Constantine wire
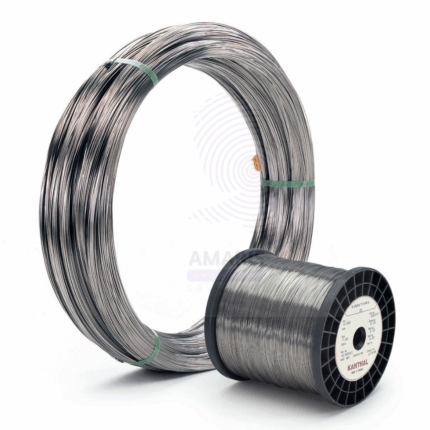
Constantine Wire is an alloy wire composed primarily of copper, nickel, and zinc, known for its high electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability. It is widely used in electrical applications requiring reliable conduction and mechanical strength. The wire exhibits excellent resistance to oxidation and mechanical wear, making it suitable for various laboratory and industrial uses.
Contact key
Product Description
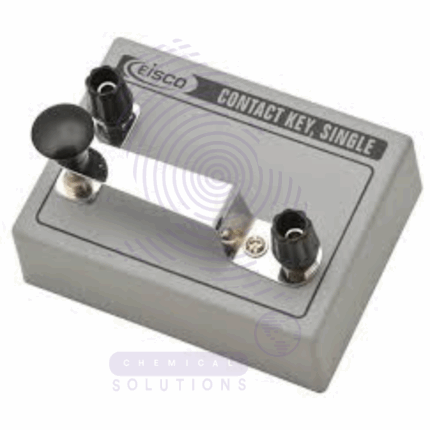
The Contact Key is a fundamental switching device used in electrical circuits to manually open or close the flow of current. Commonly used in physics laboratories for demonstration and experimentation with circuits, it enables controlled activation of current for brief or sustained durations. Made from durable, conductive metals with insulating bases, Contact Keys are essential components in circuit testing, timing devices, and low-voltage experimental setups.
Contact key
Product Description
The Contact Key is a fundamental switching device used in electrical circuits to manually open or close the flow of current. Commonly used in physics laboratories for demonstration and experimentation with circuits, it enables controlled activation of current for brief or sustained durations. Made from durable, conductive metals with insulating bases, Contact Keys are essential components in circuit testing, timing devices, and low-voltage experimental setups.
copper connecting wire
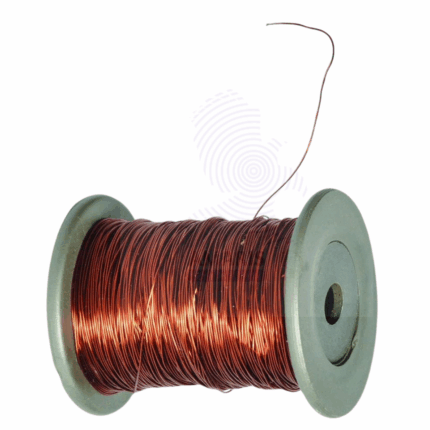
Copper Connecting Wire is a high-conductivity electrical wire used to establish electrical connections in laboratory and industrial setups. Manufactured from pure or high-grade copper, it ensures minimal resistance and maximum current transfer. The wire is typically insulated with flexible PVC or rubber to provide durability, flexibility, and protection. Available in various gauges and lengths, it is a critical component for assembling circuits, powering devices, and conducting experimental setups.
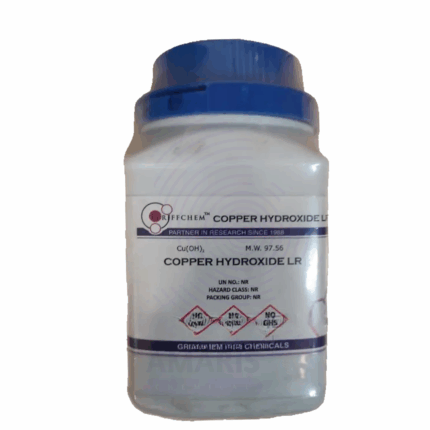
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate
Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate (CuSO₄·5H₂O) is a bright blue crystalline solid widely used as a chemical reagent, agricultural fungicide, and analytical reagent. It consists of copper, sulfur, oxygen, and water molecules, forming a distinctive pentahydrate structure. This inorganic salt is highly soluble in water, exhibiting antifungal, algaecidal, and bactericidal properties. Copper Sulphate Pentahydrate is extensively employed in agriculture, industry, and laboratory applications due to its effectiveness, affordability, and well-understood chemistry.
