melting, and dosing in manufacturing processes. Cetyl Alcohol 98% Flakes contributes to the texture, stability, and moisturizing properties of various formulations, providing a non-greasy, smooth finish.
Cross Carmellose Sodium BP
Cross Carmellose Sodium BP (also known as Croscarmellose Sodium or CCS) is a cross-linked sodium carboxymethyl cellulose polymer. It is a highly efficient, super-disintegrant commonly used in pharmaceutical tablet and capsule formulations. This white to off-white, odorless, and tasteless powder exhibits excellent swelling properties and rapid water uptake, which facilitates fast tablet disintegration and improves drug bioavailability. It is chemically stable, non-toxic, and compatible with a wide range of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Dextrose Anhydrous BP Injectable
Dextrose Anhydrous BP Injectable is a sterile, highly purified crystalline form of glucose that serves as a critical energy source in intravenous therapy. It is widely used in parenteral nutrition, rehydration, and hypoglycemia management. The anhydrous form contains no water, allowing precise control of concentration in injectable solutions. Meeting British Pharmacopoeia (BP) standards, it ensures pharmaceutical-grade purity and sterility, suitable for direct injection or as a component in compounded IV fluids. It provides readily available carbohydrates metabolized to supply energy, regulate osmolarity, and maintain fluid-electrolyte balance in clinical care.
Dextrose Monohydrate
Dextrose Monohydrate is a crystalline form of glucose containing one molecule of water (monohydrate). It is a primary carbohydrate source widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and clinical nutrition applications. It provides readily available energy, serves as a sweetening agent, and acts as an osmotic agent in formulations. Dextrose Monohydrate meets pharmacopoeial standards (such as BP, USP) ensuring high purity, consistency, and safety for use in medical and food-grade products. Its solubility and stable crystalline form make it suitable for intravenous fluids, oral rehydration solutions, and food industry applications.
Dicalcium Phosphate
Dicalcium Phosphate (DCP) is an inorganic compound commonly used as a dietary supplement, food additive, and a key raw material in pharmaceuticals and animal nutrition. It appears as a white crystalline powder or granules and provides a highly bioavailable source of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for bone health, metabolic functions, and overall growth. DCP is widely used in the feed industry, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and various industrial applications, appreciated for its purity, stability, and nutritional value.
Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate
Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate (DCP Dihydrate) is an odorless, white crystalline powder or granule composed of calcium and phosphate in a hydrated form. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical, food, animal feed, and industrial sectors. It serves as a calcium and phosphorus supplement, excipient, and abrasive agent, valued for its stability, bioavailability, and neutral taste. DCP Dihydrate complies with various pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP, BP, FCC) depending on the grade.
Dill Seed Oil Terpeneless
Dill Seed Oil Terpeneless is a refined essential oil obtained by steam distillation of the seeds of Anethum graveolens, with terpenes removed to reduce its sharpness and volatility. It has a mild, sweet, herbaceous aroma with faint spicy undertones. This oil is prized for its improved stability, softer fragrance profile, and enhanced suitability in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and cleaning applications. Traditionally used for digestive support and antimicrobial properties, dill seed oil terpeneless is incorporated in natural personal care products, aromatherapy, and household formulations.
HPMC Vivapharm E50
HPMC Vivapharm is a high-quality, pharmaceutical-grade hydroxypropyl methylcellulose polymer widely used as an excipient and functional ingredient. It appears as a fine, white to off-white, odorless powder with excellent solubility in cold water and forms clear, viscous solutions. This cellulose ether derivative offers excellent film-forming, thickening, emulsifying, and controlled-release properties. Vivapharm E50 is prized in pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries for its versatility, stability, and safety profile.
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose HPMC, also known as hypromellose, is a semi-synthetic, non-ionic cellulose ether derived by chemically modifying cellulose through methylation and hydroxypropylation. It is a white to off-white, odorless, tasteless powder that dissolves in cold water to form clear, viscous solutions. HPMC is renowned for its thickening, film-forming, emulsifying, and controlled-release properties. It is widely used in pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, construction, and industrial applications due to its safety profile, versatility, and compatibility with various ingredients.
Lactose Monohydrate 200 Mesh
Lactose Monohydrate 200 Mesh is a fine, white, crystalline powder derived from milk sugar with a particle size of 200 mesh, indicating very fine granules. It is widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and confectionery industries as a filler, binder, and stabilizer. Lactose Monohydrate is valued for its excellent compressibility, low hygroscopicity, and compatibility with many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The monohydrate form contains one molecule of water, enhancing its stability and flow properties.
Magnesium Stearate BP
Magnesium Stearate BP is a fine, white, hydrophobic powder composed of the magnesium salt of stearic acid. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as a lubricant and anti-adherent in tablet and capsule manufacturing. Due to its excellent flow-enhancing properties, Magnesium Stearate BP improves powder flowability and prevents ingredients from sticking to equipment during processing. It is also used in cosmetics, food, and various industrial applications for its emulsifying and stabilizing properties.
Maninitol BP
Maninitol BP is a white, crystalline, sugar alcohol derived from mannose, widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. It functions as a sweetener, humectant, and excipient. Mannitol BP is non-hygroscopic and has low sweetness compared to sucrose, making it ideal for sugar-free formulations. It is commonly employed in tablet manufacturing as a filler and binder, and in medical settings as an osmotic diuretic to reduce intracranial pressure. The British Pharmacopoeia (BP) grade ensures compliance with pharmacopeial standards for purity and quality.
Methlyl Paraben Sodium BP
Methlyl Paraben Sodium BP is the sodium salt form of methyl paraben, a widely used preservative in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food products. It exhibits excellent antimicrobial properties, particularly against molds, yeasts, and some bacteria, extending the shelf life and safety of formulations. It is a white to off-white crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, and stable across a range of pH levels.
Methyl Cellulose 400mpc
Methyl Cellulose 400mpc is a chemically modified cellulose derivative in powder form. It is a non-ionic, water-soluble polymer widely used as a thickener, binder, emulsifier, and film former. It exhibits excellent water retention, viscosity control, and thermal gelation properties, making it ideal for applications in construction, pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.
Microcrystalline Cellulose
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) is a purified, partially depolymerized cellulose prepared by treating alpha-cellulose with mineral acids. It appears as a white, odorless, crystalline powder widely used as a binder, filler, and disintegrant in pharmaceutical tablets and capsules. MCC exhibits excellent compressibility and flow properties, making it ideal for direct compression tableting.
Polyethyl Glycol( PEG 6000)
Polyethyl Glycol( PEG 6000) is a high-molecular-weight polymer derived from ethylene oxide. It appears as a white, waxy solid or flake and is non-toxic, water-soluble, and chemically stable. PEG 6000 is widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food processing, industrial formulations, and biotechnology, valued for its lubricating, solubilizing, binding, and moisturizing properties. It is odorless and tasteless, making it suitable for sensitive formulations.
Povidone PVP25 USP
Povidone PVP25 USP is a synthetic polymer of vinylpyrrolidone with an average molecular weight of approximately 25,000. It is a water-soluble, non-toxic, and biodegradable polymer widely used as a binder, film former, stabilizer, and solubilizing agent in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications. Its excellent adhesive properties and compatibility with a wide range of substances make it essential in tablet formulations, topical products, and adhesives.
Pullulan
Pullulan is a natural polysaccharide polymer produced by the fermentation of starch by the fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. It is a water-soluble, tasteless, and odorless biopolymer widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its excellent film-forming, adhesive, and oxygen barrier properties. Pullulan is biodegradable, non-toxic, and approved for use in various applications requiring edible and biodegradable films.
PVP K 30 USP
PVP K 30 USP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30) is a water-soluble polymer widely used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. It serves as a binder, stabilizer, and film-forming agent, known for its excellent adhesive properties and compatibility with a wide range of ingredients. PVP K 30 USP is characterized by its medium molecular weight, making it ideal for tablet binding, enhancing solubility of poorly soluble drugs, and providing viscosity control in liquid formulations. This grade complies with USP standards ensuring suitability for pharmaceutical use.
PVP K 90 USP
PVP K 90 USP (Polyvinylpyrrolidone K-90) is a high molecular weight water-soluble polymer widely used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications. Known for its excellent film-forming, adhesive, and thickening properties, PVP K 90 is particularly valued where higher viscosity and stronger binding are required. This grade meets USP standards, ensuring purity and suitability for pharmaceutical use, especially in sustained-release formulations, suspensions, and topical products.
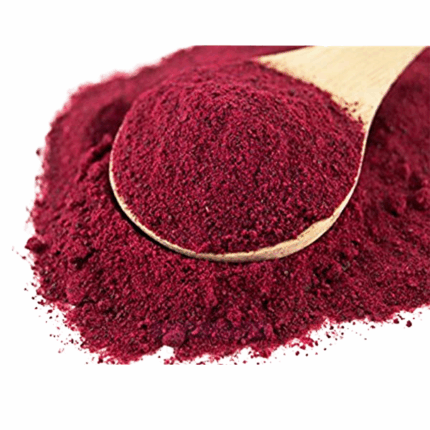
Red Cherry Powder Flavor
Red Cherry Powder Flavor is a high-quality, concentrated flavoring agent designed to impart a natural and vibrant cherry taste to a variety of food and beverage applications. This fine powder is made from carefully selected ingredients to ensure consistent flavor intensity, solubility, and stability. Ideal for use in dry mixes, confectionery, beverages, and baked goods, Red Cherry Powder Flavor provides a convenient and versatile way to enhance taste profiles without altering texture.
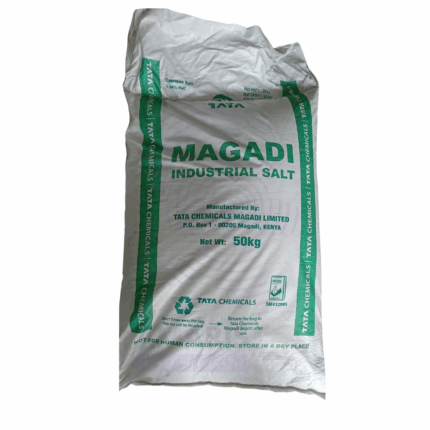
Sodium Chloride (Industrial Salt)
Sodium Chloride (Industrial Salt) is a highly purified, sterile, and non-pyrogenic salt intended for intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous administration. It is commonly used in medical and pharmaceutical settings as a key component of intravenous fluids, for rehydration therapy, electrolyte replenishment, and as a diluent for injectable drugs. This grade meets stringent pharmacopoeial standards (British Pharmacopoeia) ensuring safety and compatibility with parenteral use.
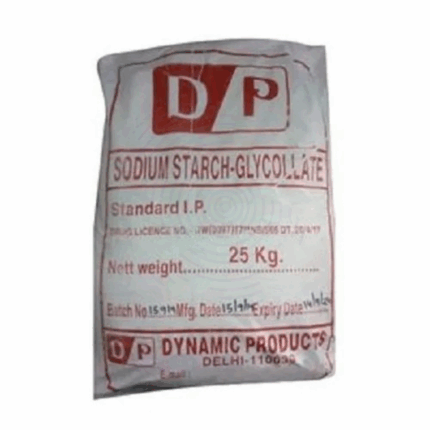
Sodium Starch Glycolate
Sodium Starch Glycolate (SSG) is a white to off-white, odorless, tasteless powder derived from potato or maize starch and chemically modified with carboxymethylation and cross-linking. It has the chemical formula (C₆H₁₀O₅)nNa and is widely used in solid dosage pharmaceutical formulations as a superdisintegrant. This 25kg grade is supplied in high-purity pharmaceutical and food-grade quality, offering excellent swelling capacity and rapid disintegration properties even at low concentrations.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders