Citric Acid Anhydrous
Citric Acid Anhydrous is a white, crystalline organic acid widely used across food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial sectors. It is the anhydrous form of citric acid, meaning it contains no water molecules in its crystal lattice, resulting in higher purity and more concentrated acidic properties compared to its monohydrate form. Derived from natural sources like citrus fruits or produced via microbial fermentation, citric acid anhydrous is valued for its sour taste, excellent chelating ability, and buffering capacity. It serves as a natural preservative, pH adjuster, antioxidant synergist, and cleaning agent, making it a versatile ingredient in many formulations.
Citric Acid Monohydrate
Citric Acid Monohydrate is a white, crystalline powder or granule form of citric acid containing one molecule of water per molecule of acid. It is a natural organic acid commonly derived from citrus fruits or produced by fermentation processes. Citric Acid Monohydrate is widely used as an acidulant, preservative, and chelating agent in various industries. Compared to the anhydrous form, it has a slightly lower acid concentration due to the water molecule but offers excellent solubility and stability. It is prized for its sour flavor, buffering capacity, and ability to bind metal ions, making it indispensable in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications.
Cocoa Butter
Cocoa Butter, also known as Theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from cocoa beans, primarily from Theobroma cacao. It has a smooth, creamy texture and a mild, characteristic chocolate aroma. Cocoa Butter is solid at room temperature but melts near body temperature, which gives it a luxurious feel when applied to skin or consumed. It is highly valued for its emollient, moisturizing, and protective properties. Cocoa Butter is widely used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food, and confectionery industries. Its stable composition rich in fatty acids such as stearic, palmitic, and oleic acids imparts excellent oxidative stability and a long shelf life.
Coconut Liquid Flavour
Coconut Liquid Flavour is a premium food-grade flavoring agent that delivers the sweet, creamy, and tropical aroma and taste of natural coconut in a convenient liquid form. It is specially formulated to provide consistent flavor and excellent stability in a variety of food and beverage applications. This flavor enhances bakery, confectionery, dairy, beverages, and savory products with its authentic coconut profile, making it ideal for creating delicious and exotic culinary experiences.
Condence Milk Liquid Flavor
Condence Milk Liquid Flavor is a high-quality food-grade flavoring agent that replicates the rich, creamy, and sweet aroma and taste of traditional condensed milk. It is designed to provide consistent and authentic dairy notes in a liquid form, making it ideal for a wide range of food and beverage applications. This flavor enhances the sensory appeal of bakery items, desserts, confectionery, dairy products, and beverages by adding a smooth, milky sweetness that is both comforting and indulgent.
Corn Starch Food Grade
Corn Starch Food Grade is a fine, white, powdery carbohydrate extracted from the endosperm of corn kernels (Zea mays). It is a natural, tasteless, and odorless polysaccharide composed primarily of amylose and amylopectin. Corn starch is widely used as a thickening, stabilizing, and binding agent in food products due to its excellent gelatinization properties. It serves as a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour in many culinary and industrial applications. Corn starch is valued for its versatility, digestibility, and neutral flavor profile, making it a staple ingredient in both home cooking and commercial food production.
Corn Syrup
Corn Syrup is a viscous, sweet liquid derived from the enzymatic hydrolysis of corn starch. It consists primarily of glucose and maltose along with higher saccharides, providing sweetness, viscosity, and moisture retention in food formulations. Corn Syrup is widely used in food and beverage industries as a sweetener, humectant, and texture enhancer. Its ability to prevent crystallization and retain moisture makes it essential in confectionery, baking, and processed foods. Industrial grades of corn syrup are also used in pharmaceuticals and other manufacturing applications where its binding and stabilizing properties are valued.
Cream of Tartar
Cream of Tartar, chemically known as Potassium Hydrogen Tartrate (KC4H5O6), is a fine, white, acidic powder that is a byproduct of winemaking. It is a natural crystalline acid salt obtained from tartaric acid during the fermentation of grapes. This odorless and tasteless powder is widely used in culinary, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications due to its stabilizing, acidifying, and leavening properties. Cream of Tartar is valued for its ability to stabilize egg whites, prevent sugar crystallization, and act as an acidulant in various formulations.
Desiccated Coconut
Desiccated Coconut is finely shredded, dried coconut meat derived from mature coconuts (Cocos nucifera). It is produced by removing the coconut water, then drying the white coconut kernel to reduce moisture content to less than 3%. The drying process preserves the natural flavor, aroma, and nutritional content while extending shelf life. Desiccated coconut is commonly available in various particle sizes and grades, suitable for culinary, bakery, confectionery, and food processing applications. It is valued for its rich texture, nutty flavor, and ability to add moisture and fat to food products.
Dextrose Anhydrous BP Injectable
Dextrose Anhydrous BP Injectable is a sterile, highly purified crystalline form of glucose that serves as a critical energy source in intravenous therapy. It is widely used in parenteral nutrition, rehydration, and hypoglycemia management. The anhydrous form contains no water, allowing precise control of concentration in injectable solutions. Meeting British Pharmacopoeia (BP) standards, it ensures pharmaceutical-grade purity and sterility, suitable for direct injection or as a component in compounded IV fluids. It provides readily available carbohydrates metabolized to supply energy, regulate osmolarity, and maintain fluid-electrolyte balance in clinical care.
Dextrose Monohydrate
Dextrose Monohydrate is a crystalline form of glucose containing one molecule of water (monohydrate). It is a primary carbohydrate source widely used in pharmaceutical, food, and clinical nutrition applications. It provides readily available energy, serves as a sweetening agent, and acts as an osmotic agent in formulations. Dextrose Monohydrate meets pharmacopoeial standards (such as BP, USP) ensuring high purity, consistency, and safety for use in medical and food-grade products. Its solubility and stable crystalline form make it suitable for intravenous fluids, oral rehydration solutions, and food industry applications.
Diammonium Phosphate
Diammonium Phosphate (DAP) is a highly water-soluble, white crystalline fertilizer containing nitrogen and phosphorus. It is one of the most widely used phosphate fertilizers globally, providing a balanced source of nutrients essential for plant growth. DAP supplies ammonium nitrogen (NH₄⁺) and phosphate (PO₄³⁻), which promote vigorous root development, improve soil fertility, and enhance crop yield and quality. Besides agriculture, DAP serves important roles in food additives, fire retardants, and industrial applications. It’s favored for its high nutrient content, ease of application, and compatibility with other fertilizers and soil amendments.
Dicalcium Phosphate
Dicalcium Phosphate (DCP) is an inorganic compound commonly used as a dietary supplement, food additive, and a key raw material in pharmaceuticals and animal nutrition. It appears as a white crystalline powder or granules and provides a highly bioavailable source of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for bone health, metabolic functions, and overall growth. DCP is widely used in the feed industry, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food processing, and various industrial applications, appreciated for its purity, stability, and nutritional value.
Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate
Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate (DCP Dihydrate) is an odorless, white crystalline powder or granule composed of calcium and phosphate in a hydrated form. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical, food, animal feed, and industrial sectors. It serves as a calcium and phosphorus supplement, excipient, and abrasive agent, valued for its stability, bioavailability, and neutral taste. DCP Dihydrate complies with various pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP, BP, FCC) depending on the grade.
Dill Herb Oil
Dill Herb Oil is a steam-distilled essential oil extracted from the fresh or partially dried herbaceous parts of the Anethum graveolens plant, commonly known as dill. Unlike dill seed oil, which is distilled from the seeds, dill herb oil has a lighter, fresher, and slightly grassy aroma with a faint sweetness and subtle spicy undertones. It is valued for its carminative, digestive, antispasmodic, antimicrobial, and calming properties.
This oil is traditionally used in digestive remedies, culinary formulations, aromatherapy blends, and topical preparations. It’s a common ingredient in natural health products, skincare, and child-friendly wellness products due to its mildness and effectiveness. Dill herb oil is also employed in food and beverage applications and niche perfumery for its green, aromatic character.
Dill Seed Oil Terpeneless
Dill Seed Oil Terpeneless is a refined essential oil obtained by steam distillation of the seeds of Anethum graveolens, with terpenes removed to reduce its sharpness and volatility. It has a mild, sweet, herbaceous aroma with faint spicy undertones. This oil is prized for its improved stability, softer fragrance profile, and enhanced suitability in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and cleaning applications. Traditionally used for digestive support and antimicrobial properties, dill seed oil terpeneless is incorporated in natural personal care products, aromatherapy, and household formulations.
Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate
Dipotassium Hydrogen Phosphate (also known as dipotassium phosphate, DKP) is an inorganic salt used widely as a buffering agent, emulsifier, and nutritional supplement in various industries. It is a white, crystalline, highly water-soluble powder with alkaline properties. DKP plays a vital role in food processing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and agriculture due to its ability to stabilize pH, improve texture, and supply essential potassium and phosphate ions.
Distilled Monoglycerides Remosoft
Distilled Monoglycerides Remosoft are purified monoglycerides derived from the glycerolysis of edible fats and oils, followed by a distillation process that removes impurities and enhances purity. They are colorless to pale yellow, odorless, and possess excellent emulsifying properties. DMG is widely used in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its surface-active properties, ability to stabilize emulsions, and function as an anti-caking and lubricating agent. The distilled grade ensures high purity and low free fatty acid content, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
Egg Yellow Color Water Soluble
Egg Yellow Color Water Soluble is a bright synthetic yellow dye with excellent water solubility and color fastness. It is widely used across textile, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, cleaning, and paint industries to provide vibrant yellow coloration with uniform application and stability in aqueous systems.
Ellagic Acid
Ellagic Acid is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound found in numerous fruits, nuts, and vegetables such as pomegranates, strawberries, raspberries, walnuts, and cranberries. It is a potent antioxidant known for its ability to scavenge free radicals and chelate metal ions. Due to its significant anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, and anti-viral properties, Ellagic Acid has gained extensive interest in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. It appears as a yellow to light brown crystalline powder, insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and DMSO.
Erythrosine
Erythrosine is a high-purity red synthetic dye classified as a tetraiodofluorescein salt, commonly used as a colorant in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and industrial applications. It is a water-soluble, dark red to reddish-brown powder with excellent tinting strength and brightness. Erythrosine is valued for its vivid red color, good stability under normal conditions, and compatibility with a variety of formulation systems. It is widely used to impart red hues in candies, beverages, cosmetics, and diagnostic reagents.
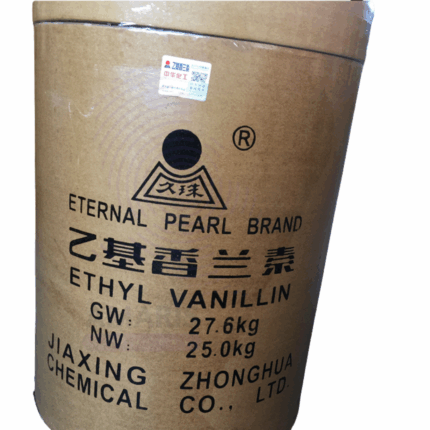
Ethylvanilin
Ethylvanilin (3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) is a synthetic aromatic aldehyde widely used as a flavoring agent and fragrance ingredient. It is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder with a strong, sweet vanilla-like odor, but more intense than natural vanillin. Ethylvanillin offers excellent flavor stability, solubility in alcohol and oils, and is valued for its enhanced vanilla aroma in food, beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical formulations. Due to its potent scent and flavor profile, it is a preferred substitute or complement to natural vanilla extract.
Ferric Ammonium Citrate
Ferric Ammonium Citrate is a dark green to black crystalline or granular inorganic compound composed of iron, ammonium ions, and citrate ions. It is a complex salt of citric acid with ferric iron (Fe³⁺) and ammonium. This compound is highly soluble in water, forming a greenish solution, and is widely utilized as a source of iron in various chemical, pharmaceutical, photographic, and food applications. It acts as a mild oxidizing agent and an iron supplement, valued for its bioavailability and ease of incorporation into formulations. Ferric Ammonium Citrate is typically available in different formulations distinguished by their water and ammonium content, such as green and brown types.
Ferrous Gluconate
Ferrous Gluconate is an iron salt of gluconic acid, appearing as a pale greenish-blue or green crystalline powder or granules. It is widely used as a nutritional iron supplement and food additive due to its good bioavailability and relatively low toxicity compared to other iron salts. Ferrous Gluconate is water-soluble, providing a stable source of ferrous iron (Fe²⁺) that is easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. This compound is commonly employed in pharmaceuticals, food fortification, and medical formulations to treat or prevent iron deficiency anemia. It is also used as a reducing agent and color stabilizer in various industrial applications.
Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate
Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate, also known as iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, is a pale green crystalline solid containing seven molecules of water of crystallization (FeSO₄·7H₂O). It is a widely used inorganic iron compound characterized by its high iron content (approximately 20% Fe) and good solubility in water. This hydrated salt is commonly used in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and various industrial processes. The heptahydrate form is preferred for many applications due to its stability, ease of handling, and cost-effectiveness.
Ferulic Acid
Ferulic Acid is a naturally occurring hydroxycinnamic acid classified as a phenolic compound with potent antioxidant properties. It exists as a pale yellow to light brown crystalline powder with a faint characteristic odor. Ferulic Acid is commonly found in the cell walls of various plants such as rice bran, wheat, oats, coffee, apples, and fruits, where it plays a role in plant structural integrity and defense against environmental stress. It is valued across multiple industries—cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, food, and agriculture—due to its ability to neutralize free radicals, absorb UV radiation, and exhibit anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities.
Fish Collagen
Fish Collagen is a natural protein derived from the skin, scales, and bones of various fish species through enzymatic hydrolysis or acid extraction. It is predominantly Type I collagen, known for its excellent bioavailability and biocompatibility. Fish Collagen typically appears as a fine white to off-white powder with low odor and high solubility in water and acidic solutions. It is widely prized in cosmetics, nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and food industries due to its superior absorption compared to mammalian collagen, making it highly effective in skin, joint, and bone health applications. Fish Collagen supports the body’s extracellular matrix, promoting skin elasticity, hydration, and tissue repair.
Flax
Flax (Linum usitatissimum) is an ancient crop cultivated primarily for its seeds and fibers. The flax seeds are small, flat, and oval, ranging from golden yellow to brown in color, and are rich in nutrients including omega-3 fatty acids (alpha-linolenic acid), lignans, dietary fiber, proteins, and vitamins. Flax fibers are derived from the stem and used in textile and industrial applications. Flaxseed oil, extracted from the seeds, is highly valued for its nutritional and therapeutic properties. Flax is utilized across food, nutraceutical, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors due to its multifunctional health benefits, fiber content, and sustainable nature.
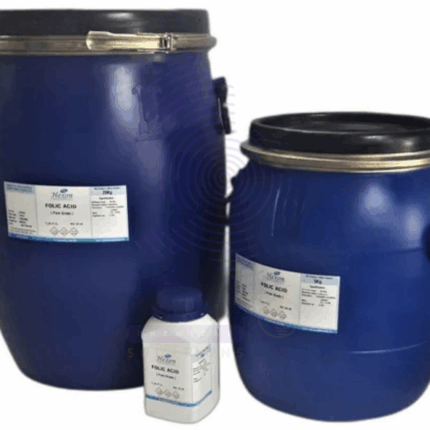
Folic Acid
Folic Acid, also known as Vitamin B9 or pteroylmonoglutamic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for numerous physiological processes including DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation, as well as amino acid metabolism. It appears as a yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder, odorless or with a faint characteristic odor. Folic Acid is vital for cell division and growth, making it critical during pregnancy and periods of rapid growth. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, food fortification, and cosmetic industries due to its role in preventing folate deficiency anemia, neural tube defects in newborns, and supporting overall cellular health.
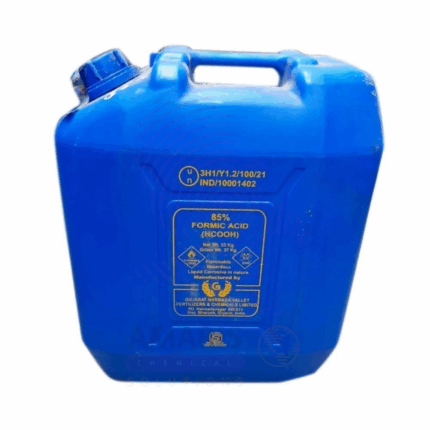
Formic Acid
Formic Acid (methanoic acid) is the simplest carboxylic acid, typically supplied as an 85% aqueous solution. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, penetrating odor and strong acidic properties. Formic Acid naturally occurs in insect stings and plant secretions and is widely used in chemical synthesis, agriculture, textile, leather, and rubber industries. The 85% solution balances potency and safe handling for industrial applications. It serves as a preservative, antibacterial agent, and intermediate chemical in numerous manufacturing processes.
Fresh Milk Liquid Flavour
Fresh Milk Liquid Flavour is a premium food-grade flavoring agent designed to replicate the authentic creamy and slightly sweet aroma of fresh milk. It enhances the taste and sensory appeal of a wide variety of food and beverage products by adding a smooth, natural dairy note. This liquid flavor is formulated for easy blending and consistent performance in diverse applications such as dairy products, bakery items, beverages, and confectionery. Its stable composition ensures long-lasting flavor quality throughout the product shelf life.
Fructose
Fructose, also known as fruit sugar, is a naturally occurring monosaccharide found in many plants, fruits, honey, and root vegetables. It is a simple sugar with a sweet taste and is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, alongside glucose and galactose. Fructose appears as a white crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, and is commonly used as a sweetener in food and beverage industries due to its high relative sweetness. It plays important roles in metabolism and is used extensively in the production of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and other sweetening agents.
Fumaric Acid
Fumaric Acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid characterized by its white crystalline powder form and a slightly acidic taste. It is an unsaturated organic acid with the chemical formula C4H4O4 and is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle in biological systems. Fumaric Acid is commonly found in various plants and fungi and is commercially produced by isomerization of maleic acid or by fermentation. It is widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, chemical, and polymer industries due to its acidulant, antioxidant, and crosslinking properties.
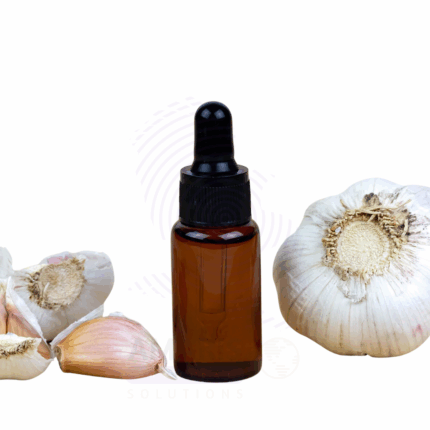
Garlic Oil
Garlic Oil is a potent essential oil extracted from the bulbs of the Allium sativum plant, primarily through steam distillation or solvent extraction. Known for its strong, pungent aroma and rich sulfur-containing compounds such as allicin, diallyl disulfide, and ajoene, Garlic Oil is widely recognized for its antimicrobial, antifungal, antiviral, and antioxidant properties. Traditionally used in herbal medicine, it has applications in pharmaceuticals, natural personal care products, food flavoring, and agricultural pest management. Its therapeutic properties also make it a valuable ingredient in formulations aimed at cardiovascular health and immune system support.
Gelatin Powder 180 Bloom
Gelatin Powder 180 Bloom is a high-quality, partially hydrolyzed collagen protein derived primarily from the skin, bones, and connective tissues of animals such as pigs and cows. The “180 Bloom” rating indicates its gel strength, meaning it forms a firm gel, making it suitable for various industrial, food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. Gelatin is a natural biopolymer, pale yellow to off-white in color, odorless, and tasteless. It is widely used due to its excellent gelling, film-forming, emulsifying, and stabilizing properties. The powder form offers ease of handling, storage, and precise dosing.
Gin Liquid Flavour
Gin Liquid Flavour is a high-quality, food-safe flavoring designed to replicate the characteristic herbal, botanical, and juniper-forward profile of traditional gin. Crafted for use in food and beverage applications, this liquid flavor captures the complex notes of gin without containing alcohol, making it ideal for non-alcoholic beverages, gourmet culinary creations, and confectionery. The flavor is stable under a range of processing conditions and is suitable for cold and hot applications, offering excellent dispersion and flavor retention.
Ginger Liquid Flavour
Ginger Liquid Flavour is a high-quality, concentrated flavoring agent that delivers the warm, spicy, and slightly sweet taste of fresh ginger. Crafted using nature-identical or natural components, this liquid flavor is ideal for a wide range of food and beverage applications requiring the distinctive kick of ginger without the need for fresh root. It provides excellent solubility and flavor stability in both hot and cold formulations. Ginger Liquid Flavor is heat-resistant, making it suitable for baked goods, beverages, sauces, and confections where a natural and robust ginger profile is desired.
Glacial Acetic Acid Food Grade
Glacial Acetic Acid Food Grade is a clear, colorless liquid organic compound with a pungent vinegar-like odor. It is a high-purity form of acetic acid specifically produced and processed for safe use in food applications. As the main component of vinegar (after dilution), it serves as a critical flavoring agent, pH adjuster, and preservative in the food industry. Food-grade acetic acid typically has a concentration of 80-100% (glacial acetic acid) or is diluted to lower concentrations (4-20%) for specific applications.
Glycerin
Glycerin, also known as glycerol, is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid with a sweet taste and hygroscopic properties. It is a trihydroxy alcohol (triol) used extensively across food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications. Food-grade glycerin is produced through hydrolysis, saponification, or transesterification of fats and oils, ensuring compliance with stringent purity standards. It is supplied in bulk (e.g., 250kg drums) for large-scale applications where non-toxic, biodegradable humectants or solvents are required. Glycerin is widely appreciated for its moisture-retaining ability, solubility, lubricity, and stabilizing properties.
Glycerol Monostearate
Glycerol Monostearate is a white to off-white, free-flowing powder composed of 50% monoglycerides of stearic and palmitic acids, typically derived from vegetable oils. It is a non-ionic emulsifier widely used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, plastics, and industrial applications. GMS functions as an emulsifying agent, stabilizer, thickener, anti-staling agent, and opacifier. In food, it improves texture and extends shelf life. In cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, it enhances creaminess and stability. GMS 50% is often blended with other emulsifiers or surfactants and is valued for its versatile functionality, safety, and compatibility with a wide range of ingredients.
Glycerol Monostearate Flakes
Glycerol Monostearate Flakes is a white to off-white waxy flake form emulsifier composed of 40% monoglycerides of fatty acids, primarily stearic and palmitic acids, combined with other glycerides and esters. Derived mainly from vegetable oils, this food-grade emulsifier is widely utilized in food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors for its multifunctional properties. GMS 40% flakes serve as effective emulsifiers, stabilizers, anti-caking agents, and texture enhancers, with excellent compatibility and versatility in formulations requiring semi-solid or solid fats.
Guar Gum
Guar Gum is a natural polysaccharide extracted from the endosperm of the guar bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba). It appears as an off-white to cream-colored powder with a neutral odor and bland taste. Guar Gum is a galactomannan composed mainly of mannose and galactose units, known for its excellent water-binding, thickening, and stabilizing properties. It forms highly viscous solutions even at low concentrations, making it a versatile hydrocolloid used widely across food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, oilfield, and industrial applications.
High Gluten Wheat Flour
High Gluten Wheat Flour is a finely milled powder derived from hard wheat varieties known for their high protein content, typically ranging from 12% to 14.5%. This flour has a superior gluten-forming capacity which imparts strong dough elasticity and excellent gas retention properties. It appears as an off-white to pale yellow powder with a neutral to slightly nutty aroma. High Gluten Wheat Flour is prized in baking industries and food manufacturing for producing products with enhanced chewiness, volume, and texture. It is essential for applications requiring strong dough structure and resilience.
Honey Special Liquid Flavour
Honey Special Liquid Flavour is a premium food-grade flavoring agent designed to replicate the rich, sweet, and natural aroma and taste of pure honey. This liquid flavor is ideal for enhancing the sensory qualities of a variety of food and beverage products. It offers excellent stability and solubility, making it suitable for use in drinks, baked goods, confectionery, dairy products, and sauces. The flavoring is carefully formulated to provide an authentic honey experience without the viscosity of natural honey, allowing for easy blending and consistent flavor delivery. Manufactured under strict quality control, it complies with food safety regulations and supports clean-label product development.
Hop Oil
Hop Oil is a volatile essential oil extracted via steam distillation from the cone-shaped flowers (strobiles) of the hop plant (Humulus lupulus). It has a complex, herbaceous, slightly bitter aroma with earthy, floral, and spicy undertones. Known for its calming, sedative, and antimicrobial effects, Hop Oil is widely used in aromatherapy, cosmetics, herbal formulations, and specialty beverages.
Traditionally linked with beer production, Hop Oil also finds application in natural perfumery, body care, and wellness products aimed at promoting relaxation. Its bioactive compounds such as humulene, myrcene, and caryophyllene contribute to its diverse functional and aromatic value.
Hydrazine Food Grade
Hydrazine Food Grade is a high-purity form of hydrazine (N₂H₄), a highly reactive, colorless, and fuming liquid with a pungent ammonia-like odor. It is a powerful reducing agent and chemical intermediate widely used in industrial applications. The food-grade specification ensures purity and controlled impurity levels suitable for limited and specialized food industry uses, primarily as a processing aid or sterilizing agent. Hydrazine exhibits strong nucleophilic and reducing properties, enabling various chemical transformations and sterilization processes.
Hydrogen Peroxide Food Grade
Hydrogen Peroxide Food Grade is a highly concentrated aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), formulated specifically for use in food processing and related applications. It appears as a clear, colorless liquid with a slightly sharp, acrid odor. Renowned for its powerful oxidizing and bleaching properties, hydrogen peroxide is a strong antimicrobial agent and environmentally friendly disinfectant that decomposes into water and oxygen, leaving no harmful residues. The food-grade designation ensures compliance with strict purity standards, making it suitable for direct and indirect food contact uses, including sterilization, sanitation, and preservation.
Icing Sugar
Icing Sugar, also known as powdered sugar or confectioners’ sugar, is a finely ground sugar with a powdery consistency. It is typically made by milling granulated sugar into a fine powder and blending it with a small amount of anti-caking agent (usually cornstarch or tricalcium phosphate) to prevent clumping. Icing Sugar is white, odorless, and has a sweet taste. It is widely used in baking, confectionery, and culinary applications to provide sweetness, texture, and decorative finishes.
Iodised Salt
Iodised Salt is table salt (sodium chloride) fortified with a small, controlled amount of iodine, typically in the form of potassium iodate or potassium iodide. It appears as fine white crystalline granules, odorless, and with a characteristic salty taste. The addition of iodine helps prevent iodine deficiency disorders (IDD) such as goiter, mental impairment, and developmental abnormalities. Iodised Salt is widely used in households, food processing, and animal nutrition to ensure adequate dietary iodine intake.
Iodised Salt Extra Pure
Iodised Salt Extra Pure is a refined form of sodium chloride enriched with a precise amount of iodine, typically in the form of potassium iodate or iodide. It is primarily used to prevent iodine deficiency disorders, making it essential in nutritional and public health applications. Beyond its dietary use, iodised salt also serves in laboratory settings for controlled experiments involving iodine content and salt solubility studies. Its high purity ensures minimal contamination, making it suitable for analytical and pharmaceutical applications where quality and consistency are critical. Proper storage in airtight containers is recommended to prevent iodine loss due to air exposure.


 Preservatives(food)
Preservatives(food) Flavor Enhancers
Flavor Enhancers Acidulants
Acidulants Sweeteners
Sweeteners Antioxidants
Antioxidants Colorants(food)
Colorants(food) Nutraceutical Ingredients (food)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (food) Nutrient Supplements
Nutrient Supplements Emulsifiers
Emulsifiers
 Collectors
Collectors Dust Suppressants
Dust Suppressants Explosives and Blasting Agents
Explosives and Blasting Agents Flocculants and Coagulants
Flocculants and Coagulants Frothers
Frothers Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents pH Modifiers
pH Modifiers Precious Metal Extraction Agents
Precious Metal Extraction Agents
 Antioxidants(plastic)
Antioxidants(plastic) Colorants (Pigments, Dyes)
Colorants (Pigments, Dyes) Fillers and Reinforcements
Fillers and Reinforcements Flame Retardants
Flame Retardants Monomers
Monomers Plasticizers
Plasticizers Polymerization Initiators
Polymerization Initiators Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
Stabilizers (UV, Heat)
 Antifoaming Agents
Antifoaming Agents Chelating Agents
Chelating Agents Coagulants and Flocculants
Coagulants and Flocculants Corrosion Inhibitors
Corrosion Inhibitors Disinfectants and Biocides
Disinfectants and Biocides Oxidizing Agents
Oxidizing Agents pH Adjusters
pH Adjusters Scale Inhibitors( water)
Scale Inhibitors( water)
 Antioxidants(cosmetic)
Antioxidants(cosmetic) Emollients
Emollients Fragrances and Essential Oils
Fragrances and Essential Oils Humectants
Humectants Preservatives
Preservatives Surfactants(cosmetic)
Surfactants(cosmetic) Thickeners
Thickeners UV Filters
UV Filters
 Fertilizers
Fertilizers Soil Conditioners
Soil Conditioners Plant Growth Regulators
Plant Growth Regulators Animal Feed Additives
Animal Feed Additives Biostimulants
Biostimulants Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
Pesticides (Herbicides, Insecticides, Fungicides)
 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Excipients
Excipients Solvents(pharmaceutical)
Solvents(pharmaceutical) Antibiotics
Antibiotics Antiseptics and Disinfectants
Antiseptics and Disinfectants Vaccine Adjuvants
Vaccine Adjuvants Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical)
Nutraceutical Ingredients (pharmaceutical) Analgesics & Antipyretics
Analgesics & Antipyretics
 Analytical Reagents
Analytical Reagents Solvents(lab)
Solvents(lab) Chromatography Chemicals
Chromatography Chemicals Spectroscopy Reagents
Spectroscopy Reagents microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents
microbiology-and-cell-culture-reagents Molecular Biology Reagents
Molecular Biology Reagents Biochemical Reagents
Biochemical Reagents Inorganic and Organic Standards
Inorganic and Organic Standards Laboratory Safety Chemicals
Laboratory Safety Chemicals Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
Specialty Laboratory Chemicals(Special Laboratory Equipment)
 Demulsifiers
Demulsifiers Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids
Hydraulic Fracturing Fluids Scale Inhibitors(oil)
Scale Inhibitors(oil) Surfactants(oil)
Surfactants(oil) Drilling Fluids
Drilling Fluids
 Dyes and Pigments
Dyes and Pigments Bleaching Agents
Bleaching Agents Softening Agents
Softening Agents Finishing Agents
Finishing Agents Antistatic Agents
Antistatic Agents
 Admixtures
Admixtures Waterproofing Agents
Waterproofing Agents Sealants and Adhesives
Sealants and Adhesives Curing Compounds
Curing Compounds Concrete Repair Chemicals
Concrete Repair Chemicals Anti-Corrosion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
 Surfactants(cleaning)
Surfactants(cleaning) Builders
Builders Enzymes
Enzymes Solvents (Cleaning)
Solvents (Cleaning) Fragrances
Fragrances
 Electronic Chemicals
Electronic Chemicals Catalysts
Catalysts Lubricants
Lubricants Photographic Chemicals
Photographic Chemicals Refrigerants
Refrigerants Automotive chemicals
Automotive chemicals Pyrotechnic Chemicals
Pyrotechnic Chemicals
 Biodegradable Surfactants
Biodegradable Surfactants Bio-based Solvents
Bio-based Solvents Renewable Polymers
Renewable Polymers Carbon Capture Chemicals
Carbon Capture Chemicals Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
Wastewater Treatment Chemicals
 Pigments
Pigments Solvents(paint)
Solvents(paint) Specialty Coatings
Specialty Coatings Binders/Resins
Binders/Resins Additives
Additives Driers
Driers Anti-Corrosion Agents
Anti-Corrosion Agents Functional Coatings
Functional Coatings Application-Specific Coatings
Application-Specific Coatings
 Fresh Herbs
Fresh Herbs Ground Spices
Ground Spices Whole Spices
Whole Spices Spice Blends
Spice Blends Dried Herbs
Dried Herbs
 Leavening Agents
Leavening Agents Dough Conditioners
Dough Conditioners Flour Treatments
Flour Treatments Fat Replacers
Fat Replacers Decoratives
Decoratives Preservatives(baking)
Preservatives(baking)
 Plasticizers & Softeners
Plasticizers & Softeners Reinforcing Agents
Reinforcing Agents Adhesion Promoters
Adhesion Promoters Vulcanizing Agents
Vulcanizing Agents Antidegradants
Antidegradants Blowing Agents
Blowing Agents Fillers & Extenders
Fillers & Extenders Accelerators & Retarders
Accelerators & Retarders