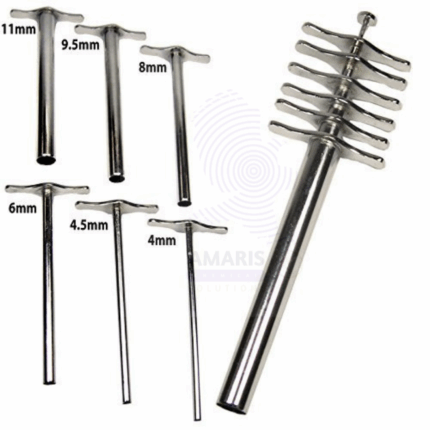
Cork borer set
The Cork Borer Set is a precision instrument set used in laboratories for cutting uniform cylindrical holes through corks, rubber stoppers, and soft polymers. Typically made of durable stainless steel, the set includes multiple hollow borers of varying diameters with sharpened edges, along with a cleaning rod or handle. It is essential for creating accurate openings to insert glass tubing or thermometers into stoppers for experimental setups involving sealed vessels or distillation systems.
cork borer set sharpener
The Cork Borer Set Sharpener is a specialized tool designed for honing and maintaining the cutting edges of cork borers. Essential for extending the life and performance of laboratory cork borers, this sharpener typically features a conical or tapered grinding surface made of hardened steel or fine abrasive material. It ensures precision cutting by restoring sharpness, which is critical for clean, accurate boring through rubber stoppers, corks, and similar materials. Durable and easy to use, it is a vital accessory in laboratory maintenance kits.
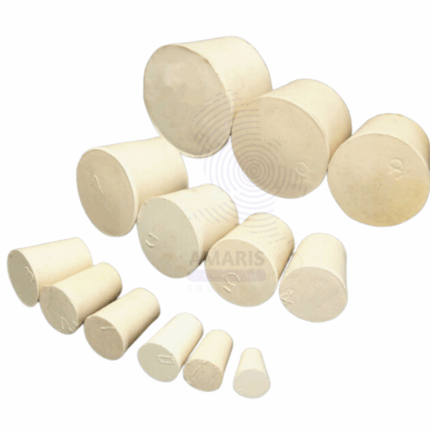
Cork to fit boiling tube cork
Cork to fit boiling tube cork is a precision-cut natural or synthetic cork designed to seal boiling tubes securely in laboratory settings. These corks provide an airtight seal while resisting mild heat and chemical exposure typically encountered in general lab procedures. They help prevent contamination, evaporation, or spillage of contents during storage, gentle heating, or experimental handling. Available in various diameters, these corks are essential for maintaining experimental integrity in both research and industrial laboratories.
Cork to fit boiling tube cork stopper
Cork to Fit Boiling Tube Cork Stopper is a precision-manufactured stopper made from natural or synthetic cork, designed specifically to fit standard boiling tubes. It ensures a snug, secure closure that prevents leaks, contamination, or evaporation during laboratory procedures. These stoppers are essential in both routine and specialized lab applications where temporary sealing of test vessels is required. With good compressibility, mild chemical resistance, and reliable sealing properties, the stopper is a staple in laboratory glassware accessories.
Cork to fit conical flask
Cork to Fit Conical Flask is a tapered sealing component made from natural or synthetic cork, designed to provide a snug, airtight closure for conical (Erlenmeyer) flasks. These stoppers are essential for laboratory procedures requiring the containment of samples, prevention of evaporation, or protection from airborne contaminants. Their compressibility, resistance to mild chemicals, and reusability make them ideal for both general lab work and industrial testing environments. The corks are precisely sized to fit standard flask openings, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of flask volumes.
Cork to fit test tube
Cork to Fit Test Tube is a conical sealing component made from natural or synthetic cork, designed specifically to fit snugly into standard laboratory test tubes. It ensures a tight seal that prevents contamination, limits evaporation, and maintains sample integrity during storage or handling. Due to its compressible and chemically resistant structure, it is ideal for routine laboratory operations and industrial testing processes. These corks are available in various sizes to accommodate a wide range of test tube diameters and are compatible with both glass and plastic tubes.
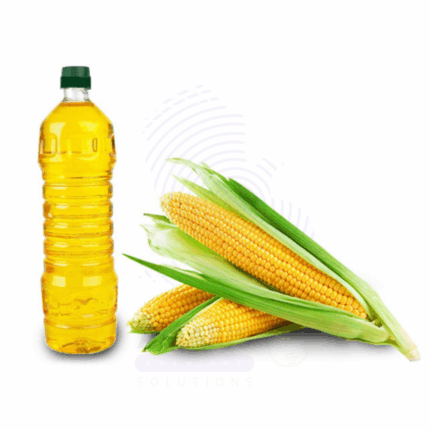
Corn Oil
Corn Oil is a versatile, plant-based oil extracted from the germ of corn kernels (Zea mays) through mechanical pressing and solvent extraction, followed by refining. It is light yellow in color with a mild, neutral scent and a high smoke point, making it suitable for culinary, industrial, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical applications. Rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially linoleic acid, and vitamin E, corn oil is valued for its emollient, antioxidant, and cholesterol-lowering properties.
Commonly used as a cooking and frying oil, it is also widely incorporated into margarine, salad dressings, and processed foods. In cosmetics, it functions as a skin-conditioning agent and emollient. Corn oil further finds use in pharmaceutical formulations, biofuel production, and industrial lubricants.
Corn Starch Food Grade
Corn Starch Food Grade is a fine, white, powdery carbohydrate extracted from the endosperm of corn kernels (Zea mays). It is a natural, tasteless, and odorless polysaccharide composed primarily of amylose and amylopectin. Corn starch is widely used as a thickening, stabilizing, and binding agent in food products due to its excellent gelatinization properties. It serves as a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour in many culinary and industrial applications. Corn starch is valued for its versatility, digestibility, and neutral flavor profile, making it a staple ingredient in both home cooking and commercial food production.
Corn Starch Industrial Grade
Corn Starch Industrial Grade is a finely milled, white powder derived from the endosperm of maize (Zea mays). Unlike food-grade starch, industrial grade is tailored for non-food applications where its thickening, adhesive, and film-forming properties are exploited. It consists primarily of amylose and amylopectin polysaccharides and is valued for its biodegradability, renewability, and cost-effectiveness. Industrial corn starch is used extensively as a raw material or functional additive across a wide variety of manufacturing processes, including paper, textiles, adhesives, and packaging industries.
Corn Syrup
Corn Syrup is a viscous, sweet liquid derived from the enzymatic hydrolysis of corn starch. It consists primarily of glucose and maltose along with higher saccharides, providing sweetness, viscosity, and moisture retention in food formulations. Corn Syrup is widely used in food and beverage industries as a sweetener, humectant, and texture enhancer. Its ability to prevent crystallization and retain moisture makes it essential in confectionery, baking, and processed foods. Industrial grades of corn syrup are also used in pharmaceuticals and other manufacturing applications where its binding and stabilizing properties are valued.
Costus Oil
Costus Oil is a rare essential oil derived from the steam-distilled roots of Saussurea costus (also known as Saussurea lappa), a Himalayan herb long valued in traditional systems such as Ayurveda, Unani, and Chinese medicine. The oil has a deep amber to brown color and a rich, earthy, woody, and musky aroma. It is well-known in perfumery as a natural fixative and is widely used in spiritual rituals, incense making, high-end fragrances, and therapeutic blends.
Due to its grounding scent and potential anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and calming properties, Costus Oil is incorporated into personal care, topical formulations, and aromatherapy. It is a powerful aromatic oil that must be used in moderation and diluted due to its strong sensitizing compounds.
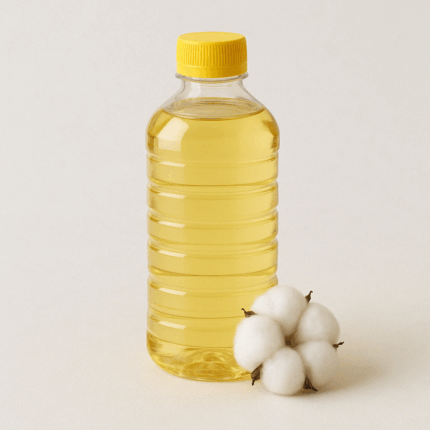
Cotton Seed Oil
Cotton Seed Oil is a light, odorless, vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the cotton plant (Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium herbaceum) through solvent extraction and refining processes. It is pale yellow with a neutral flavor, making it ideal for culinary, cosmetic, and industrial applications. Rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, tocopherols, and antioxidants, Cotton Seed Oil is valued for its stability and high smoke point in cooking, as well as its emollient and conditioning properties in skin and hair care products.
In cosmetic formulations, it helps soften, nourish, and protect skin and hair, while in food production, it is used in frying oils, dressings, and snacks. Industrially, it finds applications in biodiesel production and soap manufacturing.
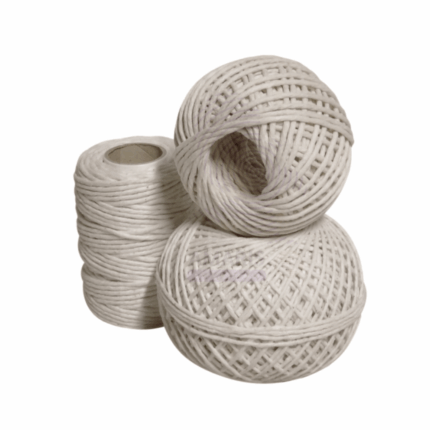
Cotton twine
Cotton Twine is a versatile filament made from twisted strands of natural cotton fibers. It is soft yet durable, offering flexibility and strength for binding, tying, or securing items in both laboratory and industrial environments. Cotton twine is non-abrasive, lint-minimal, and chemically inert to most laboratory reagents, making it suitable for specimen tying, light bundling, or general-purpose securing within controlled settings.
Craymide Epoxy Hardener
Craymide Epoxy Hardener is a high-performance epoxy hardener commonly used to cure epoxy resins. It is a polyamide-based curing agent that promotes excellent cross-linking with epoxy groups, resulting in coatings, adhesives, and composites with superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability. This hardener is widely used in industrial coatings, adhesives, and composite manufacturing due to its balanced curing profile and compatibility with a range of epoxy systems. Craymide 115 provides toughness and flexibility while maintaining strong adhesion to various substrates.
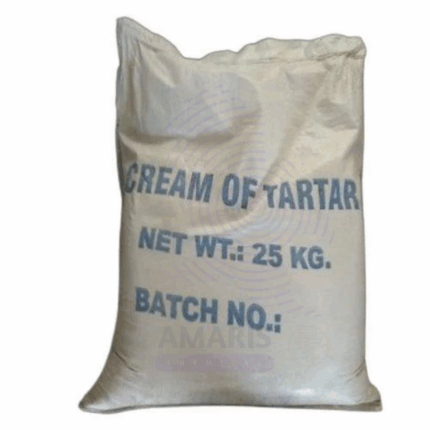
Cream of Tartar
Cream of Tartar, chemically known as Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (KC4H5O6), is a fine, white, acidic powder that is a byproduct of winemaking. It is a natural crystalline acid salt obtained from tartaric acid during the fermentation of grapes. This odorless and tasteless powder is widely used in culinary, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications due to its stabilizing, acidifying, and leavening properties. Cream of Tartar is valued for its ability to stabilize egg whites, prevent sugar crystallization, and act as an acidulant in various formulations.
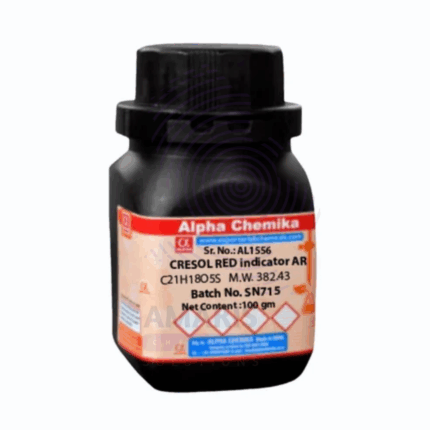
Cresol Red Indicator Extra Pure
Cresol Red Indicator Extra Pure is a high-purity pH indicator dye widely used in laboratory titrations, buffer solutions, and biochemical assays. It exhibits a clear color change from yellow to red over the pH range of approximately 7.2 to 8.8, making it suitable for detecting slight pH shifts in weakly basic environments. Its stable performance and extra pure grade ensure consistent results in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and spectrophotometric applications. Ideal for use in precise pH monitoring, Cresol Red should be handled with care and stored away from light and moisture to preserve its integrity.
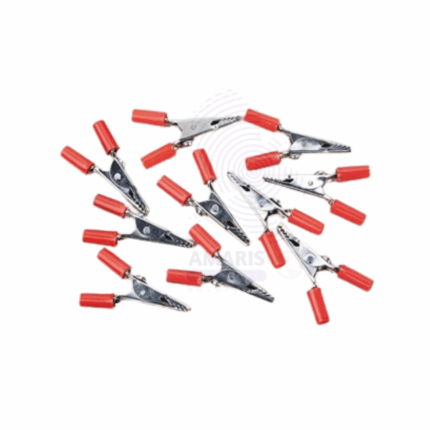
Crocodile Clips
Crocodile Clips are versatile electrical connectors featuring serrated jaws to securely grip wires or terminals. Commonly made from copper or brass with a nickel or chrome plating, these clips ensure reliable conductivity and mechanical stability. Widely used in laboratory and industrial settings for quick temporary electrical connections, testing, and circuit prototyping.
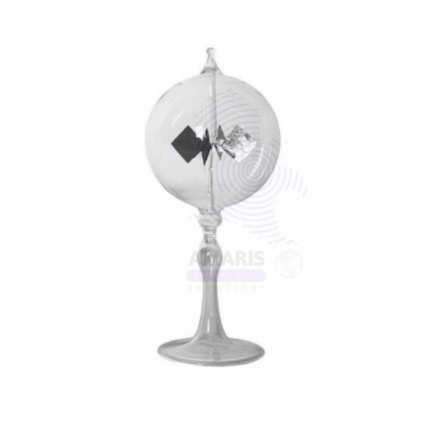
Crookes radiometer
The Crookes Radiometer, also known as a light mill, is a scientific apparatus consisting of a glass bulb containing a partial vacuum and a rotor with vanes coated black on one side and white or silver on the other. When exposed to light or radiant energy, the vanes rotate due to differential thermal transpiration, demonstrating principles of gas kinetics and energy conversion. It is commonly used for educational demonstrations of light pressure and thermodynamics.
Cross Carmellose Sodium BP
Cross Carmellose Sodium BP (also known as Croscarmellose Sodium or CCS) is a cross-linked sodium carboxymethyl cellulose polymer. It is a highly efficient, super-disintegrant commonly used in pharmaceutical tablet and capsule formulations. This white to off-white, odorless, and tasteless powder exhibits excellent swelling properties and rapid water uptake, which facilitates fast tablet disintegration and improves drug bioavailability. It is chemically stable, non-toxic, and compatible with a wide range of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
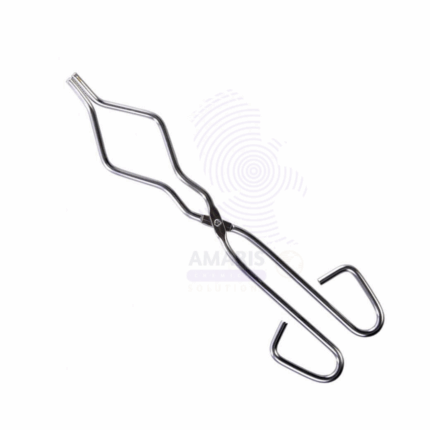
Crucible Tongs
Crucible Tongs are specialized metal tools designed for safely handling hot crucibles, evaporating dishes, and other laboratory apparatus exposed to high temperatures. Made from durable, heat-resistant metals such as stainless steel or nickel-plated steel, these tongs provide a firm grip, ensuring the safe transfer of heated items during laboratory procedures, including heating, melting, and chemical reactions.
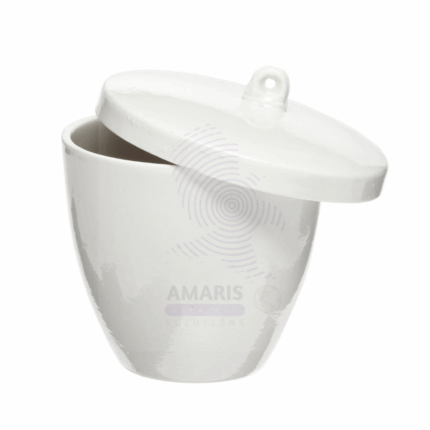
Crucible with lid
Crucible with Lid is a heat-resistant container used in laboratories and industries to heat, melt, or calcine substances at very high temperatures. Typically made from materials such as porcelain, alumina, or graphite, these crucibles can withstand thermal shock and chemical corrosion. The accompanying lid helps contain the sample, minimize contamination, and reduce material loss during heating or combustion processes.
Cubeb Oil
Cubeb Oil is an essential oil steam-distilled from the dried berries of Piper cubeba, a plant native to Java and parts of Southeast Asia. With a warm, spicy, woody, and slightly camphoraceous aroma, Cubeb Oil is rich in sesquiterpenes and monoterpenes such as sabinene, cubebene, and caryophyllene. It has traditionally been used in herbal medicine for respiratory and urinary support and in perfumery for its distinctive spicy-woody scent.
In modern formulations, Cubeb Oil is valued for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and stimulating properties. It is commonly used in natural perfumery, masculine fragrances, therapeutic massage blends, and respiratory wellness products.
Cumin Seed Oil
Cumin Seed Oil is an essential oil obtained through steam distillation of the dried seeds of Cuminum cyminum, a herbaceous plant from the Apiaceae family. Known for its warm, spicy, earthy, and nutty aroma, cumin seed oil is rich in bioactive compounds like cuminaldehyde, cymene, and terpenes. It is traditionally used in Ayurvedic and Unani medicine for digestive, respiratory, and antimicrobial support.
In modern applications, cumin seed oil is valued for its antioxidant, antiseptic, and digestive-stimulating properties. It is used across cosmetic formulations, therapeutic massage products, aromatherapy blends, and flavoring applications.
Cupric Carbonate Extra Pure
Cupric Carbonate Extra Pure is a fine, green, high-purity compound used in laboratories for inorganic synthesis, analytical chemistry, and educational demonstrations. It serves as a reliable source of copper ions in reactions and decomposes upon heating to form copper oxide, making it useful for studying thermal decomposition. In qualitative analysis, it is employed to observe characteristic reactions of copper salts. Its extra pure grade ensures minimal interference from impurities, supporting accurate experimental outcomes. Cupric carbonate should be handled in a dry environment and stored in tightly sealed containers to prevent degradation and maintain stability.
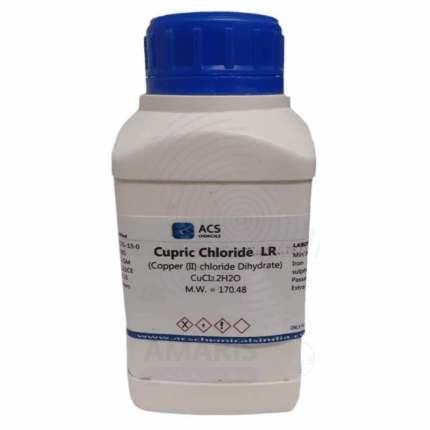
Cupric Chloride Extra Pure
Cupric Chloride Extra Pure is a green to yellowish crystalline compound widely used in laboratories as a catalyst, reagent, and source of copper ions in various chemical reactions. It plays a key role in organic synthesis, photochemical processes, and analytical chemistry procedures, especially for detecting reducing agents and halide ions. Its high solubility in water and alcohol allows for versatile application across wet-lab experiments. The extra pure grade ensures excellent reliability and minimal impurities, making it ideal for precision work in research and education. Store in a cool, dry place, protected from moisture and light to preserve its reactivity.
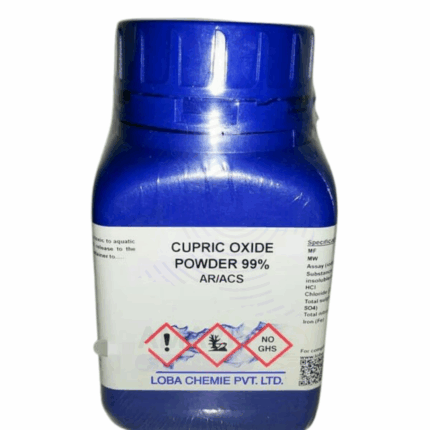
Cupric Oxide Extra Pure
Cupric Oxide Extra Pure is a black, fine powder extensively used in laboratory settings as a stable, high-purity source of copper in oxidation state +2. It is commonly applied in organic synthesis, inorganic reactions, and thermal decomposition studies, as well as in qualitative and quantitative analysis of copper. Its thermal stability also makes it suitable for ceramic glazing and as a precursor in catalyst preparation. This extra pure grade ensures low impurity levels, essential for accurate experimental results and reproducible data in both educational and research laboratories. It should be stored in a tightly sealed container away from moisture and strong acids.
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous
Cupric Sulphate Anhydrous (Copper(II) sulfate, anhydrous form) is a blue to green crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It is an inorganic compound consisting of copper, sulfur, and oxygen with the formula CuSO₄. Unlike its hydrated counterpart (CuSO₄·5H₂O), the anhydrous form contains no water molecules. It is widely used in agriculture, industry, and chemical manufacturing due to its fungicidal, algicidal, and chemical reactivity properties. The compound serves as a precursor to many copper salts and catalysts.
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate (Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate) is a bright blue crystalline solid with the chemical formula CuSO₄·5H₂O. It is the hydrated form of copper sulfate and is highly soluble in water. This compound is widely used in agriculture, chemical manufacturing, and laboratory applications due to its fungicidal, algicidal, and micronutrient properties. The pentahydrate form is the most common and commercially available, known for its vivid blue color and versatile reactivity.
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate Extra Pure
Cupric Sulphate Pentahydrate Extra Pure is a vibrant blue crystalline compound widely used in laboratories for its high solubility and consistent copper ion content. It is essential in analytical chemistry for Fehling's and Benedict’s solutions, in electrochemistry for plating and battery experiments, and as a biological nutrient in microbiological media. The pentahydrate form offers ease of handling and precise formulation in aqueous solutions. This extra pure grade ensures exceptional purity, making it suitable for teaching labs, research applications, and controlled experimental procedures. Store in a sealed container away from heat and moisture to maintain its crystalline integrity.
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is a clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid with a sharp, sweet, acetone-like odor. It is a cyclic ketone with the molecular formula C₆H₁₀O and a moderately high boiling point. Cyclohexanone is a key intermediate in the chemical industry, primarily used in the manufacture of nylon, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals. Its excellent solvency and chemical reactivity make it valuable for a wide range of industrial applications, including solvent use and chemical synthesis.
Cyclopentolate HCL
Cyclopentolate Hydrochloride (HCL) is a synthetic anticholinergic agent used primarily in ophthalmology. It appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water, with a slightly bitter taste. Cyclopentolate HCL works by temporarily paralyzing the muscles of the eye’s ciliary body and iris, causing pupil dilation (mydriasis) and paralysis of accommodation (cycloplegia). It is commonly formulated into eye drops for diagnostic procedures and therapeutic applications involving the eye.
Cypress Oil
Cypress Oil is an essential oil obtained by steam distillation of the needles, twigs, and cones of the Cupressus sempervirens tree. Known for its clean, woody, slightly spicy, and balsamic aroma, this oil contains key constituents such as alpha-pinene, delta-3-carene, and cedrol. It has been traditionally used for its astringent, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and decongestant properties.
Cypress Oil is widely used in aromatherapy, skincare, respiratory blends, muscle-relief products, and emotional wellness formulas. It is also found in perfumes, deodorants, and spa treatments for its grounding, fresh, and uplifting scent.
Cyproheptadine HCL
Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride (HCL) is a synthetic first-generation antihistamine with additional anticholinergic and serotonin antagonist properties. It appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water, with a bitter taste. Cyproheptadine HCL is widely used in medical and veterinary fields for its potent antihistaminic effects, appetite stimulation, and treatment of allergic conditions. It blocks H1 histamine receptors, helping to reduce symptoms of allergic reactions, and is also used for various off-label applications including migraine prophylaxis and serotonin syndrome management.
D-Limonene Oil
D-Limonene Oil is a naturally occurring monoterpene hydrocarbon extracted primarily from the rinds of citrus fruits, especially oranges and lemons. It is obtained through cold pressing or steam distillation of citrus peels and purified through fractional distillation. Known for its fresh, sweet, and zesty orange-like aroma, D-Limonene is widely used across multiple industries for its solvent properties, fragrance, and therapeutic benefits.
This oil is valued for its degreasing power, anti-inflammatory effects, and uplifting scent. It plays a vital role in cosmetics, cleaning formulations, pharmaceuticals, and food products, either as a solvent, active ingredient, or fragrance compound.
D-Panthenol USP
D-Panthenol USP, also known as Provitamin B5, is the dextrorotatory isomer of panthenol and is biologically active. It is a water-soluble, viscous, clear liquid with a slightly sweet odor and is widely used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, personal care, and nutraceutical applications. D-Panthenol is the alcohol analog of pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) and is converted into Vitamin B5 in the skin and body, where it plays a vital role in cellular metabolism and tissue repair. Its moisturizing, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties make it highly valuable across industries.
Daniel cell
The Daniel Cell is a classic electrochemical cell consisting of zinc and copper electrodes immersed in their respective sulfate solutions and connected by a salt bridge. It generates electrical energy through redox reactions and is used primarily for educational and laboratory demonstrations in electrochemistry.
Davana Oil
Davana Oil is a premium essential oil derived from the flowering tops of the Artemisia pallens plant through steam distillation. Native to southern India, Davana is a highly aromatic herb traditionally used in Ayurvedic practices and religious rituals. The oil features a sweet, fruity, herbaceous aroma with subtle balsamic undertones, and it is known for its adaptogenic, antimicrobial, and mood-balancing properties.
This exotic oil is widely used in high-end perfumery for its unique scent that adapts slightly to each individual's skin chemistry. It also finds applications in skincare, aromatherapy, pharmaceuticals, and natural remedies. Its complex chemical profile makes it valuable for both therapeutic and olfactory formulations.
Defoamer
Defoamer is a high-performance, silicone-based antifoaming agent designed to eliminate and prevent foam formation in aqueous and non-aqueous systems. It is typically a milky-white or translucent emulsion composed of modified polydimethylsiloxane, hydrophobic silica, and proprietary surfactants or emulsifiers. Defoamer is known for its immediate foam knockdown, long-lasting suppression, and compatibility across diverse formulations. It is widely used in industrial processes, coatings, adhesives, water treatment, textiles, and more. It is effective at low concentrations, thermally stable, and resistant to shear and pH fluctuations.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders